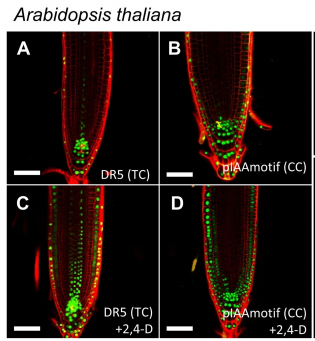
Deep conservation of cis-element variants regulating plant hormonal responses (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPromoter regions upstream of transcription start sites contain DNA regulatory elements (RE) crucial for the transcriptional control of gene expression. However, REs are short degenerated sequences with low conservation during evolution. In this paper, Lieverman-Lazarovich et al. studied REs in core hormone…
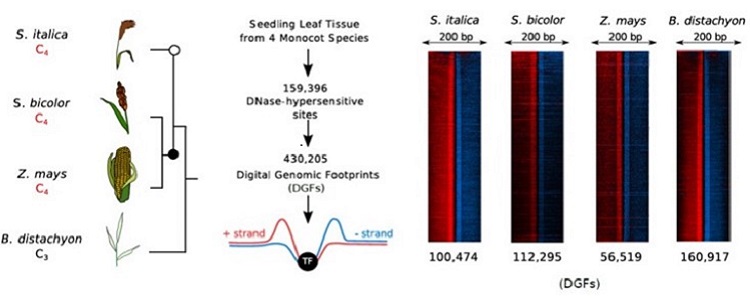
Mapping the landscape of C4 gene regulation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBurgess et al characterize genome-wide patterns of transcription factor binding to provide insight into the architecture associated with C4 photosynthesis gene expression. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00078
By Steven James Burgess (University of Cambridge, UK) and Ivan A. Reyna-Llorens…
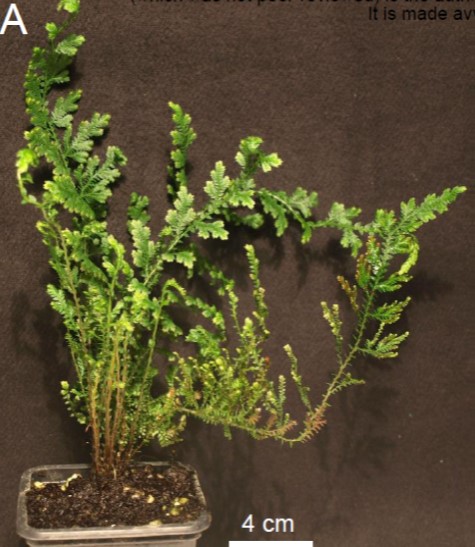

