
Root branching is not induced by auxins in Selaginella moellendorffii (Front Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin is crucial for root development across angiosperms. All the auxin signal transduction pathway components are conserved in land plants, but their role is still not completely clear in early diverged lineages. Here, Fang et al. present a comprehensive analysis of exogenous auxin addition and polar…
Multiple transcriptional factors control stomata development in rice (New Phytol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the model plant Arabidopsis, stomatal development occurs in a scattered pattern with that avoids direct contact between them. In rice and other monocots, the stomata are distributed in a uniformly oriented manner. Such unique patterning and morphology of stomata intrigued Wu et al. to examine if the…
Synergistic pectin degradation and guard cell pressurization underlie stomatal pore formation
Plant Science Research Weekly
This is a very interesting paper published by Rui et al. on the molecular mechanisms for stomatal pore formation, which includes pore initiation followed by pore enlargement. Each pore is surrounded by a pair of guard cells, which regulate the aperture of the pore and control gas exchange and water…
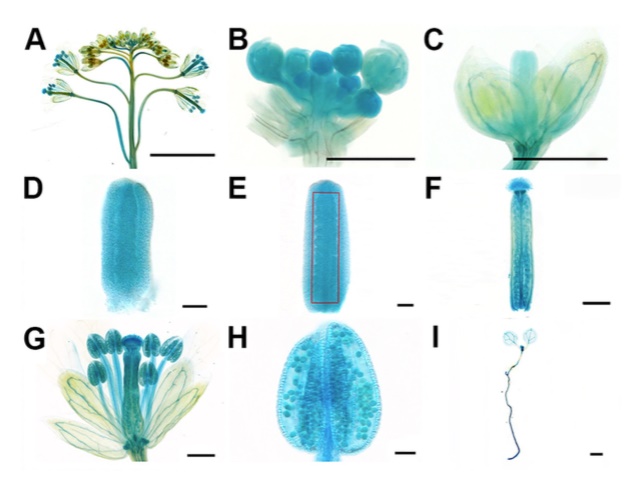

NERD1, a novel regulator of ovule number in Arabidopsis (PLOS Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed number is a critical component of crop yield; the number of ovules determines the number of seeds. Ovule initiation in the carpel margin meristem (CMM) is controlled by genetic (i.e., AINTEGUMENTA, LEUNIG, SEUSS) and hormonal factors (auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, and brassinosteroids). Most…
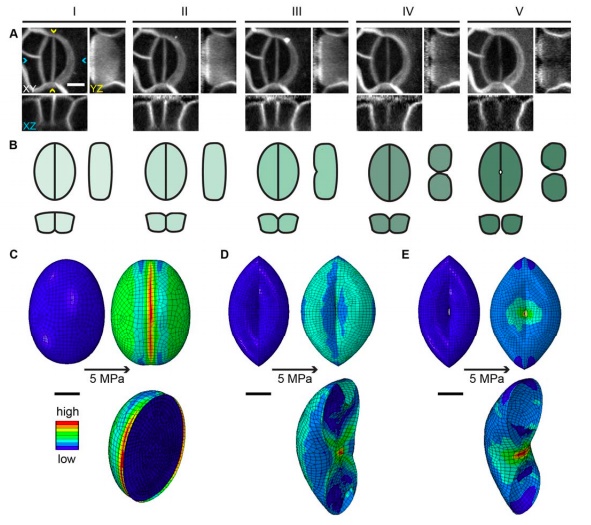
Cell geometry determines symmetric and asymmetric division plane selection in Arabidopsis early embryos (PLOS Comp Biol)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Cells proliferate via symmetric divisions while asymmetric divisions are associated with new cell types, layers and developmental patterns. The correct orientation of cell divisions planes is required for plant tissue architecture and organ morphogenesis. In plants, previous attempts to predict division…
