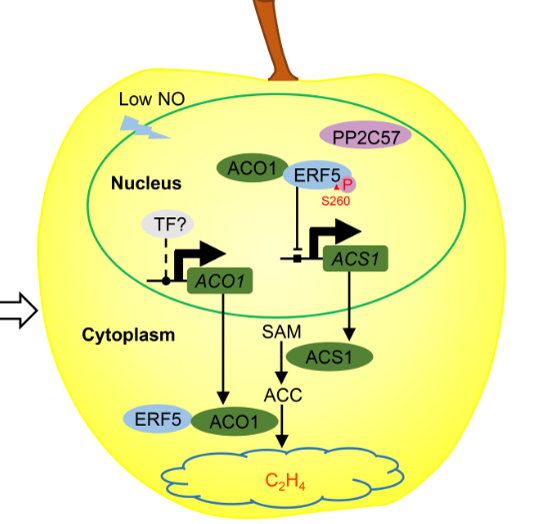
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 5 mediated by nitric oxide suppresses ethylene biosynthesis in apple fruit (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMechanisms of phytohormone modulation and their interface with other regulatory molecules are still being uncovered. Nitric oxide (NO) is a regulatory molecule which has been shown to affect ethylene biosynthesis through the action of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 5 (ERF5) in apple fruit. New work by Ji et…
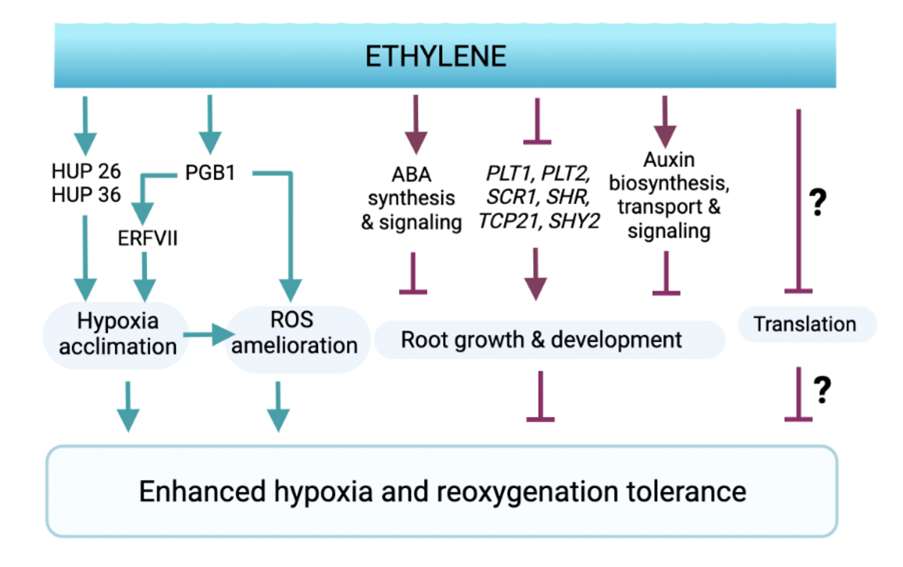
Ethylene augments root hypoxia tolerance through amelioration of reactive oxygen species and growth cessation (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlooding presents a dual threat to plants; not only is mitochondrial respiration supressed during the resulting hypoxic conditions, but once the floodwaters recede, the return to ambient oxygen levels triggers a cascade of harmful reaction oxygen species (ROS). One of the most well-studied responses…
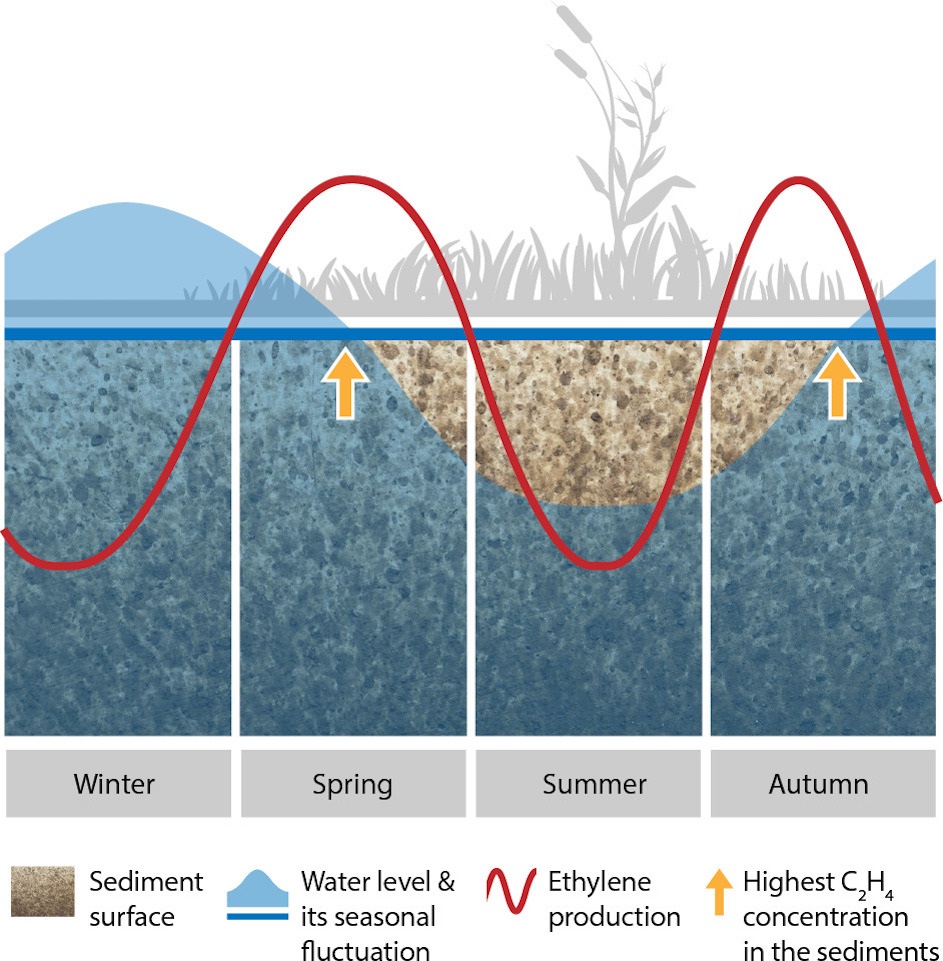
The sweet and musky scent of home: biogenic ethylene fine-tunes seed germination in wetlands (Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight, temperature, substrate moisture and oxygen availability are renowned germination triggers for wetland species. However, wetlands sediments are a significant source of gases that might shape the species germination behavior, such as ethylene –a renowned germination promoter. Still, little is…

A Rosy Scenario for Flower Opening
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellCheng et al. explore how ethylene promotes the asymmetric growth of petal bases to promote flower opening in rose. The Plant Cell (2021) https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab031
By Chengchen Xia, Junping Gao, and Nan Ma
Background: Flowers are unique structures in angiosperms that are used for…
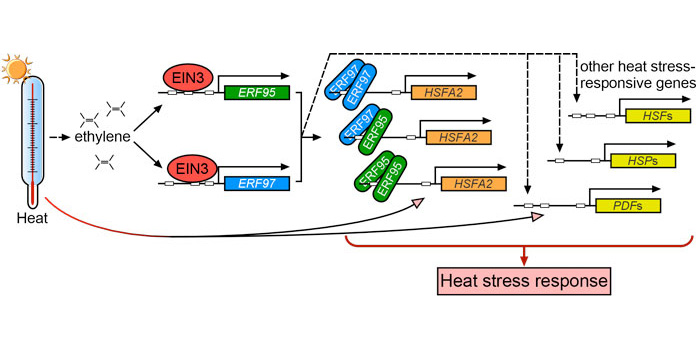
The Role of Ethylene and Ethylene Response Factors in the Heat Stress Response
