
J. Exp. Bot. Special Issue. The plant cuticle: old challenges, new perspectives ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe cuticle is a cell-wall polymer that protects against desiccation, pathogens and UV light. Domínguez et al. provide an open-access editorial that describes this fine collection of articles covering all aspects of the plant cuticle, from its evolutionary origins to its ecological significance. Within…

Chromatin accessibility changes between Arabidopsis stem cells and mesophyll cells illuminate cell type-specific
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWhat gives stem cells their plasticity and why are differentiated cells so specialized? Sijacic et al. approach this question by analyzing transcription factor (TF) accessibility to chromatin. Nuclei were isolated from shoot apical meristem (SAM) pluripotent stem cells and fully-differentiated mesophyll…
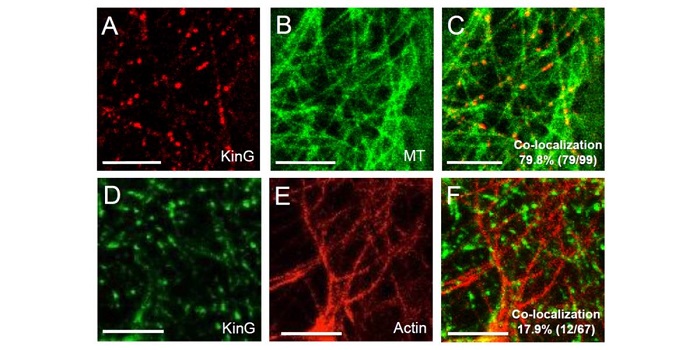
A plant-specific kinesin KinG regulates intra- and intercellular movement of SHORT-ROOT
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSHORT-ROOT (SRT) is a transcription factor that has previously been shown to move between cells and so contribute to developmental patterning. Spiegelman et al. investigated the cellular machinery that contributes to SRT’s movement. Previous work showed that the movement of SRT depends on the endosome…

SHORTROOT-mediated increase in stomatal density has no impact on photosynthetic efficiency
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSHORTROOT (SRT) is a transcription factor that contributes to developmental patterning non-cell autonomously, by moving between cells. In leaves, SRT has been shown to contribute to sub-epidermal patterning specified by distance from the vein. Schuler et al. explored whether it also contributes to epidermal…
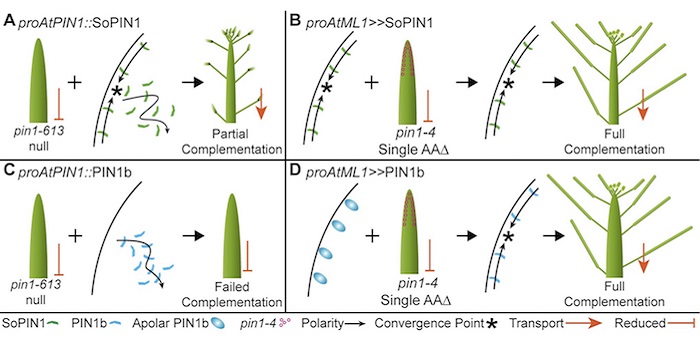
Cross-species functional diversity within the PIN auxin efflux protein family
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPolar localized PIN FORMED (PIN) efflux carriers proteins organize directional auxin flow and accumulation. Most flowering plants have another family of PIN proteins called Sister of PIN1 (SoPIN1), which Arabidopsis and members of the Brassicacea family do not have. The grass Brachypodium dystachion…

Mechanochemical polarization of contiguous cell walls shapes plant pavement cells
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog
The jigsaw-puzzle shape of the epidermis layer has been puzzling the scientists for some time now. Majda et al. examine the shape of the epidermis cells from the cell wall perspective. Mutations leading to even minor changes in cell wall composition significantly affected pavement cell geometry.…
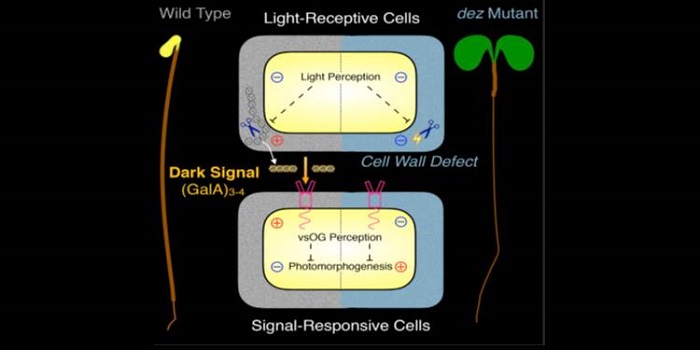
Repression of photomorphogenesis by a small cell-wall-derived dark signal ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogGenetic screens have revealed many key components of light signaling. In this new work, Sinclair et al. provide new insights into the repression of photomorphogenesis by cell-wall derived signals. They started with a mutant, de-etiolated by zinc (dez) that shows open cotyledons and a short hypocotyl…

Update: Root plasticity and internal aeration
Blog, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Takaki Yamauchi, Timothy D Colmer, Ole Pedersen, Mikio Nakazono
Introduction
Root acquisition of water and nutrients is essential for plant growth and crop productivity (Lynch, 2015). An improved understanding of root system development and functioning, to identify root traits contributing to…
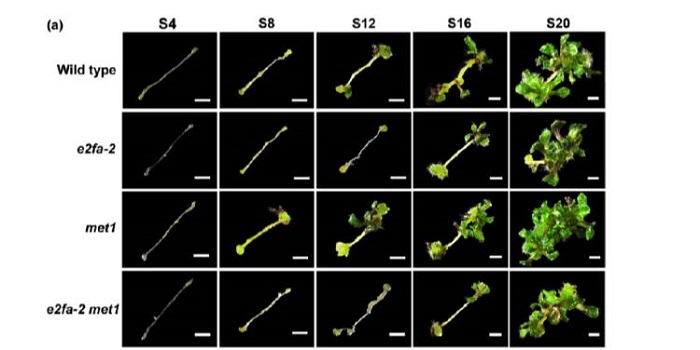
Cytokinin-induced cell cycle regulates MET1 activity during shoot regeneration ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe capacity of plants to regenerate new shoots from differentiated tissue – a process called de novo shoot regeneration – confers plasticity to plant development and has also important agricultural applications. Previous studies revealed that DNA METHYLTRANSFERASE1 (MET1) inhibits shoot regeneration…

