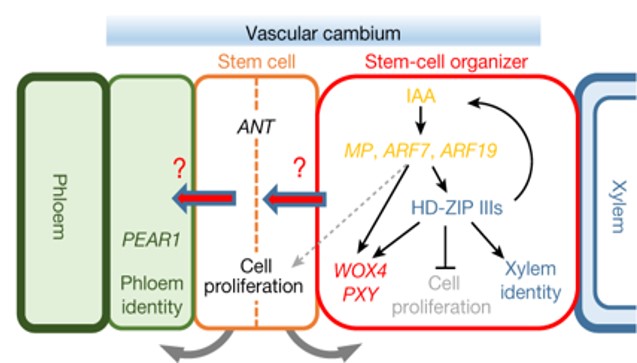
Origin and function of the root vascular cambium ($) (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe vascular cambium is a meristematic tissue that is responsible for lateral growth and the continued production of new xylem and phloem; in woody plants, the shoot vascular cambium makes wood. A new pair of papers investigates how the Arabidopsis root vascular cambium forms and how it functions. Through…
Quantitative analysis of auxin sensing in leaf primordia argues against proposed role in regulating leaf dorsoventrality (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is an interesting paper that touches on several topics. Bhatia et al. address the question of how polarity in leaves is first established: essentially, which comes first, polarity in auxin concentration or polarity in gene expression? The authors conclude that in the earliest leaf primordia, there…

Special Issue: Root Biology (Physiologia Plantarum)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe year 2019 kicks off with a special issue on root biology, with all articles free to access for six months. Topics include interactions of roots with parasites and symbionts, root branching, transport in the root system, and roots of woody species. (Summary by Mary Williams) Physiologia Plantarum…
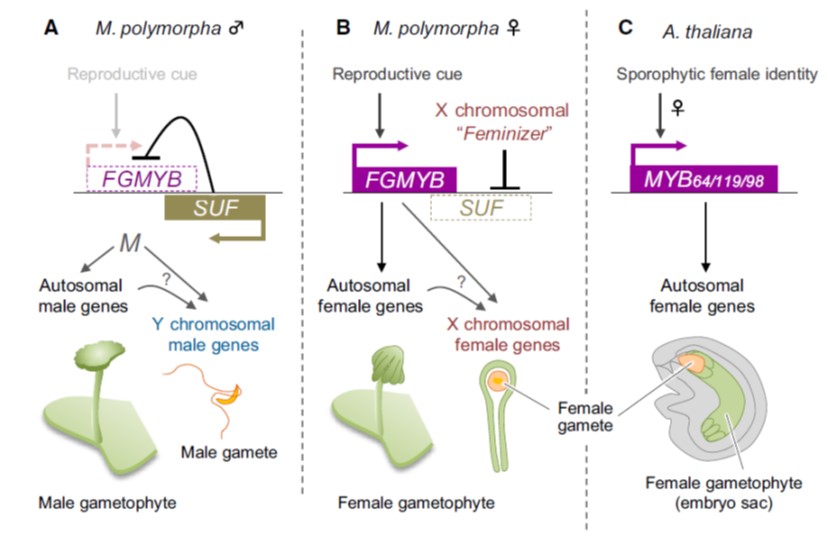
A bidirectional switch controls sexual dimorphism in the liverwort (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBryophytes spend most of their lifecycle in the haploid, gametophytic form, of which there are two types, male (sperm forming) and female (egg forming). Hisanaga et al. investigated the genetic basis that determines sex in the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. Their findings are fascinating. A single…
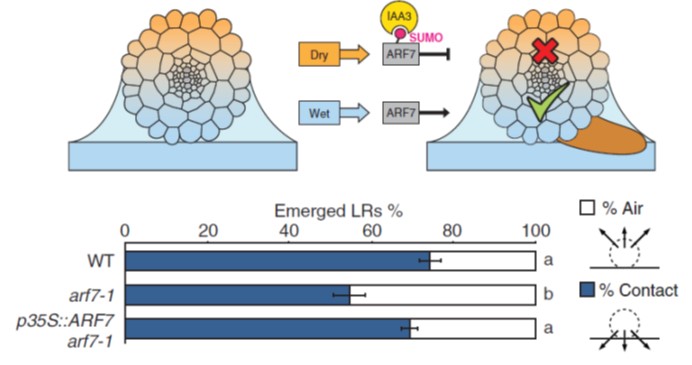
