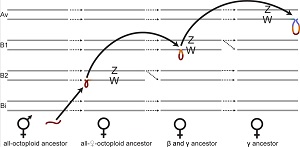
Plant sex regions can “jump” in strawberry (PLOS Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySex chromosome restructure has happened frequently during the evolution of eukaryotes, often resulting in highly differentiated sex chromosomes. However, little is known about this process in plants. The wild North American octoploid strawberries (Fragaria) have separate sexes with homomorphic, female…
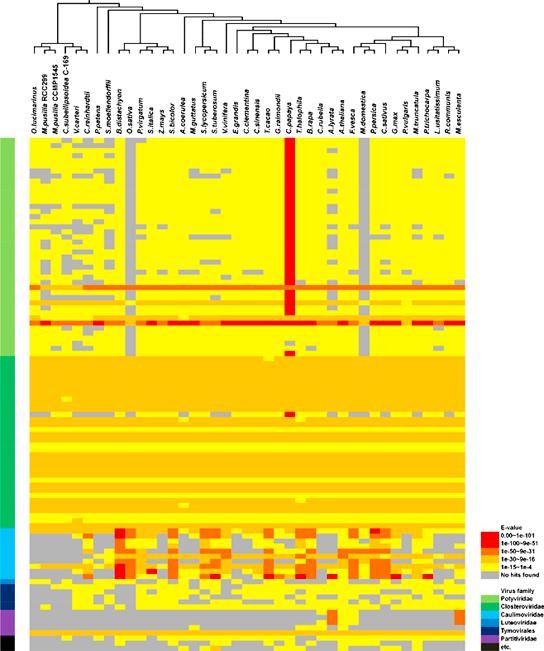
Viral sequences in the Arabidopsis genome ($) (Mol. Phylogenetics Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNumerous prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes have been identified as having homology to viral sequences. This phenomenon is the result of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) between viral pathogens and host cells. Chu and collaborators performed a proteome-wide analysis for the identification of viral domains…

The transcriptional landscape of polyploid wheat ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWheat is a tough nut to crack, as it is hexaploid, comprising three diploid genomes (the A, B and D genomes). The International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium has released a fully-annotated wheat reference genome, and Ramírez-González et al. present a thorough analysis of its transcriptome. Although…
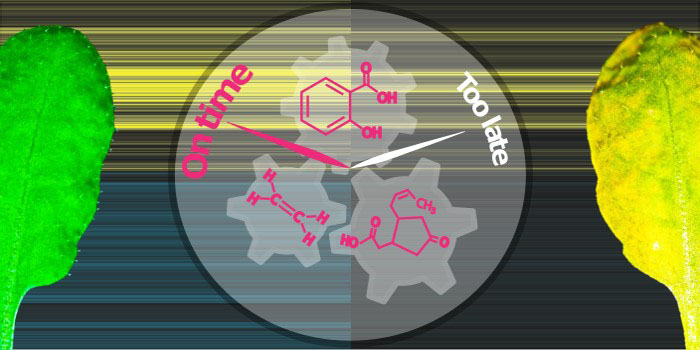
Defense or Disease: It’s a Matter of Timing
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMine et al. use RNA-seq to study RPS2-mediated bacterial resistance https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00970
By Akira Mine, Carolin Seyfferth and Kenichi Tsuda
Background: To fight against pathogens, plants can detect enemies and transduce the signal to reprogram gene expression in the cell as a defense…
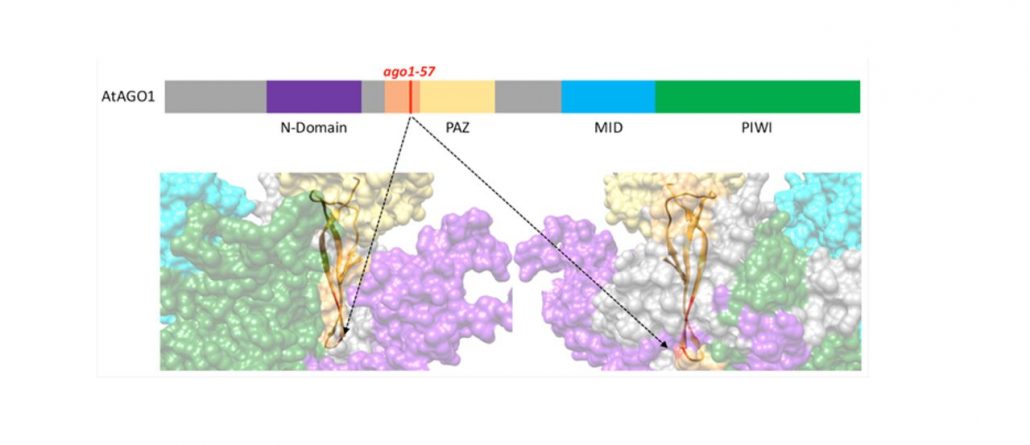
ARGONAUTE1: To Shed a Strand or Not?
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellClavel et al. investigate recognition and binding of AGO1 by viral P0 protein https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00111.
By Marion Clavel
Background: In plants, small RNAs (sRNAs) are widely used to regulate gene expression of both host genes and foreign nucleic acid, like viruses. sRNAs function…
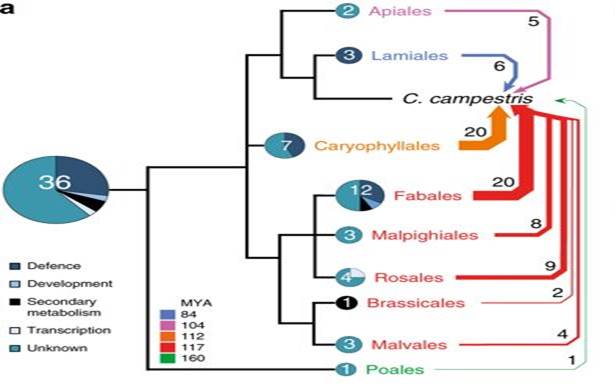
Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEven without knowing a lot about parasitic plants, you can probably guess some of the insights that come from the first parasitic plant genomic sequence. Because parasitic plants get their nutrients from another organism (functionally, they become heterotrophic), you might expect they would gradually…

