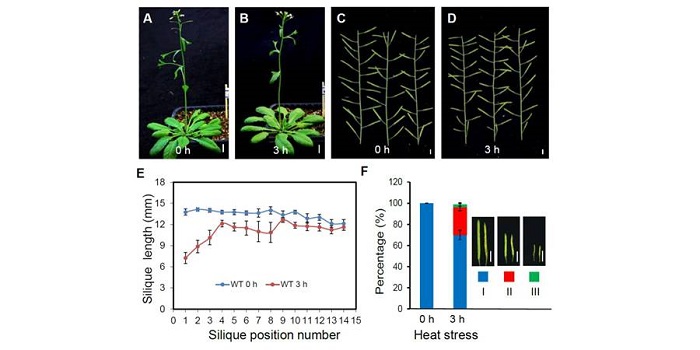
Tissue-specific transcriptomics shows the unfolded protein response’s role in maintaining fertility upon heat stress ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Plant reproduction is particularly sensitive to heat stress, so rising temperature is a major threat to food security. Zhang et al. surveyed the transcriptional responses to heat stress (3 h at 37º) in Arabidopsis and identified large differences between vegetative and reproductive tissue responses…
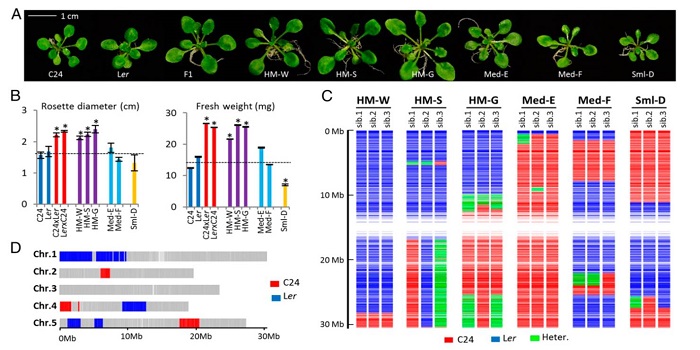
PIF4-controlled auxin pathway contributes to hybrid vigor in Arabidopsis thaliana
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHybrid vigor is a well-known but still poorly understood phenomenon in which the F1 hybrid progeny of a cross often show enhanced growth as compared to either parent. True-breeding lines that retain this enhanced growth, known as hybrid mimics, have been developed and are important tools for understanding…

H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGene silencing by chromatin marks occurs in plants and animals, but there are often some differences in the details. Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) and PRC2 were first characterized in animals and shown to repress gene expression in part through histone modification; PRC1 has histone H2A E3 ubiquitin…
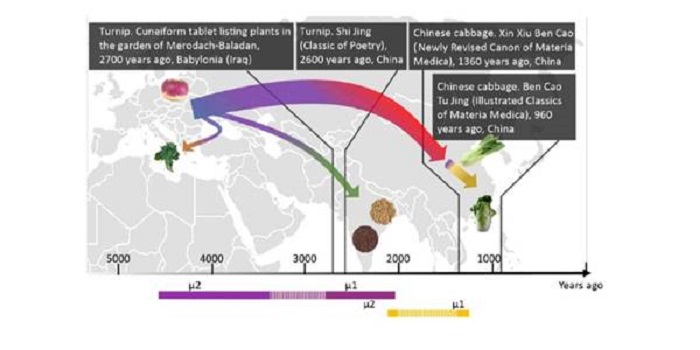
Genomic inferences of domestication events are corroborated by written records in Brassica rapa ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThere are many subspecies of Brassica rapa [including turnip (subsp. rapa) pak choi (subsp. chinensis) and Chinese cabbage (subsp. pekinensis)] but the relationships between the subspecies has remained uncertain. Qi et al. sequenced 143 accessions, including some subspecies for the first time. They then…
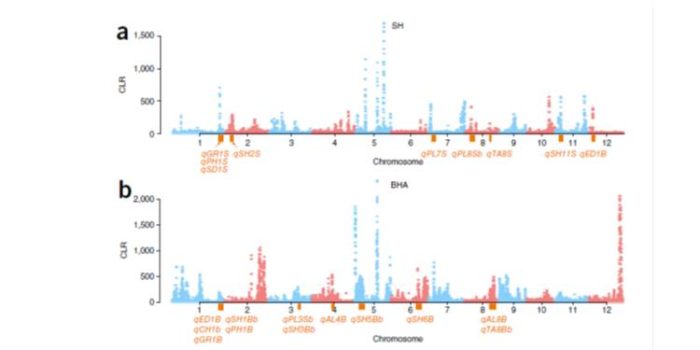
Signatures of adaptation in the weedy rice genome
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCrop domestication has been accompanied by the evolution of aggressive weedy crop relatives that compete for resources and make weed management a challenge. By using whole-genome sequencing of the two most commonly found weedy rice strains in the US (SH and BHA), and comparing them with the genomes of…

