
Fluctuating auxin response gradients determine pavement cell-shape acquisition (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe leaf epidermis is composed primarily of undulated pavement cells arranged in a jigsaw puzzle-like architecture, with neighboring cells flawlessly interlacing with one another thanks to synchronized growth, thus making it an ideal model to study morphogenesis regulation. Seeking to better understand…
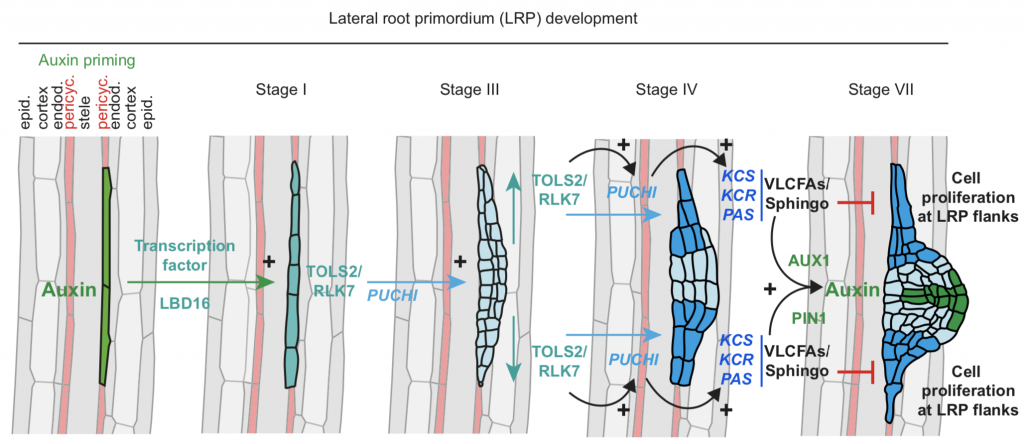
Review: Feedback mechanisms between membrane lipid homeostasis and plant development (Dev. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant development is a regulated process of cell division, expansion, and differentiation. Membrane lipids are crucial to these processes, as illustrated in this review by Boutté and Jaillais. The authors discuss the major lipid components in the different membrane systems and how these vary in space…
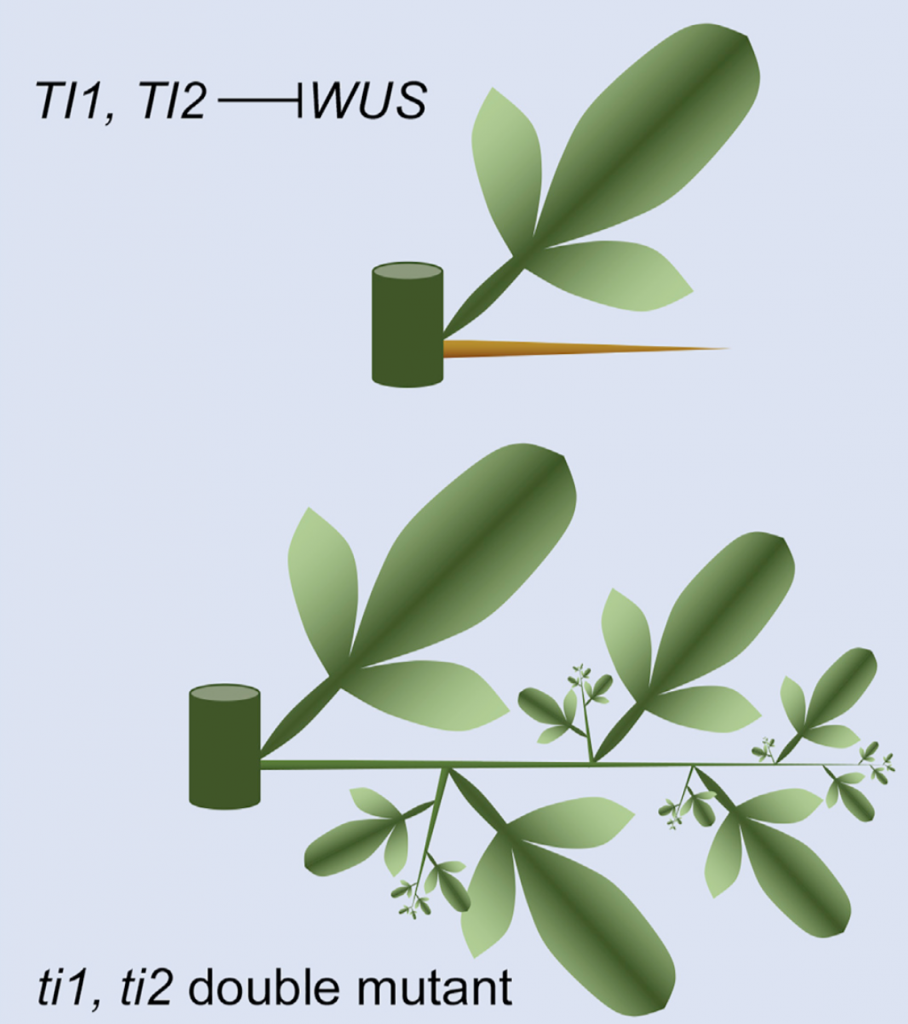
Reprogramming of stem cell activity to convert thorns into branches (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThorns are modified axillary shoots with a sharp tip that helps in deterring herbivores and are found among several families of angiosperms. Thorns develop from their meristem-like tip to their base, but unlike branches they are determinate organs. The mechanism of their terminal differentiation into…