Genome assemblies of maize lines Mo17 and W22: Extensive intraspecific variation, and resource for functional biology (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe maize genome is largely composed of transposable elements, which is one reason maize has been such a powerful genetic model. However, these transposons also mean that there is a great deal of genetic variability between inbred lines, which can contribute to heterosis (hybrid vigor). In a pair of…
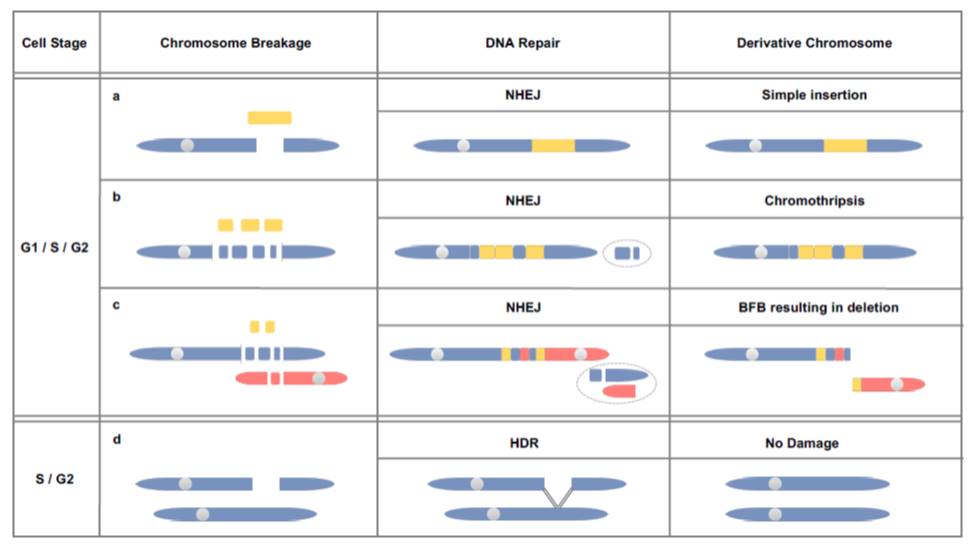
Genome-scale sequence disruption following biolistic transformation in rice and maize (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe two classic approaches to introducing DNA into a plant’s genome are by harnessing Agrobacterium tumefaciens’ fascinating gene-transfer skill, or by shooting the new DNA into the cell using a “biolistic” (gun) approach. Because of Agrobacterium’s restricted choice of hosts, the biolistic…

Co-expression networks for strawberry flower and fruit development
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe diploid strawberry (Fragaria vesca) is a useful model system for understanding non-climacteric ripening and seed-to-fruit cross-tissues communication. Previously, spatial and temporal transcriptome data from the strawberry fruit and flowers was generated. Shahan and colleagues combine the transcriptome…

