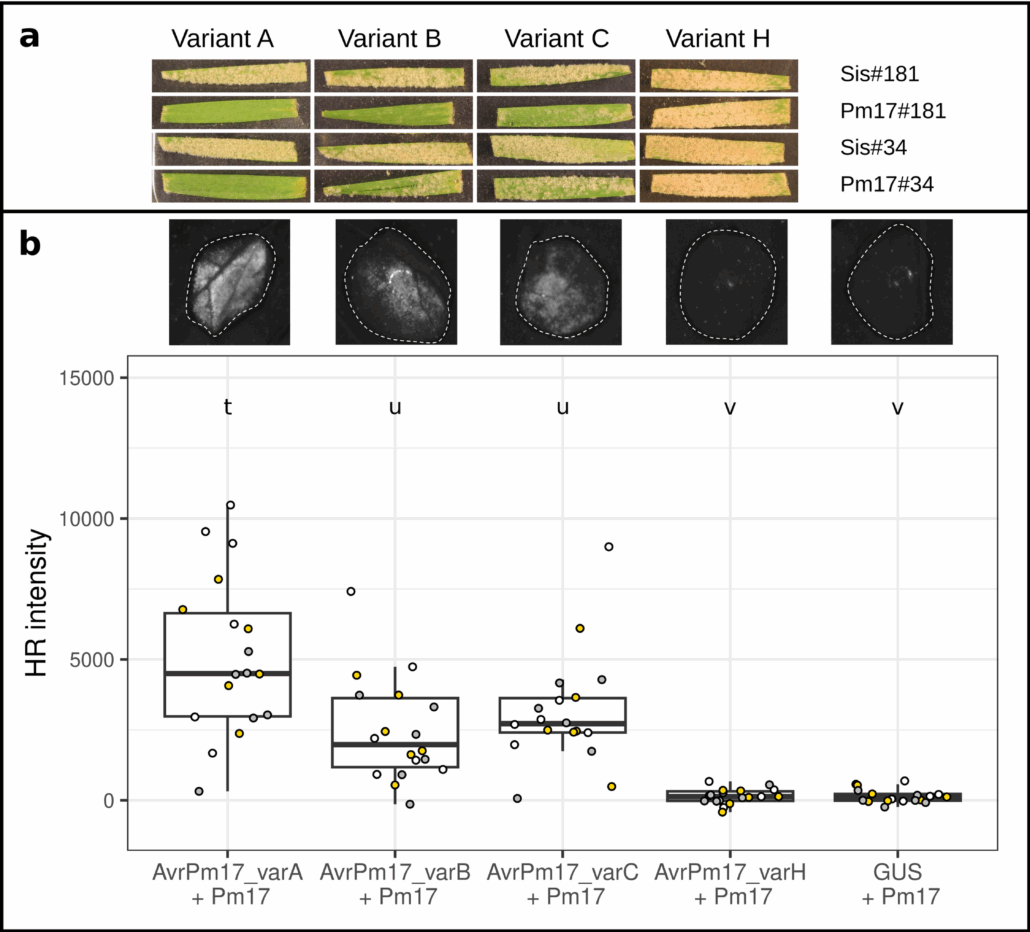
Molecular epidemiology of European wheat powdery mildew
Plant Science Research WeeklyAt the height of the Covid pandemic, epidemiologists carried out mass sequencing of the circulating virus populations to track their movements and the emergence of new variants. Such molecular epidemiological studies are rarer for plant pathogens but can be equally effective in learning about their patterns…
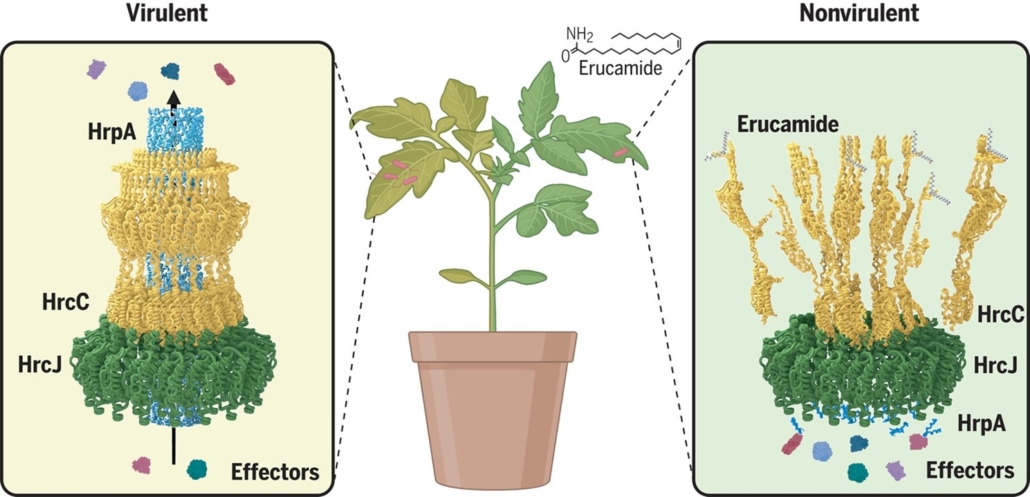
Blocking bacterial invasion: Erucamide inhibits the type III secretion system
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe interaction between plants and pathogens is often described as an evolutionary arms race, in which plants develop multilayered immune signaling to counteract direct extracellular attacks and intracellular chemical effectors. The type III secretion system (T3SS) of Gram-negative bacteria serves as…