Selaginella moellendorffii expression atlas provides insight into the origin and evolution of plant vasculature (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLand plants (embryophytes) evolved from freshwater algal predecessors over 450 million years ago and have since separated into the morphologically diverse lineages observed today. A key feature in the expansion of plant life on land was the development of the plant vasculature and complex rooting systems.…
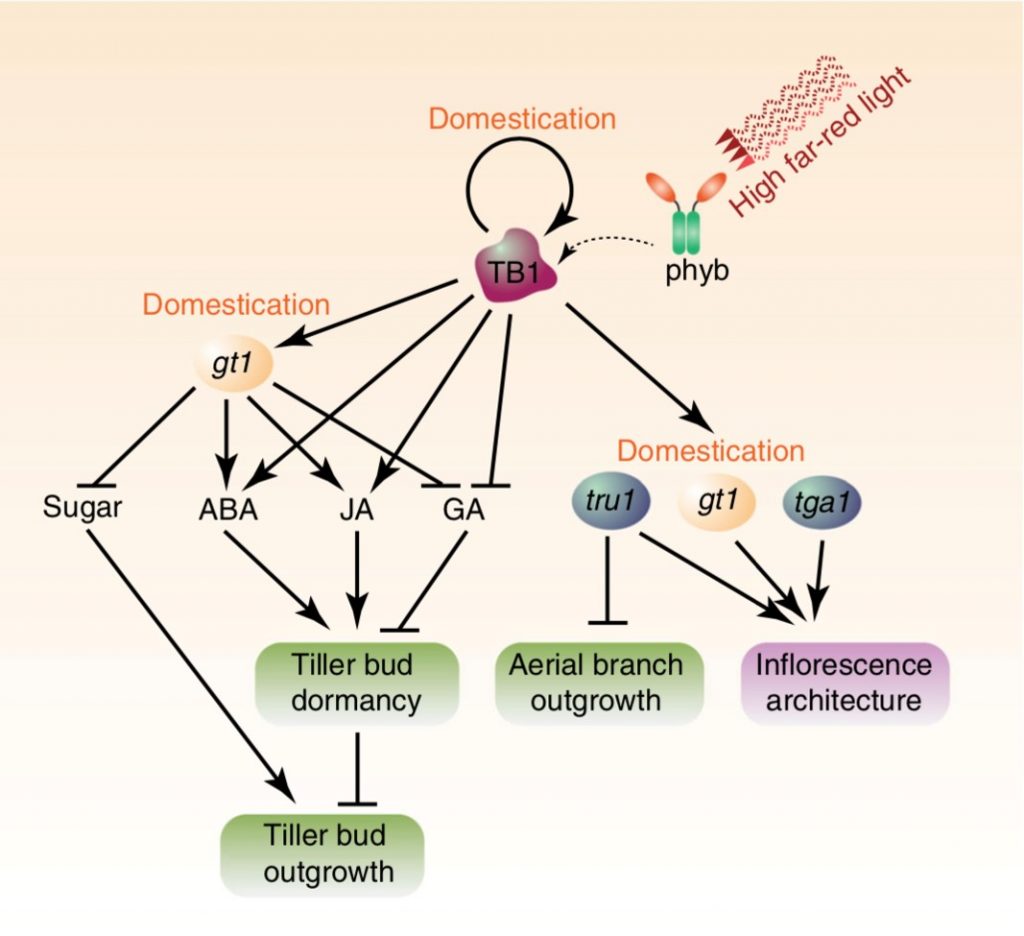
teosinte branched1 and the control of bud dormancy and growth in maize (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBranching has a significant impact on plant architecture. Maize, a domesticated species, has lower branching levels in comparison to its wild ancestor teosinte. Axillary branching is the result of lateral buds growth. Some factors such as phytohormones and transport of sugars are related to bud activation/dormancy…
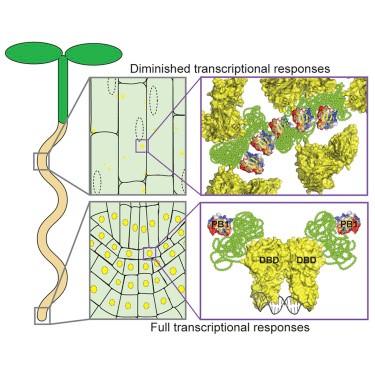
Nuclear-cytoplasmic partitioning of ARF proteins controls auxin responses ($) (Mol Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyARF (Auxin Response Factor) transcription factor proteins contain three domains: an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a variable middle region, and a C-terminal PB1 domain. Powers et al. found that ARF7 and ARF19 accumulate as large-order assemblies in the cytoplasmic region of mature root cells, but the…
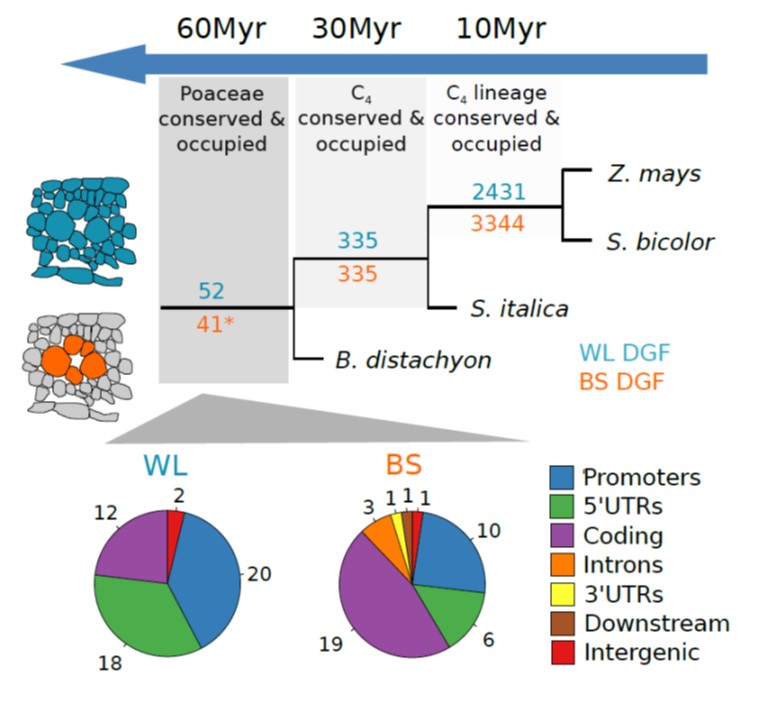
Genome-wide transcription factor binding in leaves from C3 and C4 grasses (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost plants use the C3 photosynthesis pathway, however many have evolved strategies like C4 photosynthesis that accumulate CO2 around RuBisCO. Burgess et al. performed DNAseI-SEQ in three C4 plants: S. bicolor, Z. mays and S. italica, and one C3: B. dystachion, to offer an insight into the cis-element…
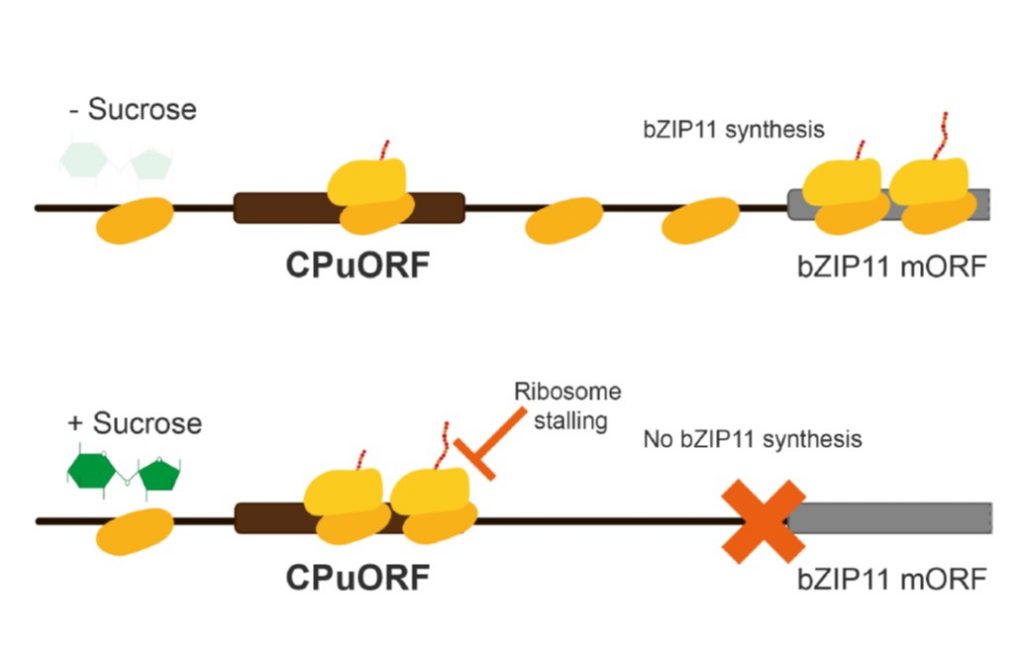
Review: Metabolite control of translation by conserved peptide uORFs: The ribosome as a metabolite multi-sensor (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNot all mRNAs are translated equally. Between 25–50% of eukaryotic mRNAs have an upstream open reading frame (uORF) that affects translation of the main ORF (mORF). Usually the presence of an uORF inhibits translation, but under some conditions the ribosome can overlook the uORF or reinitiate translation…