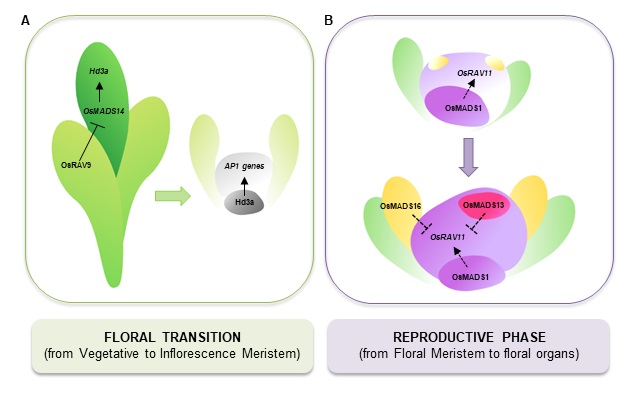
Genes of the RAV family control heading date and carpel development in rice (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed-bearing annual plants essentially get one shot at getting their reproductive timing right; too early and there won’t be enough stored nutrients to produce healthy seeds, and too late and the seeds might not mature fully before bad weather or rot sets in. Previously, the RAV (RELATED TO ABI3 AND…
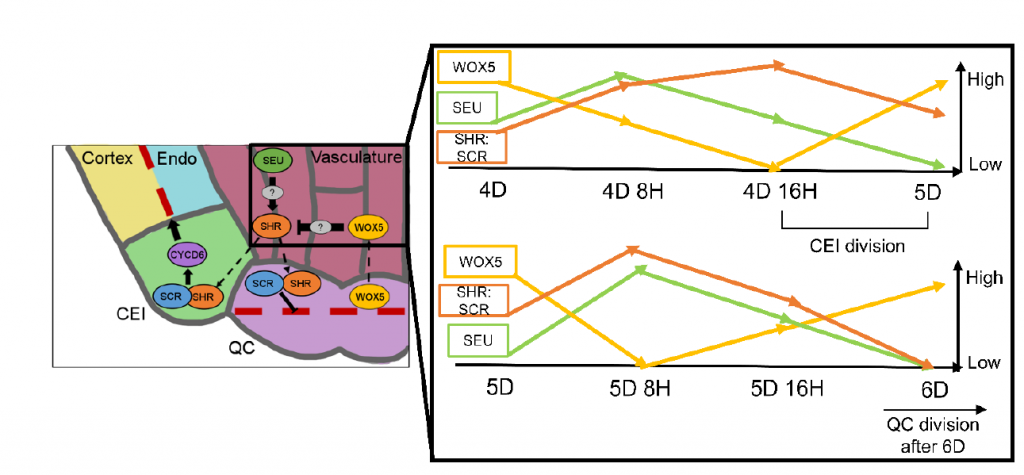
Protein complex stoichiometry and expression dynamics of transcription factors modulate stem cell division (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStem cells are a group of undifferentiated cells that can divide and differentiate to form new organs. In Arabidopsis roots, the quiescent center (QC: the mitotically inactive group of cells) helps regulate the division of surrounding initials and maintain the stem cell fate. What makes the QC different…
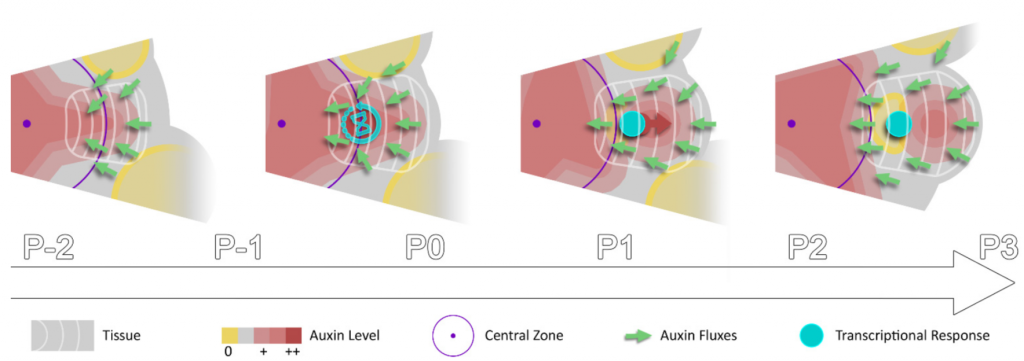