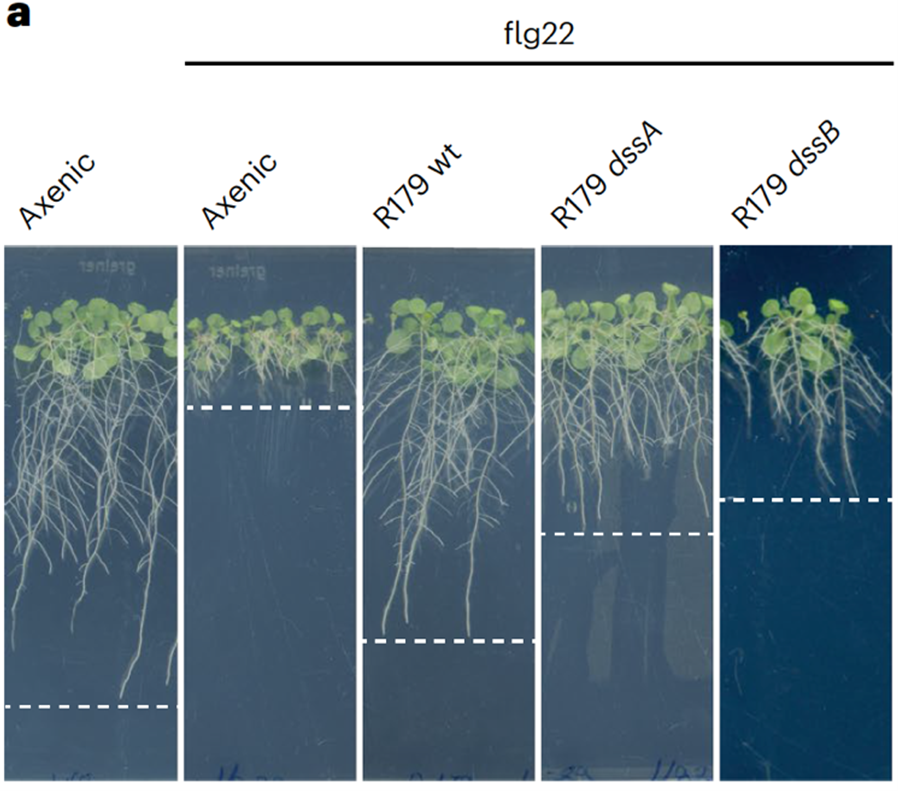
Stealth mode: How Rhodanobacter R179 evades plant immunity
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe soil microbiome harbors a vast diversity of microorganisms that can be pathogenic, beneficial, or commensal to plants. A fundamental question in plant biology is how plants actively detect, differentiate, and optimize their associations with the microbiome to maintain optimal fitness. In a recent…
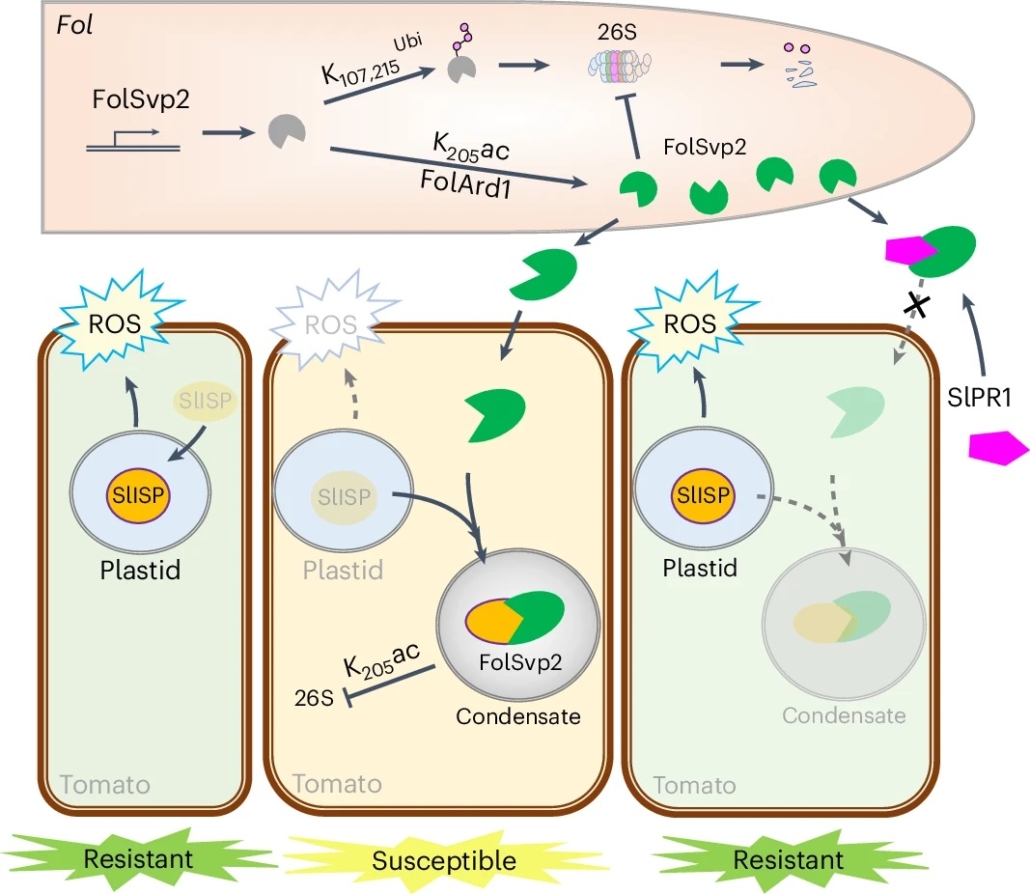
Tomato PR1 protein prevents the fungal effector FolSvp2 from suppressing SlISP-mediated ROS production
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and pathogens are locked in a co-evolutionary arms race. Pathogens secrete effectors into