Review: Insights into plant adaptation from transcriptomics and proteomics studies
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchOmics approaches have helped shed light on how plants relate to their environment and how they respond to changes in it. Although still relatively underutilized, comparative transcriptomics and proteomics approaches also can be applied to study mechanisms of plant adaptation. Voelckel et al. discuss…

Chasing Scattered Genes: Identifying Specialized Metabolite Pathway Genes through Global Co-expression Analysis
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants produce scores of specialized metabolites (SMs) to attract or repel the organisms around them and to cope with life in a variable environment. For thousands of years, we have been exploiting these compounds to feed, heal, and adorn us. Many more SMs remain to be discovered: the chemical constituents…
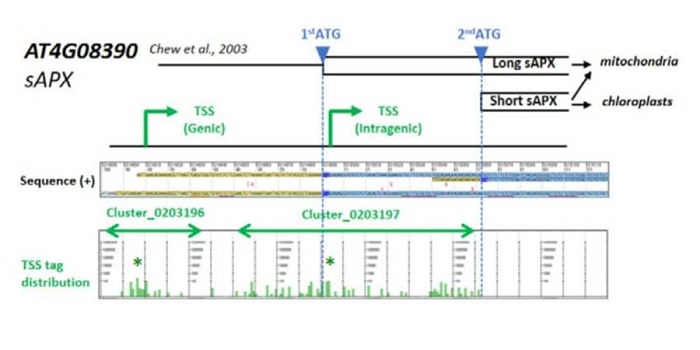
Identification of Arabidopsis genic and non-genic promoters
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA promoter is a region that “determines the position, direction, frequency, and timing of transcription”. A cell can decode the sequence of the promoter to ensure appropriate transcription, but we still can’t. Tokizawa et al. performed a large-scale survey of promoters by sequencing regions upstream…
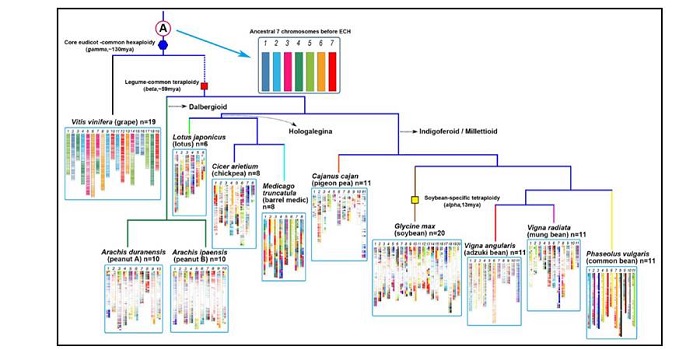
Hierarchically aligning 10 legume genomes establishes a family-level genomics platform
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMany legumes are important crops, and to date ten legume genomes have been sequenced, including soybean, common bean, mung bean, and two species of wild peanut. Wang et al. used hierarchical comparative genomics analysis of the ten legume genomes, which enabled them to detected gene colinearity between…