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSummary: Huang et al. elucidate a link between ethylene signaling and heat stress responses. Plant Cell https://bit.ly/3pTjNBK
By Jianyan Huang, Xiaobo Zhao, Marco Bürger, Yurong Wang, Joanne Chory
Background: Temperature is an environmental factor that has one of the most dramatic effects on…
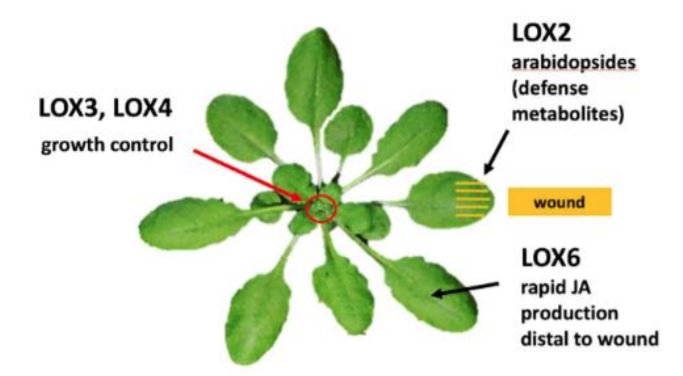
To grow or not to grow: specific lipoxygenases control wound-induced growth restriction
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchTo grow or not to grow: specific lipoxygenases control wound-induced growth restriction
Amna Mhamdi
Ghent University, Department of Plant Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, and VIB Center for Plant Systems Biology, 9052 Ghent, Belgium
Address correspondence to: amna.mhamdi@psb.ugent.be
As…
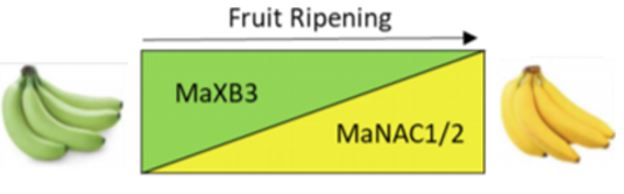
MaXB3 Limits Ethylene Production and Ripening of Banana Fruits
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: Sjon Hartman
ORCID: 0000-0002-6709-6436
Plant Ecophysiology, Institute of Environmental Biology, Utrecht University, Padualaan 8, 3584 CH, Utrecht, The Netherlands
j.g.w.hartman@uu.nl
Ripening of climacteric fruits such as banana (Musa acuminata), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), and…
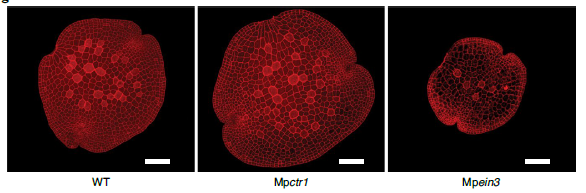
Ethylene independent functions of ACC in Marchantia polymorpha (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Ethylene is synthesized from 1-Aminocyclopropane carboxylic acid (ACC), and ACC has long been used as a substitute to induce ethylene responses. In a new study, Li and colleagues show that ACC functions as a stand-alone signaling molecule in the liverwort Marchantia. While treatment with ethylene…

Ethylene signaling mediates host invasion by parasitic plants (Science Advances)
Plant Science Research WeeklyParasitic plants cause agricultural devastation across the globe, yet the molecular basis of their parasitism is largely enigmatic. They grapple and intrude into the host roots with an organ called the haustorium. Haustoria formation is induced upon recognition of host-derived haustorium-inducing factors…