plants, leading to effector-triggered susceptibility. Plants in turn respond through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the expression of defence-related genes to defend themselves, which…

Interconnected memories: How heat stress and bacterial infection shape plant resilience
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyMemory—a mysterious cognitive process that retains information over time and shapes future interpretations and actions—is not exclusive to animals. In plants, a similar phenomenon occurs where past exposure to environmental stressors is “memorized,” enabling plants to respond more effectively…
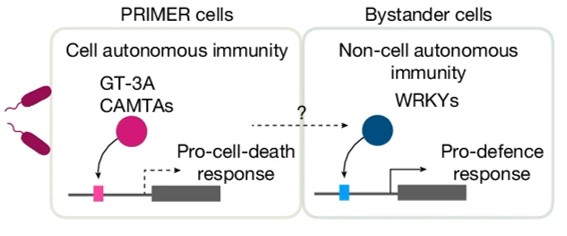
Single cell multiomic analysis of plant immunity reveals PRIMER cells
Plant Science Research WeeklySingle cell mutiomics are radically changing our understanding of pretty much every cellular process. Here, Nobori et al. integrated single-cell transcriptomic, epigenomic and spatial transcriptomic data to investigate plant responses to pathogens. The authors used three different strains of Pseudomonas…
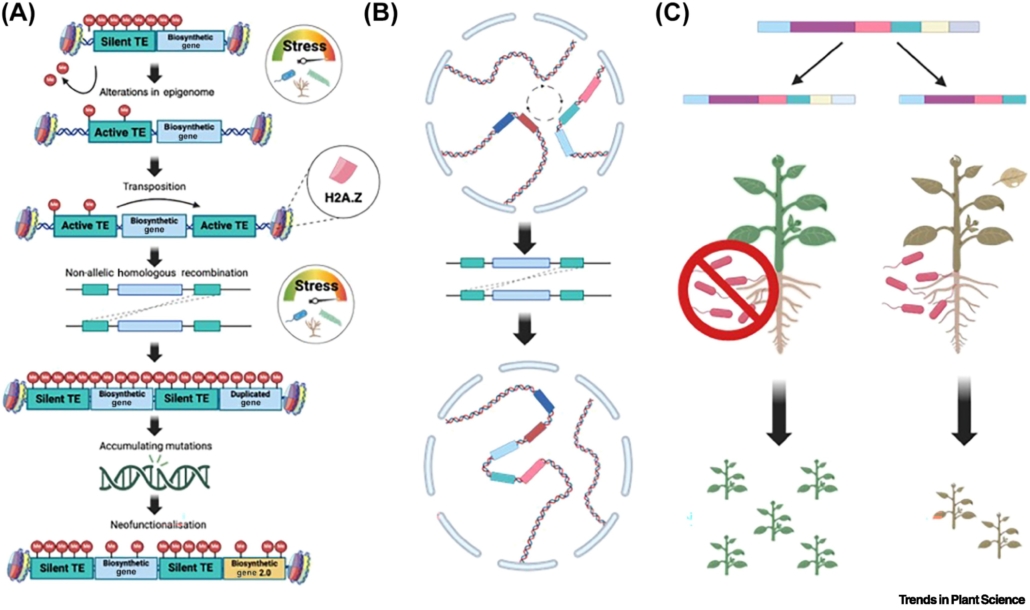
Review. Decoding resilience: Ecology, regulation, and evolution of biosynthetic gene clusters
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough clusters of functionally related genes are common in prokaryotes, until recently it was thought that they were not a feature of eukaryotic genomes. However, several studies have identified biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) in plants. Many of these gene clusters include sets of enzymes that act…
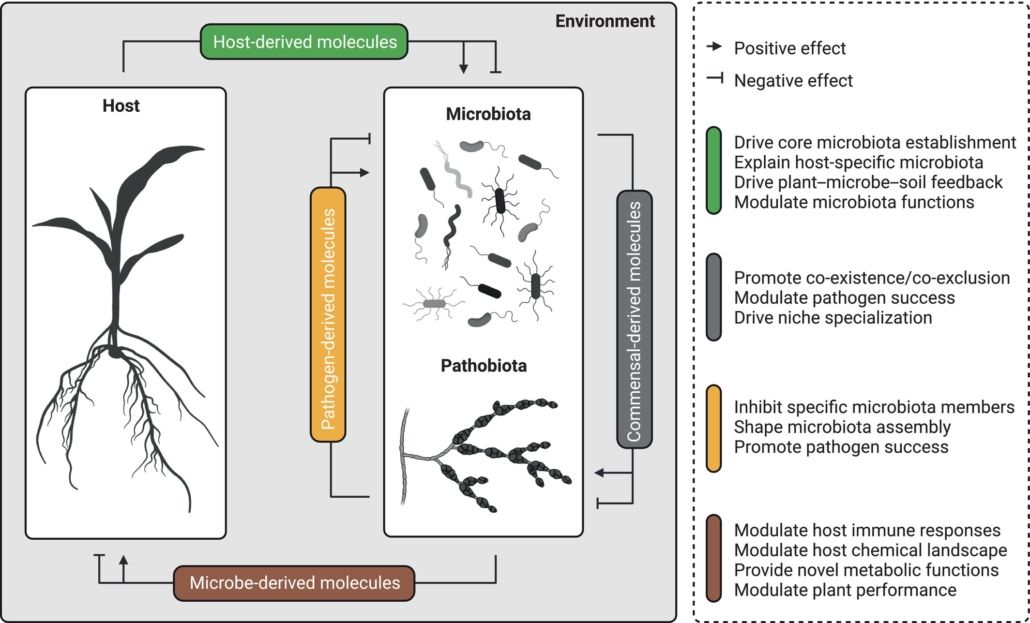
