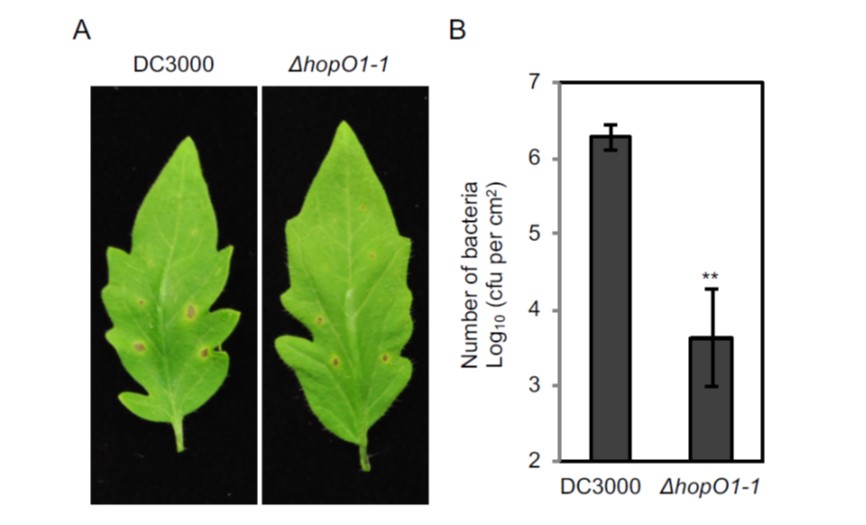
Pathogenic bacteria target plant plasmodesmata to colonize and invade surrounding tissues (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are regulated channels that connect adjacent cells, allowing movement of metabolites, RNA, proteins, and pathogens. Plants close their plasmodesmata as part of their immune response, but this closure can be interfered with by pathogens. Aung et al. examined the repertoire of effector proteins…

Review: Surface sensor systems in plant immunity (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe first line of defense is detection. Plants have numerous cell-surface receptor proteins (Pattern Recognition Receptors, PRRs) that recognize potentially harmful pathogens as well as endogenous molecules that suggest damage, known as Damage Associated Molecular Patterns or DAMPS and phytocytokines…
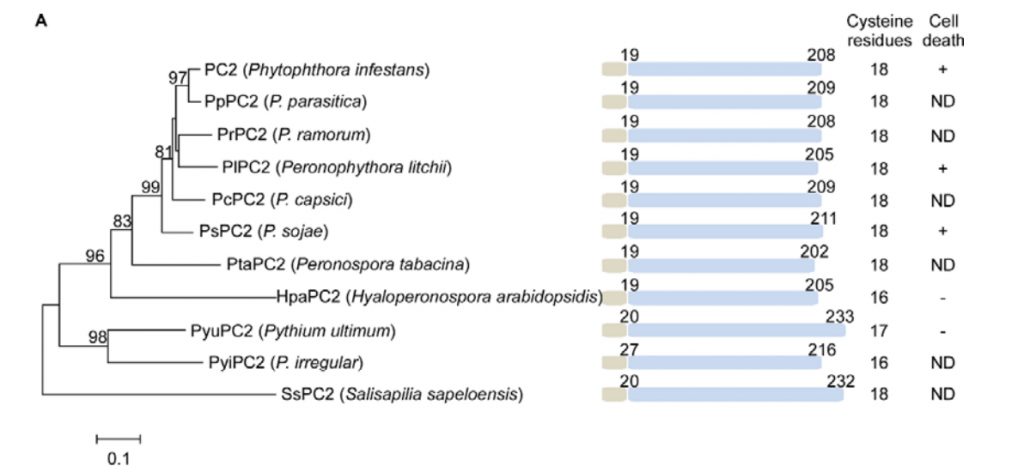
Cleavage of a pathogen apoplastic protein by plant subtilases activates immunity
