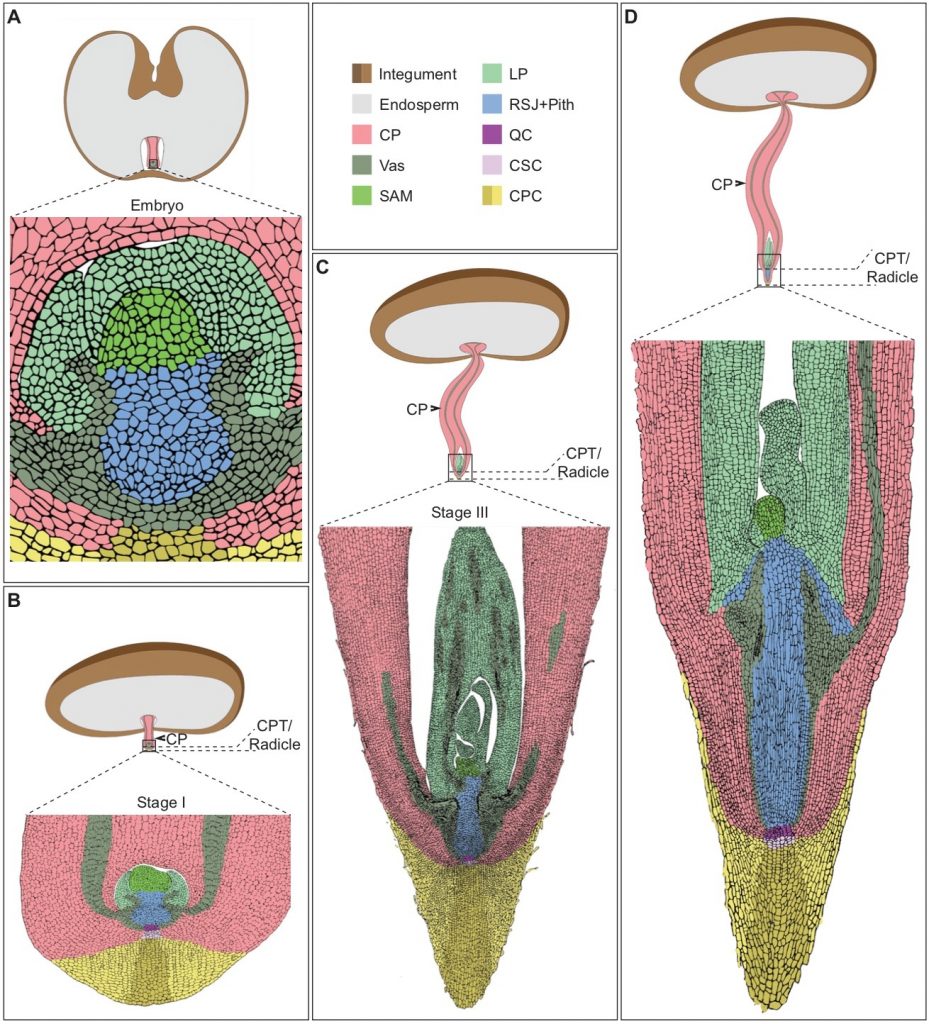
Embryo protection after germination in date palm (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant morphogenesis is a dynamic process that can be modulated in response to environmental cues. In this work, Xiao et al. characterized germination and seedling development in date palm. After germination, the cotyledonary petiole grows, but the embryo development is paused. At early stages of development…
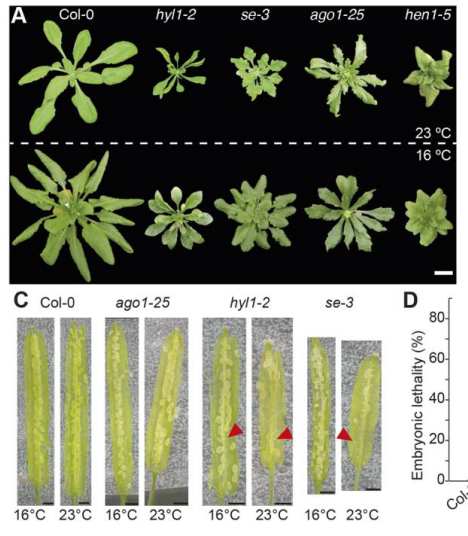

Alternative usage of miRNA-biogenesis co-factors in plants at low temperatures (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs in animals, plants produce microRNAs that are also key developmental regulators. Unlike some animals, plants are more exposed to environmental factors that alter cellular processes. Ré et al. show here that phenotypic defects produced by loss-of-function mutations in key proteins of Arabidopsis miRNA…

