
RNA composition of Processing Bodies
Liu et al. explore the RNAs present in processing bodies, a cytoplasmic subcellular condensate.
Andriani Mentzelopoulou
Department of Biology, University of Crete, Heraklion, Greece
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Foundation for Research and Technology–Hellas, Heraklion,…

Ethylene Inhibits Pear Anthocyanin Synthesis
Ni et al. explore the relationship between ethylene, the ERF9 and RAP2.4 transcription factors, and anthocyanin biosynthesis in pear.
Plant Cell
By J. Ni1,3,4, S. Bai1,3,4 and Y. Teng1,2,3,4
1 Department of Horticulture, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310058, PR China
2 Hainan Institute…

A Mediator–transcription factor module that regulates fruit ripening in tomato
Deng, Yang, Li, Chang, Sun et al. explore the interaction between EIN3-like transcription factors and subunits of the Mediator complex in tomato fruit ripening.
Background: Fruit ripening relies on the precise spatiotemporal control of RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-dependent transcription of thousands…
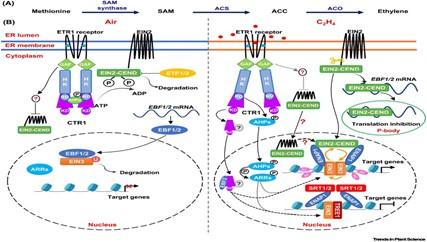
Review: The role of ethylene in plant temperature stress response
The phytohormone ethylene is known for its importance in plant development and mostly for its role in fruit ripening. However, in this review Huang et al. summarize recent findings on ethylene’s role in temperature (hot and cold) stress response and ethylene crosstalk with other hormones. Interestingly,…
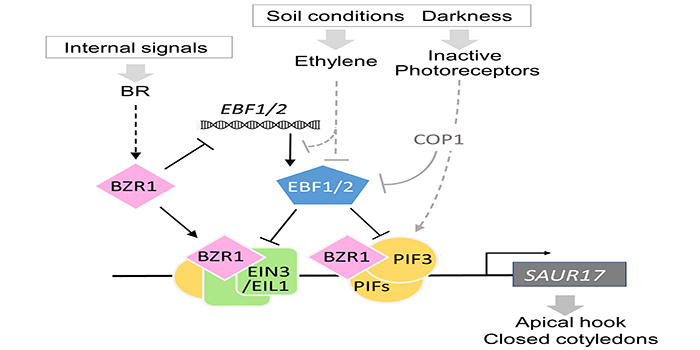
How do brassinosteroids promote etiolation of apical organs in Arabidopsis?
Wang et al. explore how plants maintain apical etiolation.
By Jiajun Wang (Southwest University, China), Haodong Chen (Tsinghua University, China), Xing Wang Deng (Peking University, China), Ning Wei (Southwest University, China)