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant-pathogen interactions are shaped by a dynamic signaling crosstalk that often leads to an arms-race between plants and pathogens. The initial pathogenic invasion starts in the apoplast, which serves as a major battlefield. This extracellular space is a harsh environment enriched with hydrolytic…
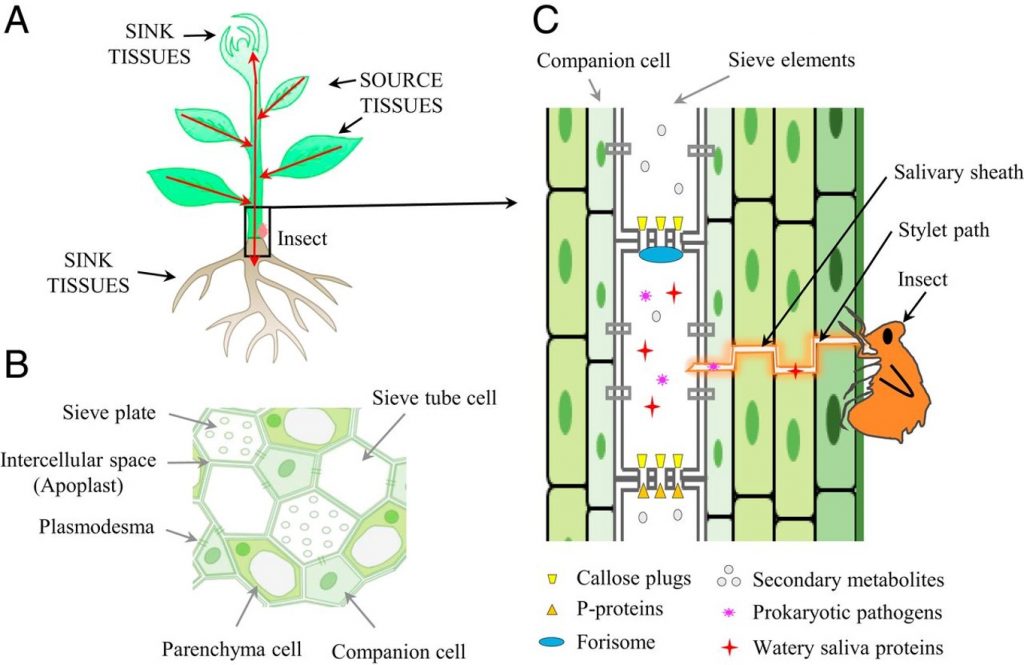
Perspective: Challenging battles of plants with phloem-feeding insects and prokaryotic pathogens (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of our understanding of plant defense response is built upon the responses that occur in leaves. Many pathogens colonize the phloem system, which is both nutrient-rich and provides an easy conduit for spreading through systemically through the plant body. These phloem-inhabiting prokaryotic pathogens…
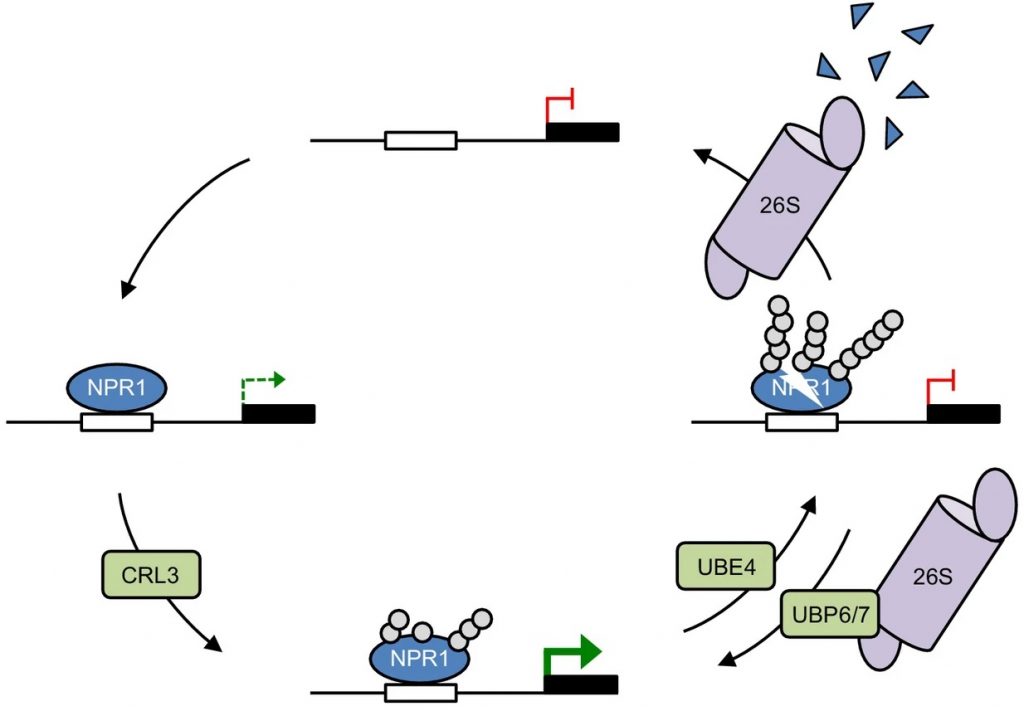
Dynamic ubiquitination determines transcriptional activity of the plant immune coactivator NPR1 (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Dynamic ubiquitination determines transcriptional activity of the plant immune coactivator NPR1
