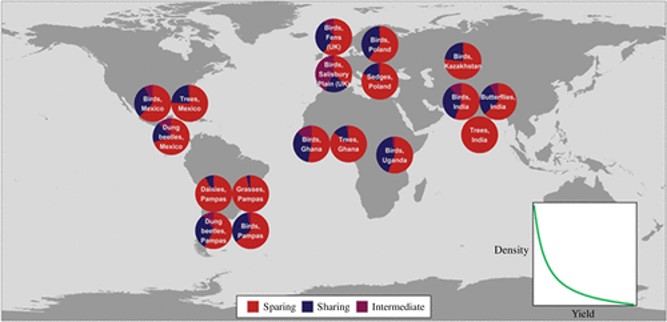
Review: High-yield farming is essential to slow biodiversity loss
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s 2025, and although we live in a world saturated with information, is increasingly difficult to sort fact from propaganda or fiction. This is true in all arenas, including plant science. Calls for strategies to improve crop yields are sometimes met with criticisms that higher yielding crops would…
Overcoming barriers to bioengineering new disease resistance
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBentham, De la Concepcion et al. fine-tuned a plant immune receptor pair to allow for engineering new specificities while avoiding autoactivation.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad204
Adam R Bentham, Mark J Banfield
Department of Biochemistry and Metabolism, John Innes Centre, Norwich Research…
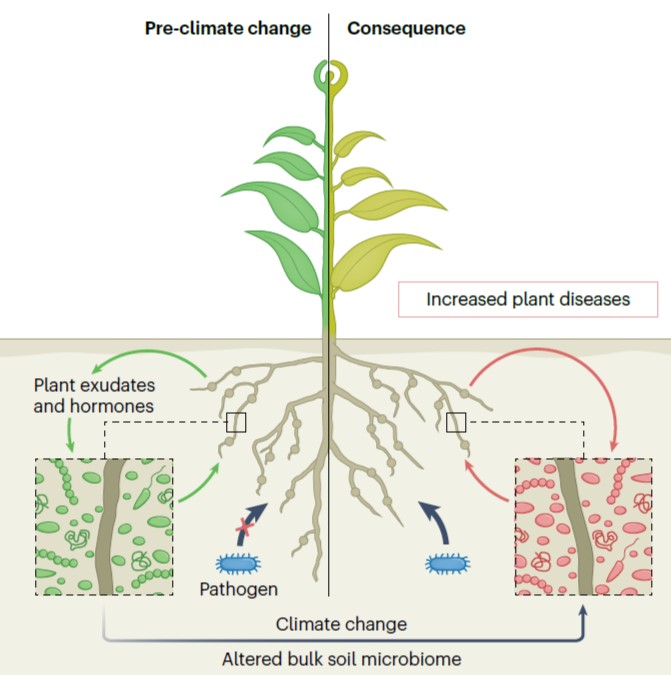
Review: Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security, and paths forward
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of what is written about the impacts of climate change on food production is focused on the abiotic stresses that plants will experience, but biotic stresses will be equally impactful, as discussed in this fine review by Singh et al. The challenges in predicting climate impacts on plant disease…

Review: One plant’s poison
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants synthesize interesting chemicals that attract, deter, amuse, and harm their predators. Some of the most harmful to humans have been selectively eliminated through the process of domestication, but others render potential food sources inedible. This review by Liu et al. discusses four approaches…
Extensive genome study to boost yield and improve agronomic traits in chickpea (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn recent years, there has been increasing awareness about the environmental impact of animal-based protein sources. Legumes such as chickpea (Cicer arientinum) are relatively cheap and sustainable sources of proteins, dietary fibres and micronutrients. Although there is a vast chickpea germplasm collection,…
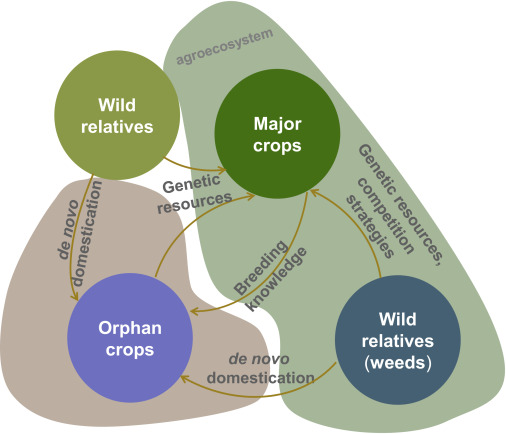
Review: Orphan crops and their wild relatives in the genomic era (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMore than half of human calories come from rice, wheat, and corn, although many other cereals have been domesticated as food crops. Several of these “orphan” cereal crops and their wild relatives are being studied with the goal of diversifying our food supply, which is particularly important due…
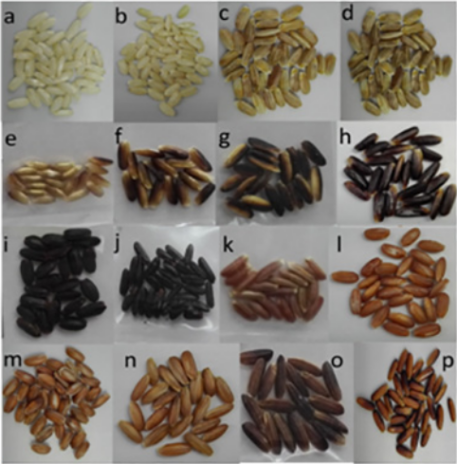

