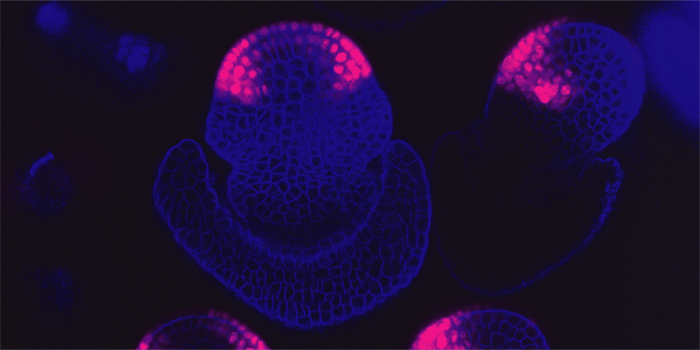
A molecular module in gibberellin signaling-mediated flowering
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang and Jian et al. reveal an epigenetic regulatory mechanism underlying gibberellin signaling-mediated flowering.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad166
By Chunyu Zhang and Xingliang Hou; South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China
Background: The timing…
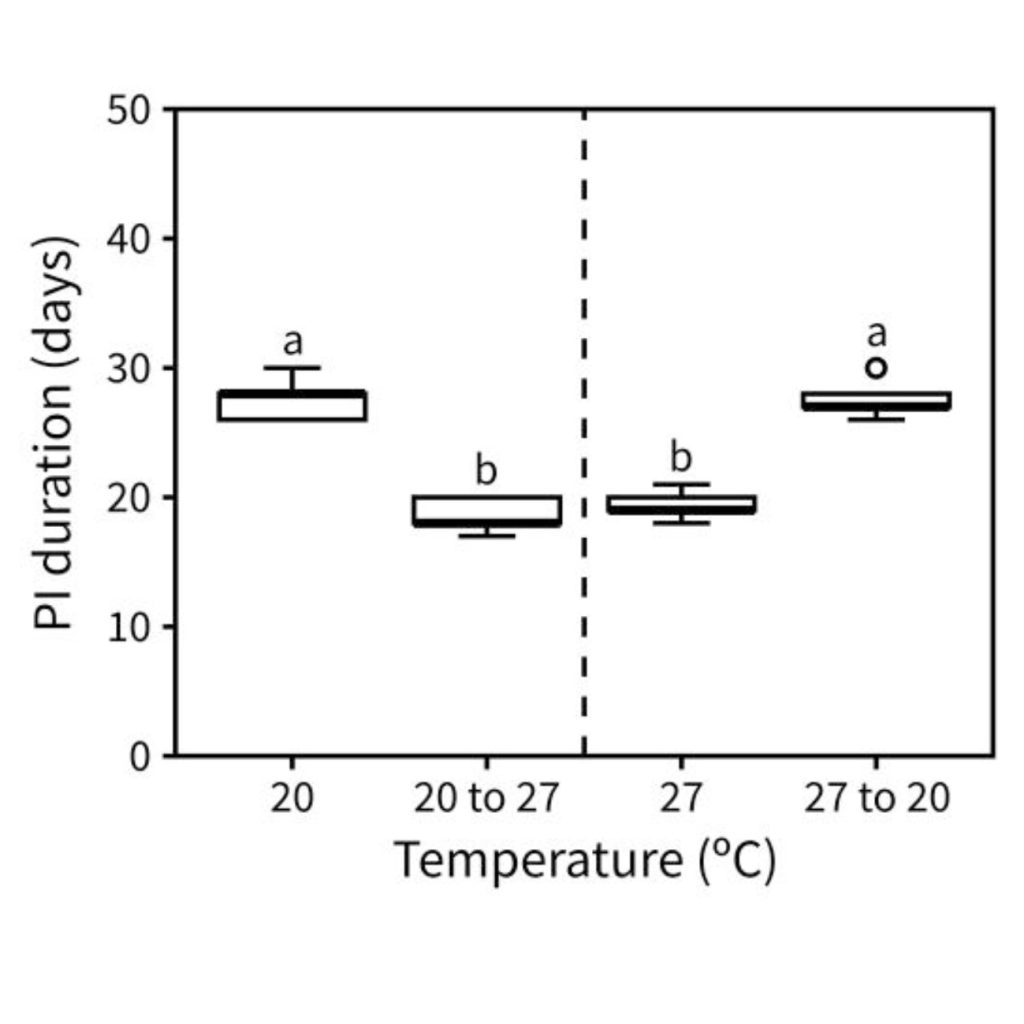
Photo-thermally controlled transcriptional regulation of FT drives the arrest of flowering time in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight and temperature are important external signals required by plants for flower initiation. These external signals along with some internal cues (plant age, gibberellins, etc.) are established factors for floral initiation, but the factors required for end-of-flowering time are not yet established.…
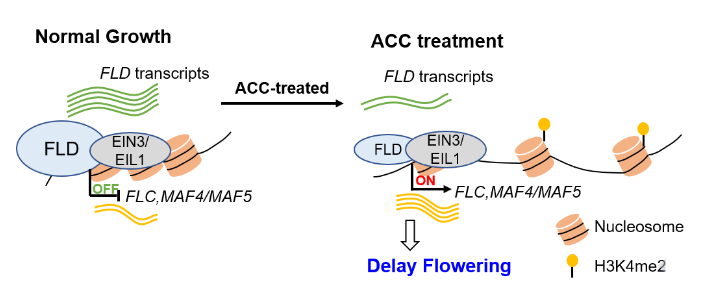
EIN3/EIN3-LIKE1 modulate FLC expression via histone demethylase interaction
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlowering time is determined by both endogenous factors and environmental cues to ensure successful reproduction. ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE 3 (EIN3) and EIN3 LIKE 1 (EIL1) are transcription factors which are the key downstream regulators of ethylene signal transduction. Rapid flowering is promoted by the…
