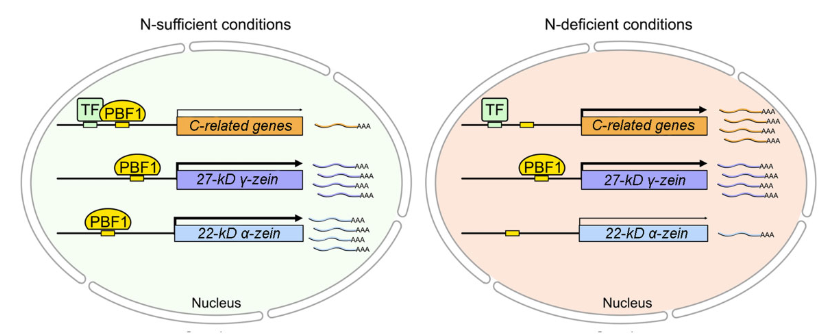
Nitrogen-dependent binding of the transcription factor PBF1 contributes to the balance of protein and carbohydrate storage in maize endosperm (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe majority of maize endosperm is made of starch (70%) and proteins (10%) and their biosynthesis is a complex process which involves many enzymes. N-containing compounds, such as enzymes, amino acids, and nucleotides are crucial for C metabolism. Thus, when N levels are altered, the storage of proteins…
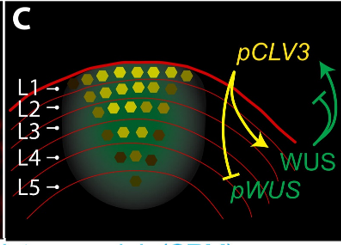
Concentration-dependent transcriptional switching through a collective action of cis-elements (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the well-known molecular pathways that regulate plant development is the one formed by the homeobox transcription factor WUSCHEL (WUS) and the secreted peptide CLAVATA 3 (CLV3). In the shoot apical meristem (SAM), WUS expression is constrained to the organizing center where it maintains the stem…
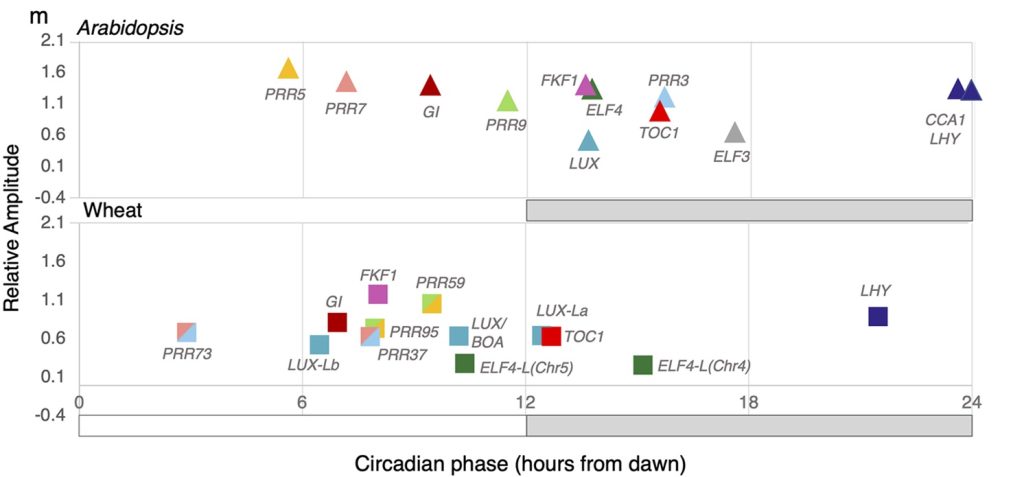
Circadian regulation of the transcriptome in a complex polyploid crop (PLoS Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCircadian regulation fine-tunes patterns of gene expression in plants in changing environments and has been selected for during crop domestication. Many studies have been done on circadian gene expression in Arabidopsis, but far less is known about this regulation in hexaploid bread wheat, especially…
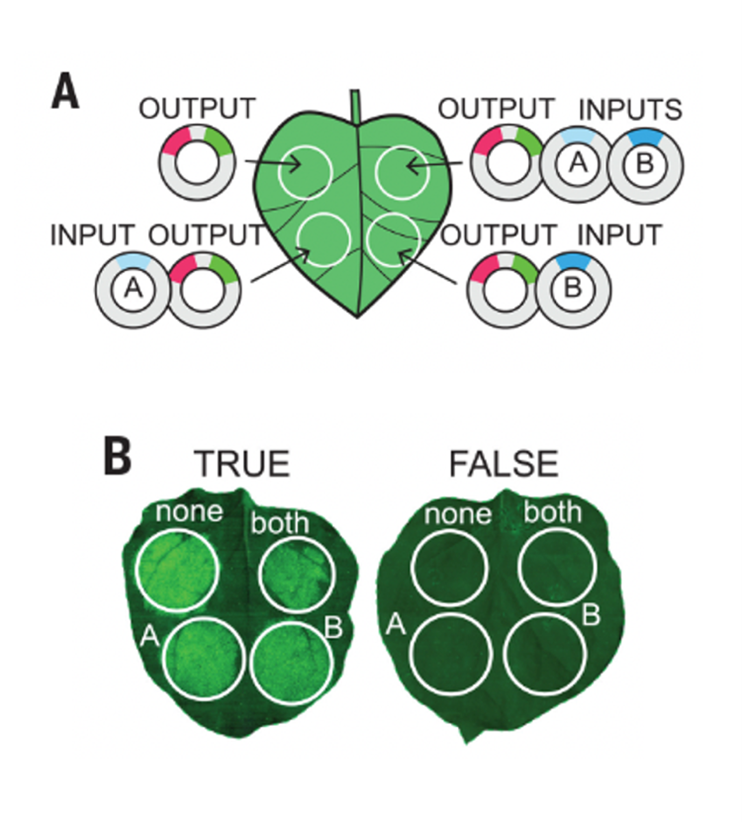
Synthetic genetic circuits as a means of reprogramming plant roots (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklySynthetic genetic circuits offer a promising method to achieve beneficial changes in plant phenotypic traits. By combining different activator or repressor transcription factors (TFs) , the expression of target genes may be fine-tuned according to Boolean operations. Here, Brophy et al. describe a method…
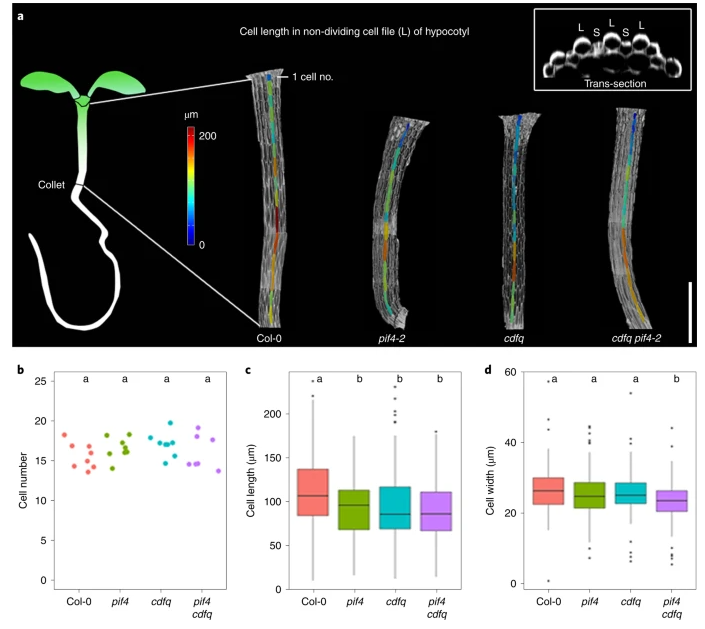
PIF4 enhances DNA binding of CDF2 to co-regulate target gene expression and promote Arabidopsis hypocotyl cell elongation (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponses to environmental and internal signals require the recruitment of transcription factors (TFs). TFs recognize simple DNA sequences to activate specific genes that will accomplish the required functions. DOF (DNA-binding with one finger) is a large family of plant TFs that encloses the CYCLING…
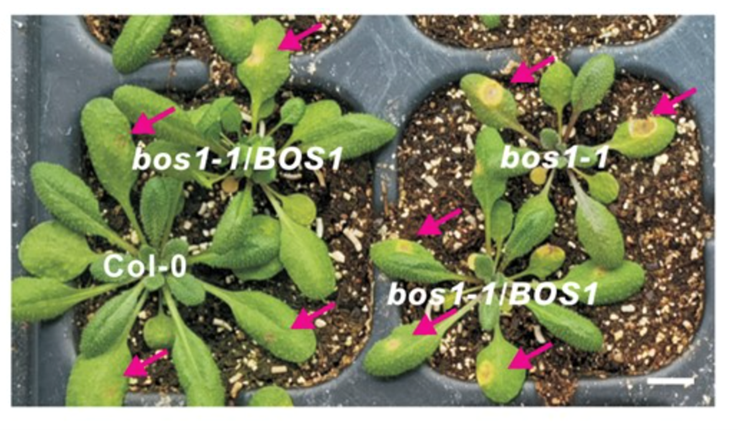