Virtual issue: The chemical language of plant–microbe–microbe associations
Plant Science Research WeeklyDon’t miss this exciting Virtual Issue from New Phytologist on “plant-microbe-microbe” interactions. That’s not a typo – many of the articles address the signals that coordinate such multi-factorial interactions, as there is a growing recognition that interrelations between microbes influence…
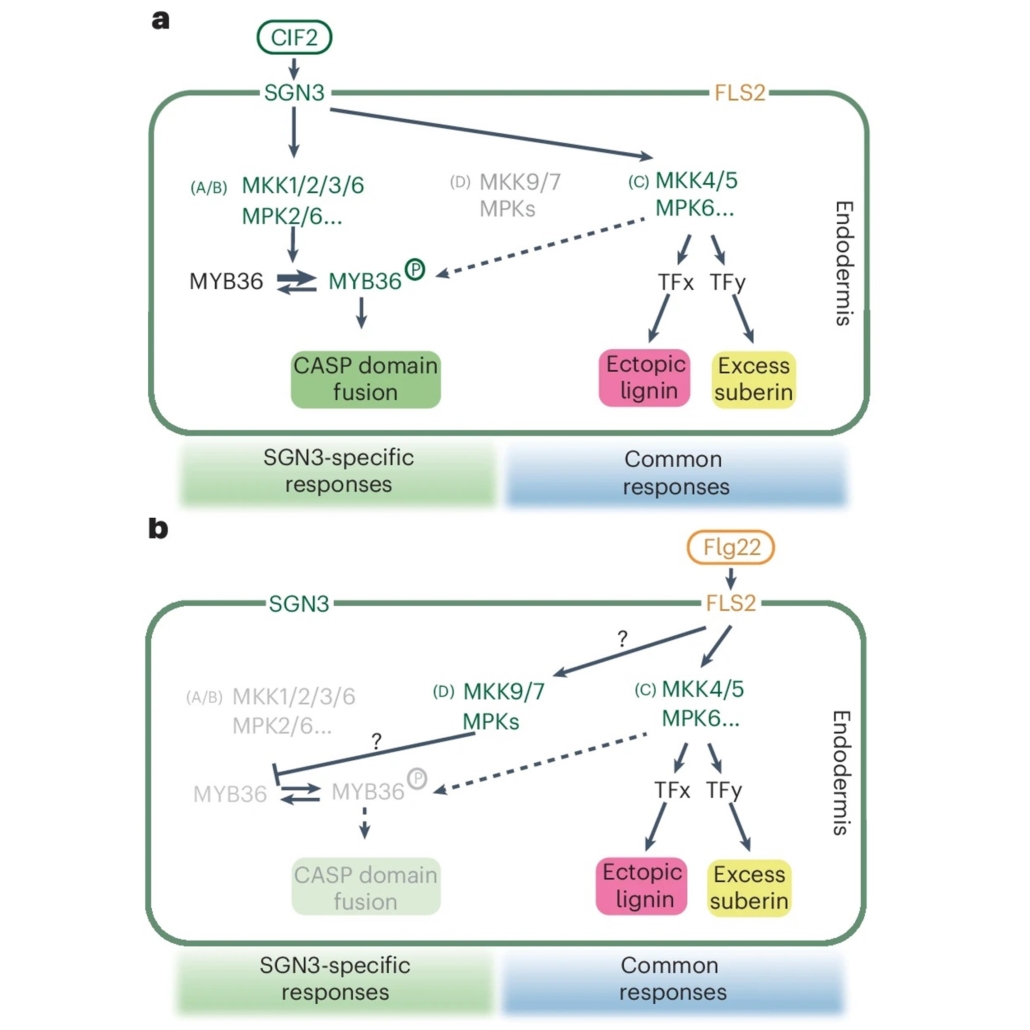
Decoding the signaling precision of receptor-MAPK pathways
Plant Science Research WeeklyHave you ever wondered how cells distinguish between the diverse array of external signals traveling through similar pathways? To understand the intricacies of plant signaling mechanisms, Ma et al. used single endodermal cells of Arabidopsis roots as a model to compare two receptor pathways. One pathway…