Background: Seeds germinate underneath the soil; to help the shoot…
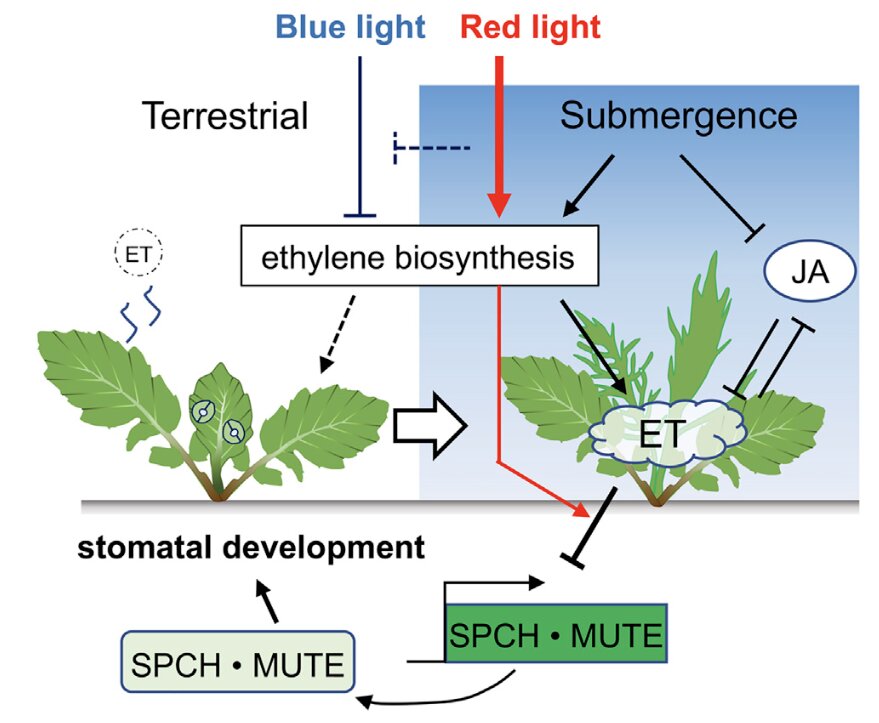
Underwater blues: Molecular rewiring of stomatal development in Rorippa aquatica
Unanticipated flooding conditions challenge the survival and overall growth and development of a plant, for example stomatal development is suppressed under submerged conditions. Stomata are microscopic pores on the surface of leaves of a plant that play an important role in the exchange of gases between…
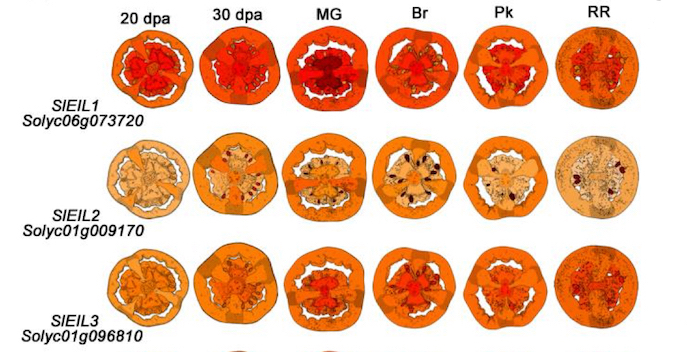
A molecular framework for ethylene-mediated tomato fruit development
Huang et al. unravel the roles of ethylene in tomato fruit growth and ripening.
Background: Fruit development is an intriguing evolutionary strategy that functions in both seed protection and seed dispersal. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) has long been used as a model system to uncover mechanisms…
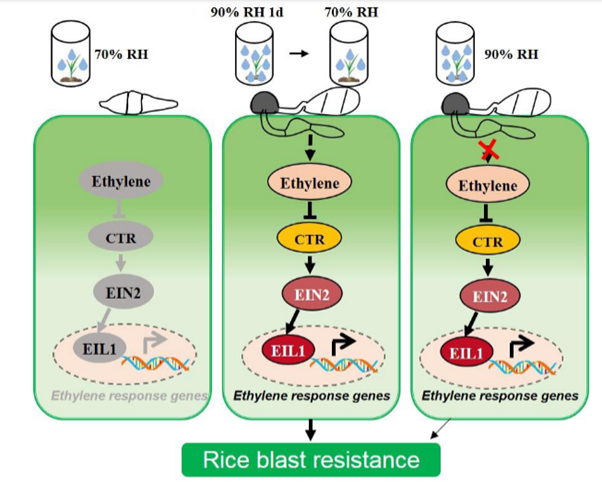
High humidity compromises plant immunity while promoting pathogen growth (Plant Cell Environ)
Humidity is considered a key component for the growth of fungal plant pathogens. For many infection assays we either maintain plants in high humidity, or wrap the infected area and keep spraying it with water. This is generally performed to facilitate fungal growth and the assumption that this may not…
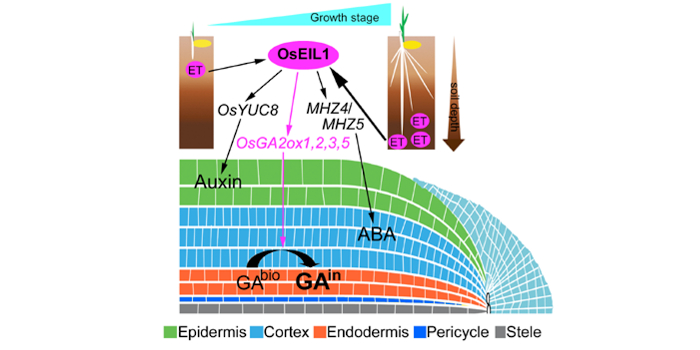
Hormone crosstalk orchestrates root development
Qin et al. identify a mechanism by which ethylene activates gibberellin catabolism to determine primary root growth in rice.
Hua Qin and Rongfeng Huang
Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Background: The optimization of root architecture is one of the…