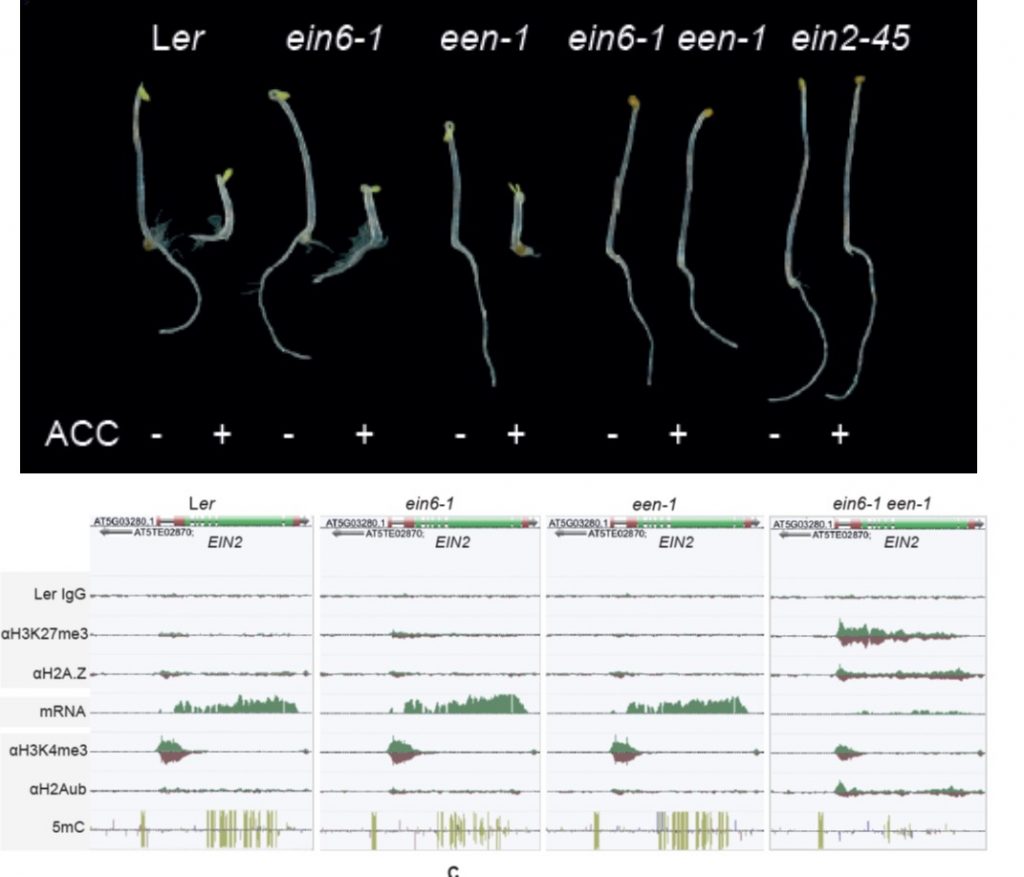
Epigenetic silencing of a multifunctional plant stress regulator EIN2 (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEIN2 is a key regulator of the ethylene response and a protein with a complex function and regulation. Zander et al. have uncovered an interesting and complex mechanism by which its expression is regulated. Many genes are regulated through histone modifications, with the histone variant H2A.Z and the…
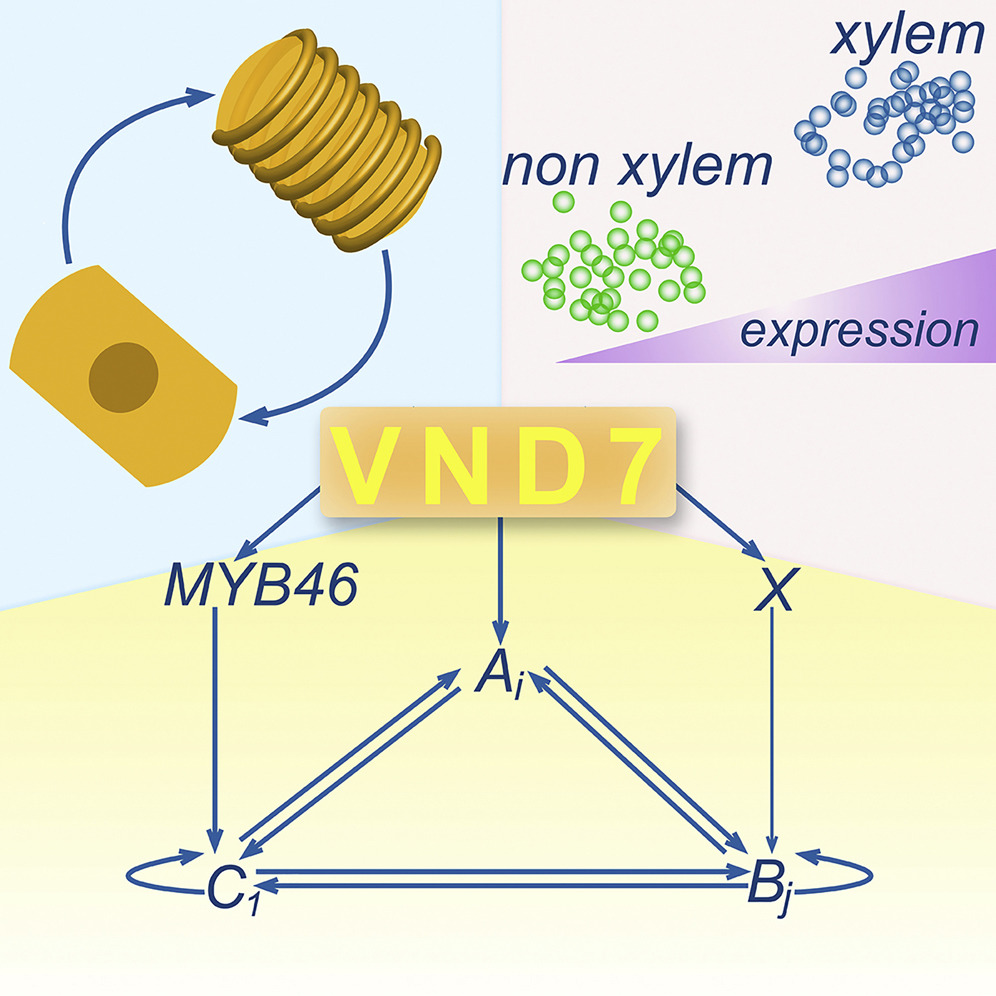
Molecular mechanisms driving switch behavior in xylem cell differentiation (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyXylem is involved in the movement of water and mineral nutrients through the plants from the roots to leaves; its cells are not totipotent and undergo programmed cell death. VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN (VND) transcription factors are master switches of xylem cell differentiation in Arabidopsis and much…