Plants (and animals) need to strike a delicate balance when activating their immune responses: not too much and not too little. The transcriptional coactivator NPR1 [nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related…
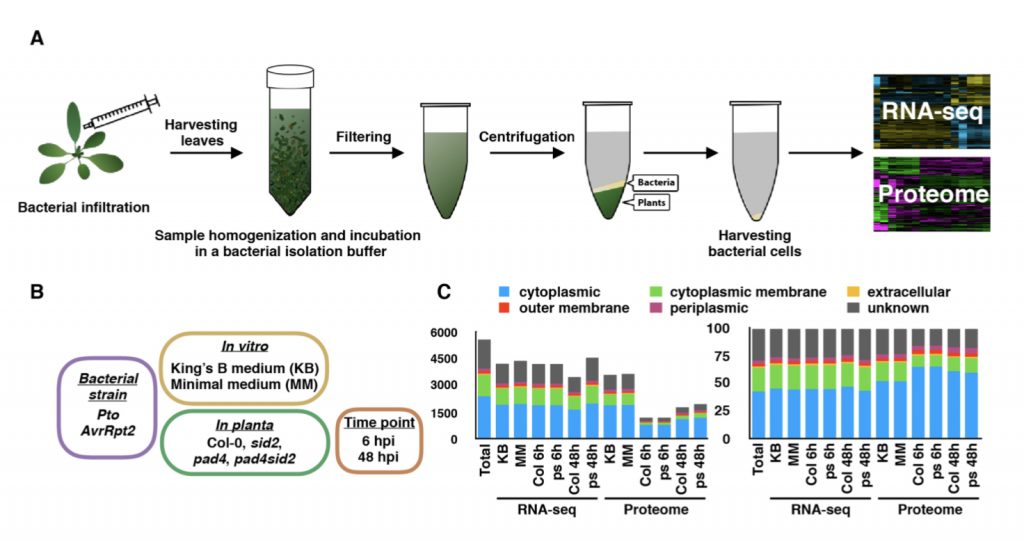
Understanding pathogenic bacterial gene expression in planta is essential to understand plant pathology (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow exactly does the plant defense system target pathogens? Nobori et al. have analyzed interactions inside the plant between the foliar bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae and Arabidopsis thaliana at transcriptomic and proteomic levels by using RNAseq and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry…
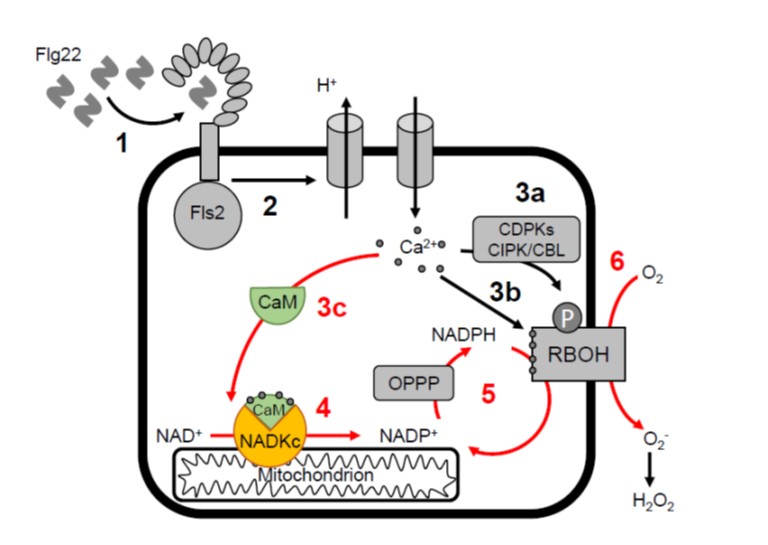
Identification of calmodulin-dependent NAD+ kinase that sustains the elicitor-induced oxidative burst (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen pathogens attack, one line of defense is the production of a burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which triggers additional defences. ROS is produced by the action of NADPH oxidases, which require NADPH as a substrate; NADPH is derived from NADP+, but where does this come from? Previous studies…