Review: The genetic basis and nutritional benefits of pigmented rice (Frontiers Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPigmented rice varieties are those in which a pigment is deposited in the bran, the outer layer of the grain. The pigment can be from brown to red (proanthocyanidins) or from purple to black (anthocyanins). In the course of domestication, humans have selected against the genetic factors responsible for…
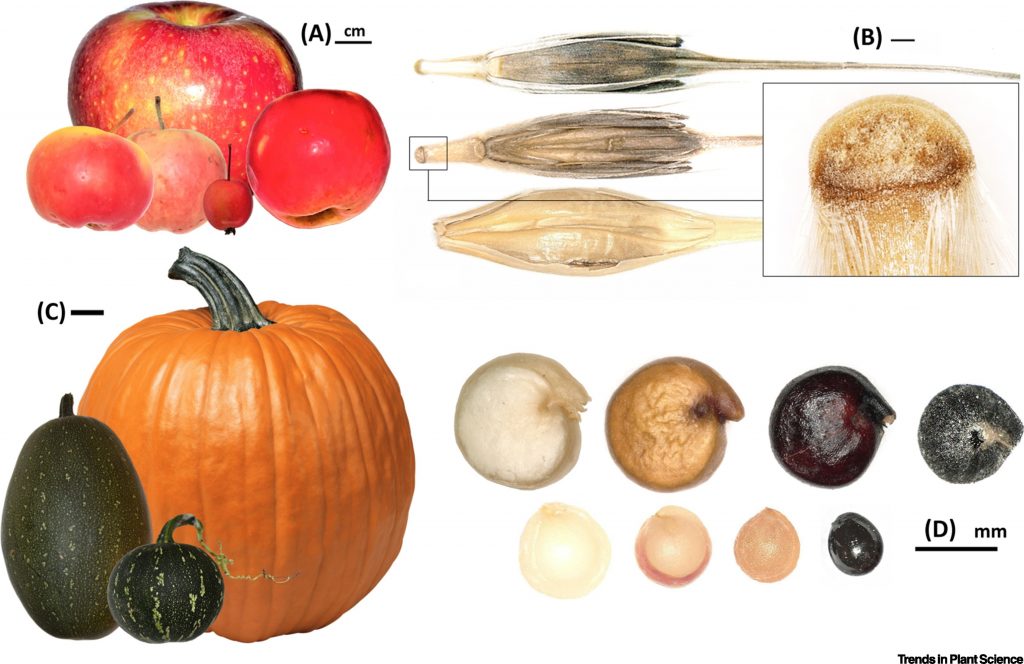
Opinion. Anthropogenic seed dispersal: Rethinking the origins of plant domestication (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStudies regarding the development of agriculture have started to integrate a plant evolutionary perspective. In this context, Spengler explores how changes in seed dispersal allowed plant domestication during the first half of the Holocene (e.g., more than 5000 years ago). He starts by redefining domestication…

From population to production: 50 years of scientific literature on how to feed the world (Global Food Security)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTamburino et al. analyzed text from more than 12,000 research articles published in the past 50 years that included the terms “global” or “world” and “food supply”, “food demand’, or “zero hunger”. From this dataset, they quantified terms related to population, total food production,…