Low oxygen levels are needed to regulate shoot meristem activity (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLittle is known about the stimuli that regulate time intervals for new leaves production (plastochrone) at the shoot apical meristem (SAM). Oxygen is a diffusible molecule with potential to regulate this process. The use of a micro-scale Clark-type oxygen electrode allowed Weits et al. to measure oxygen…
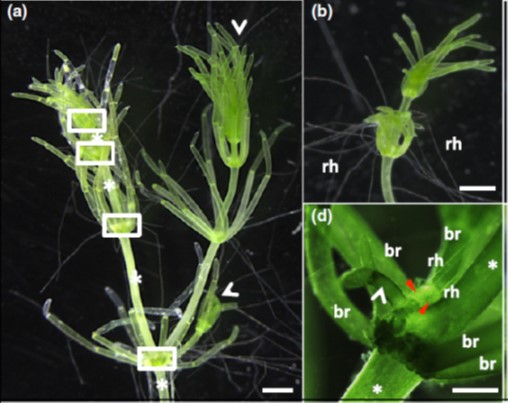
Land plants recruited an ancestral bHLH for tip-growing surface cell development ($) (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLand plants (embryophytes) evolved from freshwater charophycean algae over 450 million years ago. The transition from aquatic to terrestrial environments likely required the evolution and expansion of genetic programs controlling three dimensional growth and the formation of tip-growing surface cells…
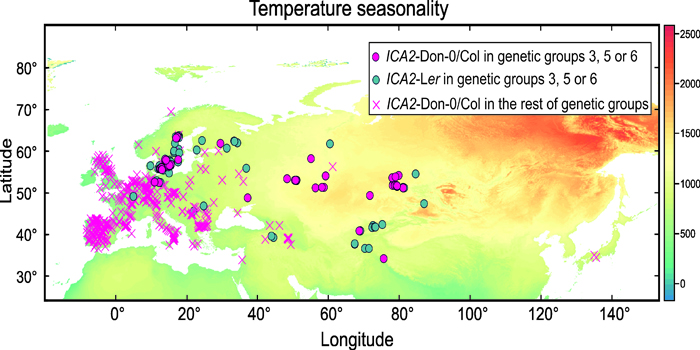
How Plants Adapt to Different Temperatures
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMéndez-Vigo et al. explore how plants from different world regions adapt to different temperature conditions. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00938.
By Belen Méndez-Vigo and Carlos Alonso-Blanco
Background: Plants adapt to seasonal and yearly fluctuations in ambient temperature…

A jasmonate signaling network activates root stem cells and promotes regeneration ($) (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess plasticity for regeneration of organs after damage by physical, biotic or abiotic stress. The mitotically less-active organizer cells, quiescent center (QC) and surrounding initials form the stem cell niche, which is known to play a very important role in activation of the regeneration…
Genetic compensation mechanisms for maintaining plant stem cell robustness ($) (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn shoot meristems, the CLAVATA (CLV)-WUSCHEL(WUS) signaling module contributes to the continuous stem cell proliferation for plant development. In Arabidopsis, core CLV-WUS signaling includes the peptide ligand CLV3 and its receptor protein kinase CLV1 together with the transcription factor WUS. These…

Review. Multicellular systems biology: Applying network science to plant organ patterning and function (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyI really enjoyed this review article, which very successfully introduces the reader to the why and how of how to apply network science to plant science. Bassel never veers off into abstraction or “math-speak”, but instead roots his explanations in familiar biological or ordinary terms. As an example,…
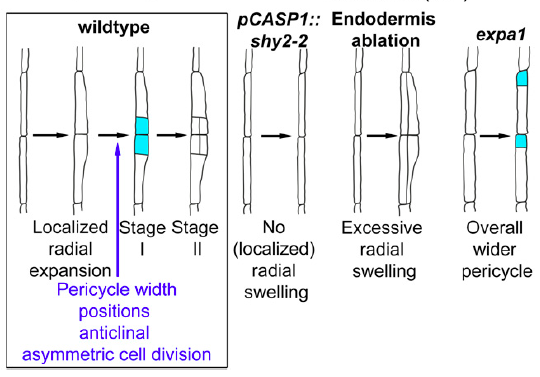
EXPANSIN A1-mediated radial swelling of pericycle cells positions anticlinal cell divisions during lateral root initiation ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLateral root development helps plants explore the soil for mineral nutrients and water, and there are environmental and internal cues that precede the formation of lateral root primordia. In Arabidopsis thaliana, some of these internal cues include increased auxin concentrations around lateral root founder…