Root branching toward water involves posttranslational modification of transcription factor ARF7 ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots do amazing things, particularly in terms of how they optimize their growth in response to their very local environment including water, nutrients, microbes, and physical obstructions. Branching in regions of contact with water is called hydropatterning, and previous studies showed that an auxin…
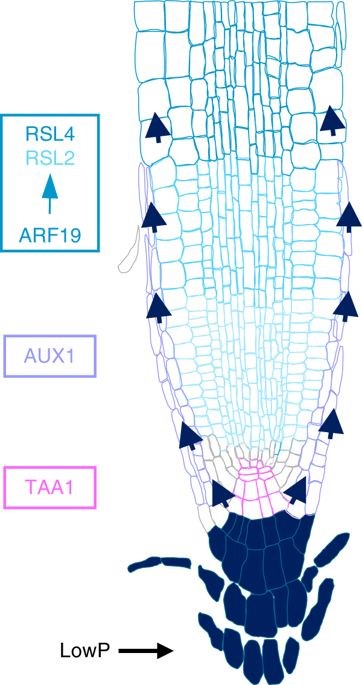
A mechanistic framework for auxin dependent Arabidopsis root hair elongation to low external phosphate (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants respond to a low phosphate environment through increased elongation of root hairs. Bhosale et al. showed that low external P increases levels of the auxin (IAA) in Arabidopsis roots through the TAA1 (TRYPTOPHAN AMINO TRANSFERASE 1)-mediated auxin biosynthesis pathway. At the same time, the auxin…

Auxin Affects Capitulum Pattern Formation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe flower head (capitulum) is a morphological feature that defines the family Asteraceae (the daisy or sunflower family). A typical capitulum consists of many flowers (florets) and phyllaries (modified bracts) compressed into a single structure that mimics a single flower. Capitula commonly have two…
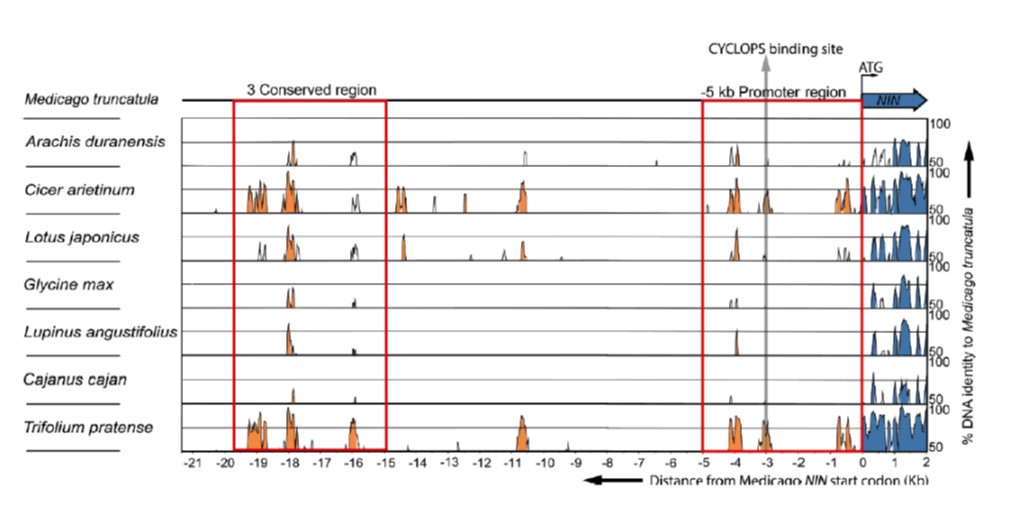
The secret of NIN (Nodule Inception) ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTwenty years ago, a genetic screen of Lotus japonicas identified NIN (NODULE INCEPTION), a transcription factor required for both early (infection thread) and late (nodule primordium development) stages of nodule formation. In daphne (a weak allele of NIN), infection threads form but not nodule primordia,…
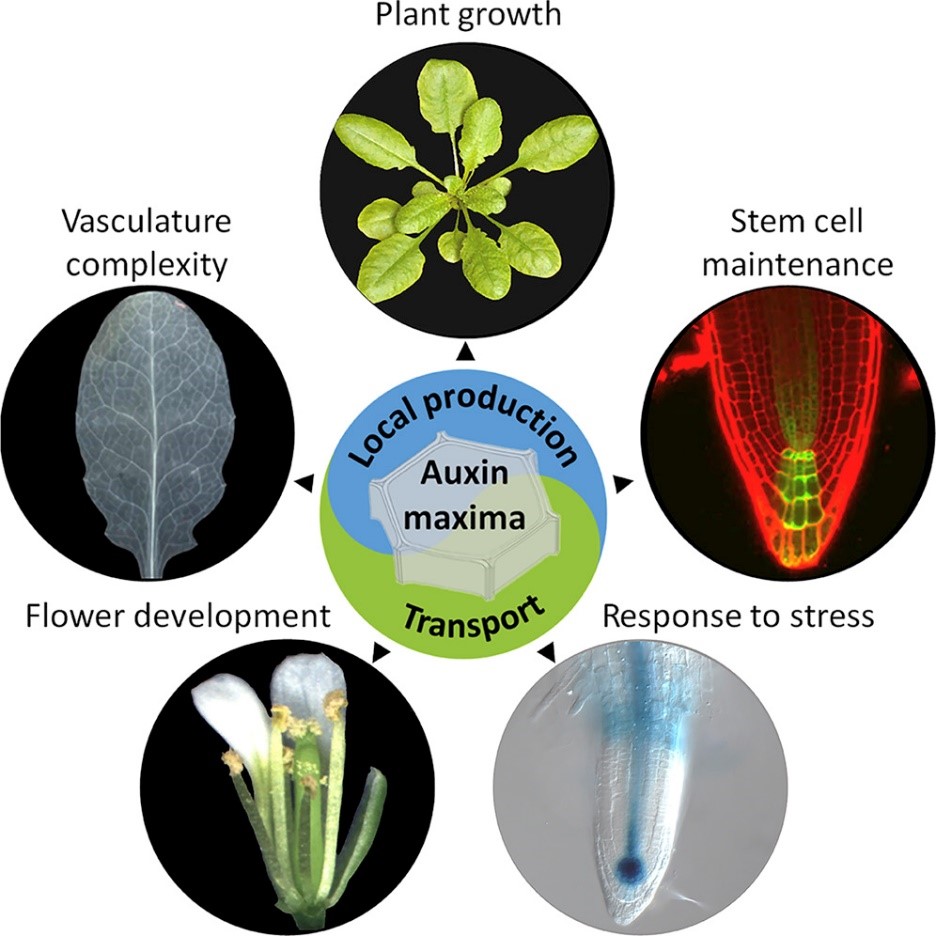
Local auxin biosynthesis is a key regulator of plant development ($) (Devel Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMorphogenic gradients of auxin are essential for plant phenotypic plasticity. Polar auxin transport plays a central role in auxin maxima generation. The exquisite spatiotemporal expression patterns of auxin biosynthesis genes suggested that local sources of auxin may contribute to the formation of auxin…