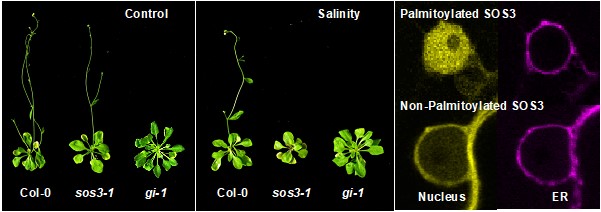
Flowering Under Stress
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellPark H.J., Gamez-Arjona F., et al. show how plants reset the time of flowering under salinity stress. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac289
Background: For plants, extremes in the cardinal conditions of light, temperature, nutrients and water availability are major drivers of natural selection.…
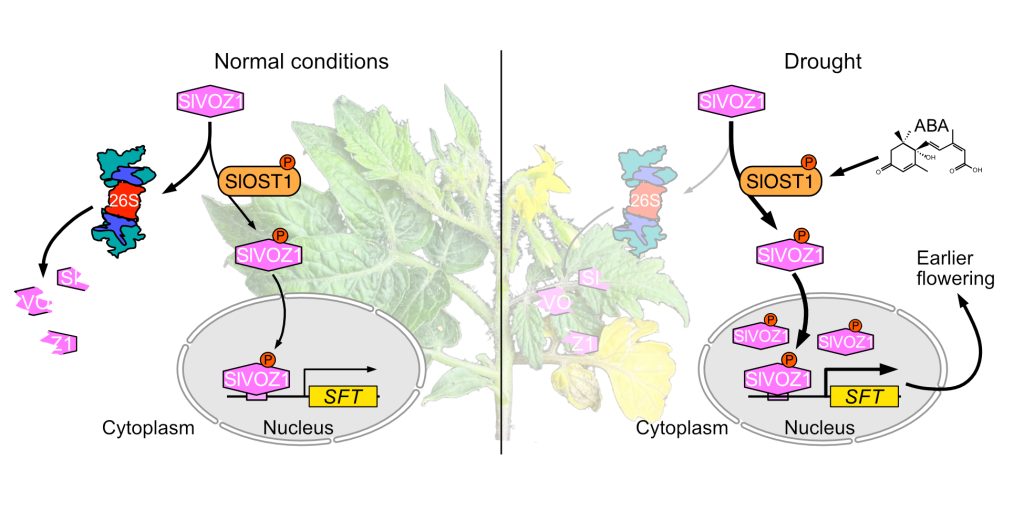
Drought and Flowering Management by SlOST1-SlVOZ1 in Tomato
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellAuthor(s) and Institutions:
Leelyn Chong and Yingfang Zhu
State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Adaptation and Improvement, School of Life Sciences,
Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, China
Sanya Institute, Henan University, Sanya, 572025, China
Leelyn Chong and colleagues provide cues as to how plants…
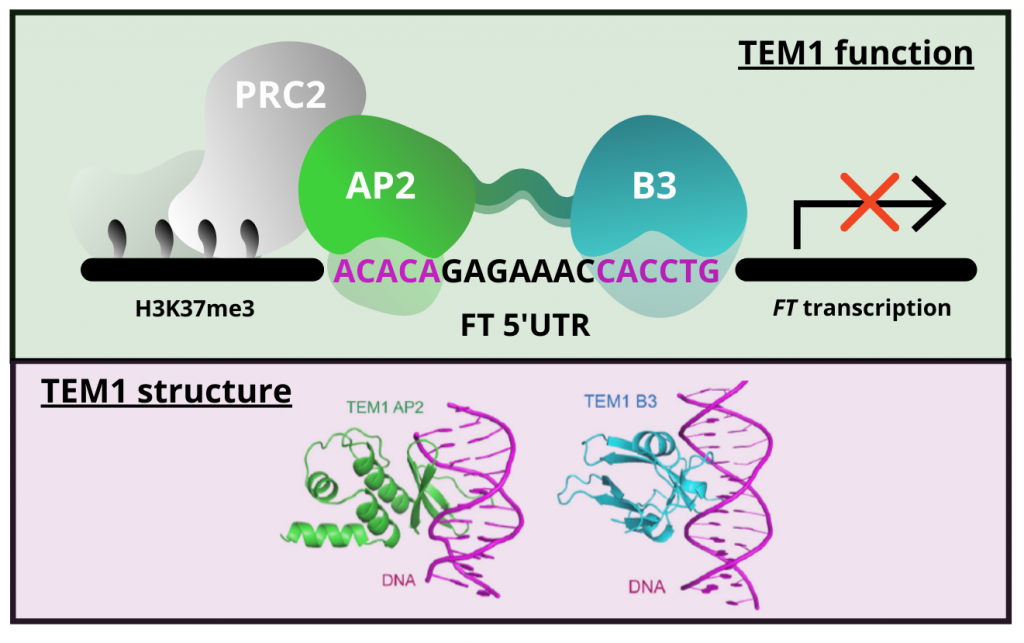
TEM1 combinatorially binds to FLOWERING LOCUS T and recruits a Polycomb factor to repress the floral transition in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGene expression is primarily controlled by transcriptional regulatory proteins able to recognize and bind short DNA sequences in downstream targets. Understanding how DNA-binding proteins achieve high precision and switch on/off the transcription of selected genes at a specific developmental stage or…