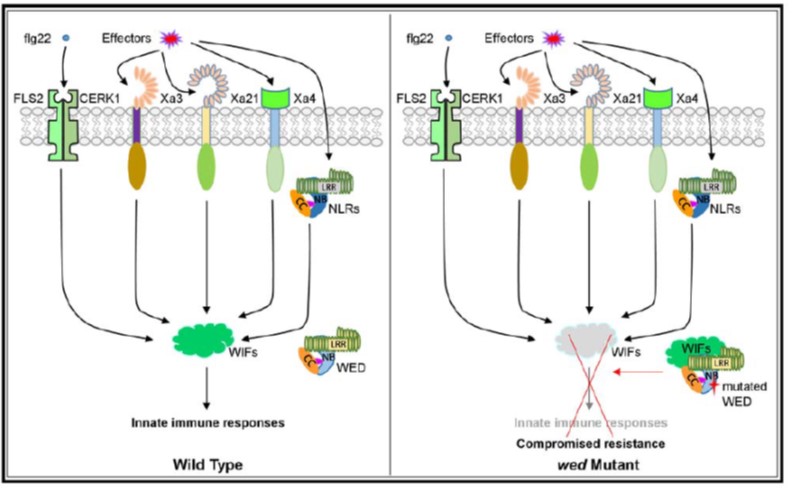
A single amino-acid substitution impairs PTI and ETI in an SA-dependent manner in rice ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess two immune strategies to prevent invasion by pathogens called pattern-triggered immunity (PTI, typically mediated by cell-surface receptors) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI). During ETI, intracellular resistance (R) proteins perceive specific pathogen effectors. Tang et al. describe…
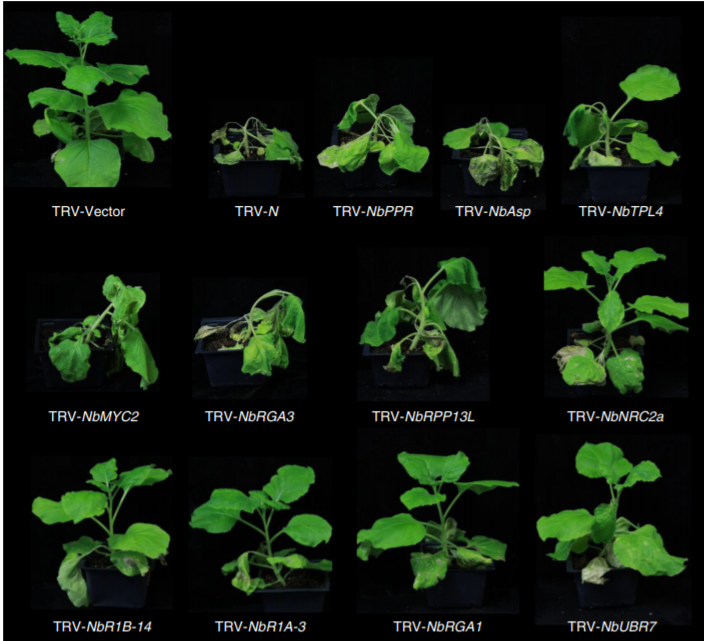

TurboID-based proximity labeling reveals that UBR7 is a regulator of N NLR immune receptor-mediated immunity (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIdentification of protein- protein interactions helps understand the signaling cascade in multiple biological process including development, biotic and abiotic stress. Previously, a proximity-based labelling approach referred to as BioID had been used to identify proteins in close proximity to a protein…