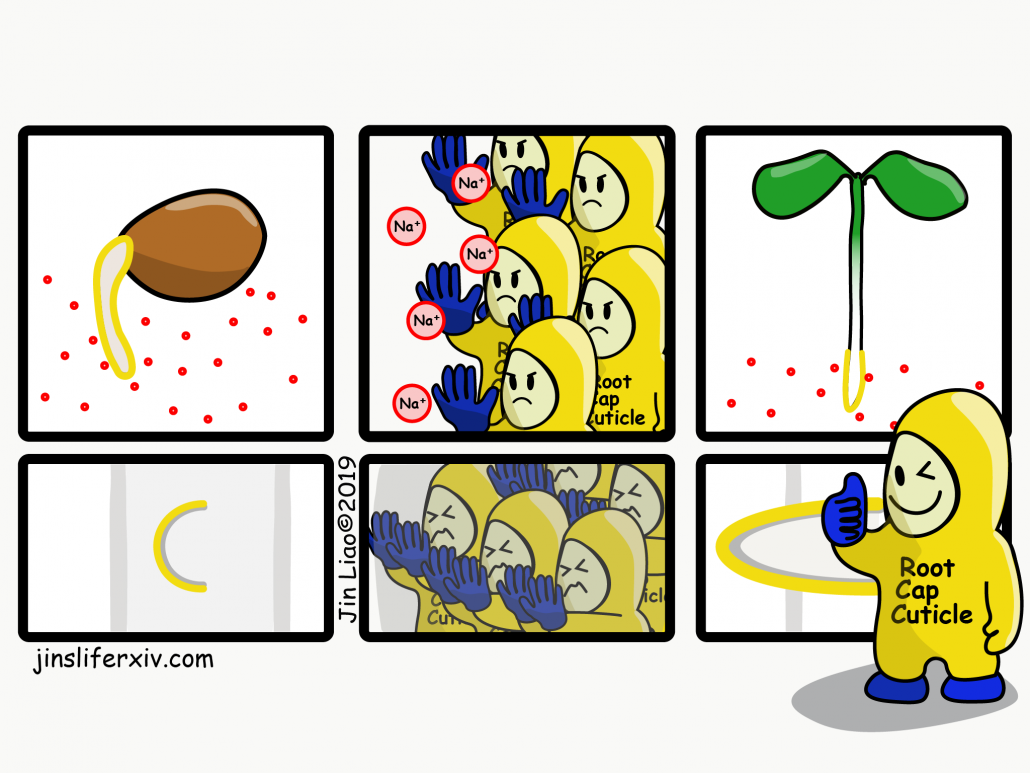
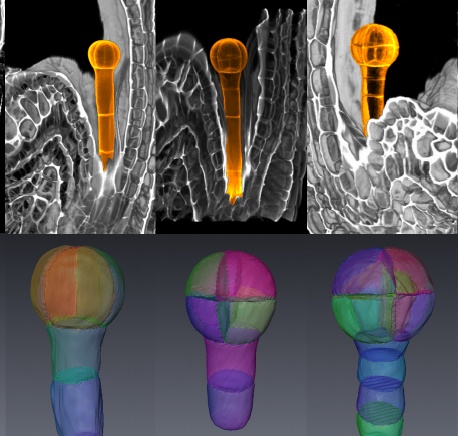
Cuticle is found in the root! The root cap cuticle protects young roots from abiotic stress and helps lateral root outgrowth (Cell) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo adapt to life on land, plants developed lipid-derived modifications on the surface of aerial organs (shoot). The cuticle forms a multi-layered structure of lipid components at the outermost surface of the organ to protect plant cells from environment stresses. Roots, as the organ specialized for the…
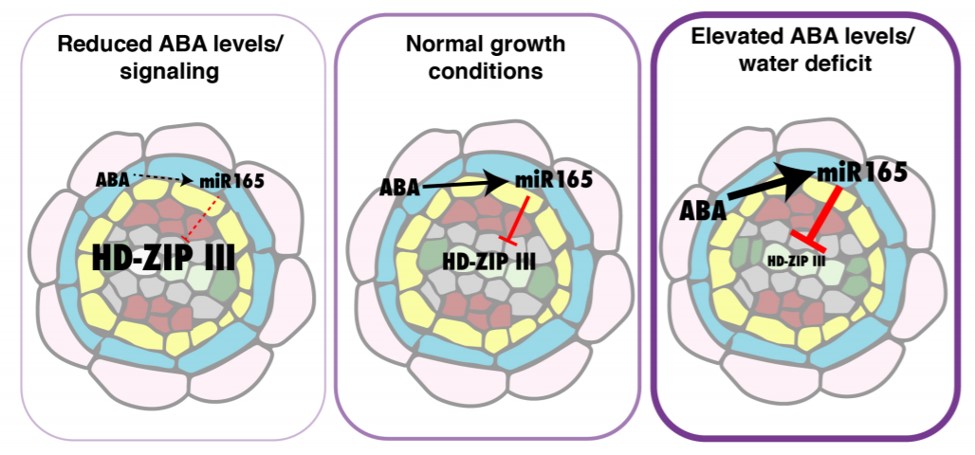
Root xylem formation and vascular acclimation to water deficit involves endodermal ABA signaling via miR166 ($) (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbiotic stress influences plant development, with the phytohormone ABA playing an important role. Ramachandran et al. have demonstrated ABA mediated activation of microRNA 166, which regulates expression levels of the HD-ZIP III transcriptional factor family. Exogenously supplied ABA alters xylem patterning…
Lipids and Auxin Signaling in Plant Salt Responses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. highlight the importance of lipid protein interactions in spatiotemporal regulation of auxin signalling. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00528
By Peipei Wang and Qun Zhang
Background: Salt stress inhibits plant growth and development, leading to many physiological reactions.…
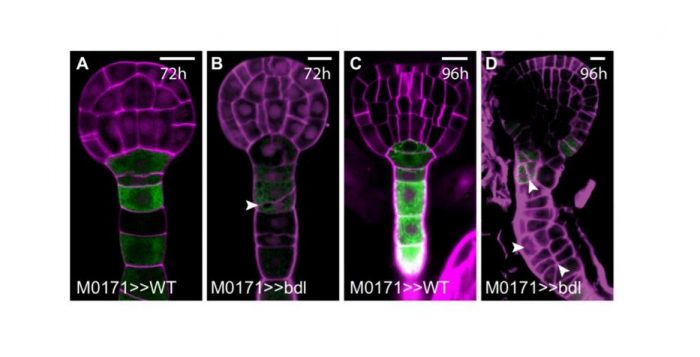
A Transcriptional Module Regulates Embryo and Suspensor Development
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellRadoeva et al. investigate a transcription module that controls aspects of embryogenesis in plants. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00518.
Background: After the start of embryo development in plants, which is marked by fertilization of the egg cell, the resulting zygote divides asymmetrically…