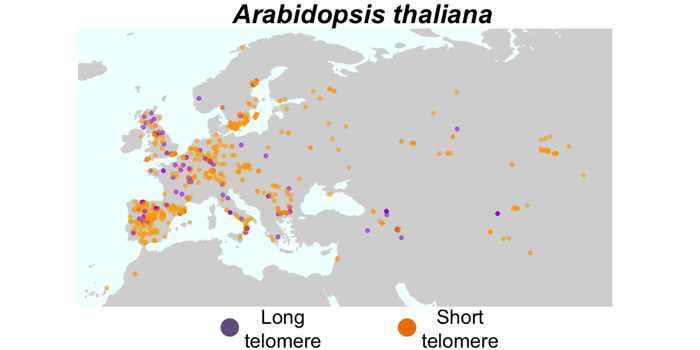
Why does telomere length vary in plants?
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellChoi et al. uncover the association between telomere length and flowering time variation in Arabidopsis, rice, and maize. The Plant Cell (2021) https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab022
Background: Telomeres are DNA-protein complexes found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes that protect the…
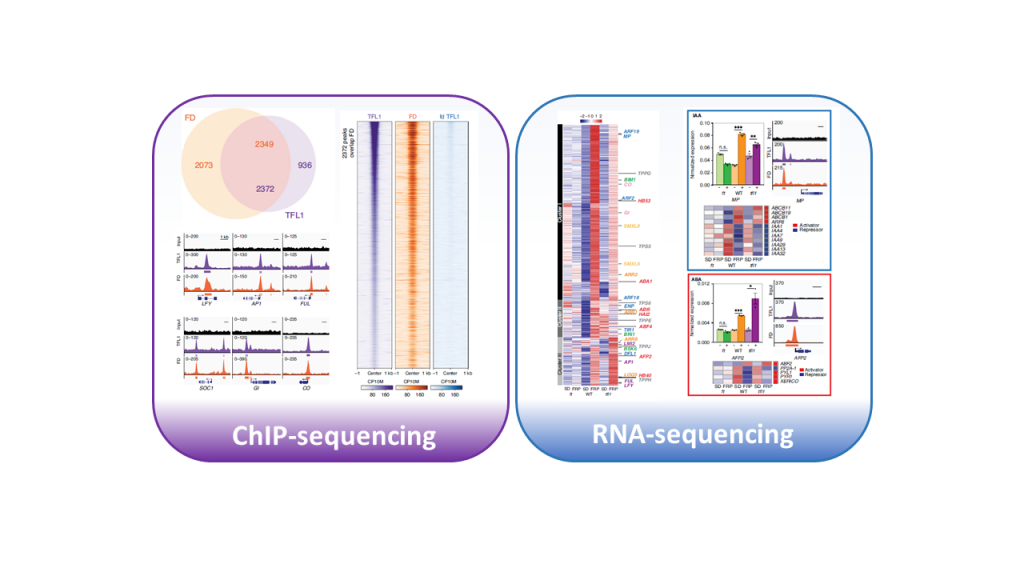
TERMINAL FLOWER 1-FD complex target genes and competition with FLOWERING LOCUS T (Nat. Commun.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe onset of reproductive development is tightly regulated in response to environmental cues as early and delayed flowering greatly affects seed production. In Arabidopsis, the timing of flower formation is controlled by members of the Phosphatidyl Ethanolamine-Binding Protein (PEBP) family: TERMINAL…

Exploring variation in a key maize regulator of floral form
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMaría Jazmín Abraham-Juárez, Amanda Schrager-Lavelle et. al. explore how variation in a key floral regulator affects floral development, downstream gene expression and protein complex assembly in maize. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00300
by Jazmin Abraham-Juarez, Biology Department,…