Ectopic expression of BOTRYTIS SUSCEPTIBLE1 reveals its function as a positive regulator of wound-induced cell death and plant susceptibility to Botrytis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProgrammed cell death (PCD) is a ubiquitous eukaryotic process in which specific cells are eliminated during development or in response to stress. Here, Fuqiang Cui and colleagues confirm for the first time the exact role of the BOS1 gene in the regulation of PCD in Arabidopsis thaliana. Originally identified…

DREB1C is a regulator of nitrogen use efficiency and flowering time in rice (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo improve the profitability and sustainability of agriculture, there has been an extensive quest to identify regulators that boost nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) without compromising yield. Wei et al. identified a DREB family transcription factor based on RNAseq analysis of rice plants exposed to low…

CCA1 is a regulator of ABA-mediated abiotic stress tolerance in rice (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn rice, the circadian clock component gene Circadian Clock Associated 1 (OsCCA1) regulates flowering and nitrogen use efficiency. CCA1 is a MYB family transcription factor that follows a rhythmic expression pattern. Wei et al. confirmed the role of CCA1as a key hub in coordinating plant growth and abiotic…
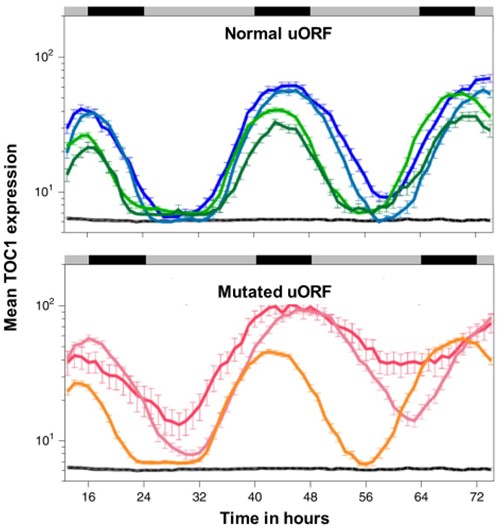
Upstream ORFs check undesired leaky protein translation and buffer noise (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring my research journey, I have come across a handful of genes that are hard to express. Sometimes, even with a strong promoter and high transcript level, the protein level is negligible. We generally considered these proteins might be degrading very fast. But maybe not. A recent article by Wu et…