How do auxin temporal dynamics regulate patterning? (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin forms spatial gradients that are implicated in organ morphogenesis. However, it is not known how temporal auxin gradients are integrated with the spatial information. In this paper, Galvan-Ampudia, Cerutti et al., showed using a ratiometric quantitative auxin reporter (quantitative DII-VENUS) that…

How far does stomatal activator and inhibitor signaling work in the plant epidermis? (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata are the pores on the plant surface surrounded by a pair of guard cells that control gaseous exchange and water loss. Among the many genes involved in stomatal patterning and development, EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR 1 (EPF1) and STOMAGEN encode signaling peptides and acts as negative (inhibitor)…
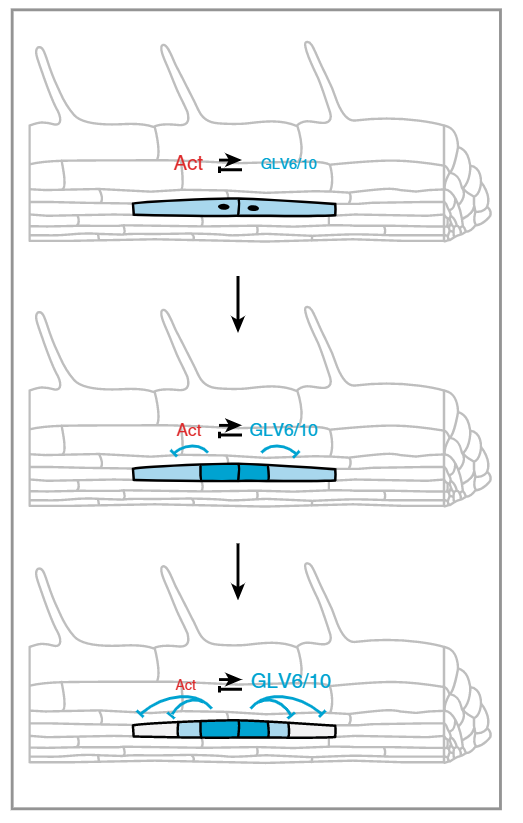
GOLVEN peptide signaling through RGI receptors and MPK6 restricts asymmetric cell division during root initiation (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLateral root starts development starts with an asymmetric cell division in the founder cell. In this study, Fernandez et al. explored the role of peptide signaling this process. The authors started with the previous finding that GOLVEN peptides are involved in lateral root initiation, as overexpression…
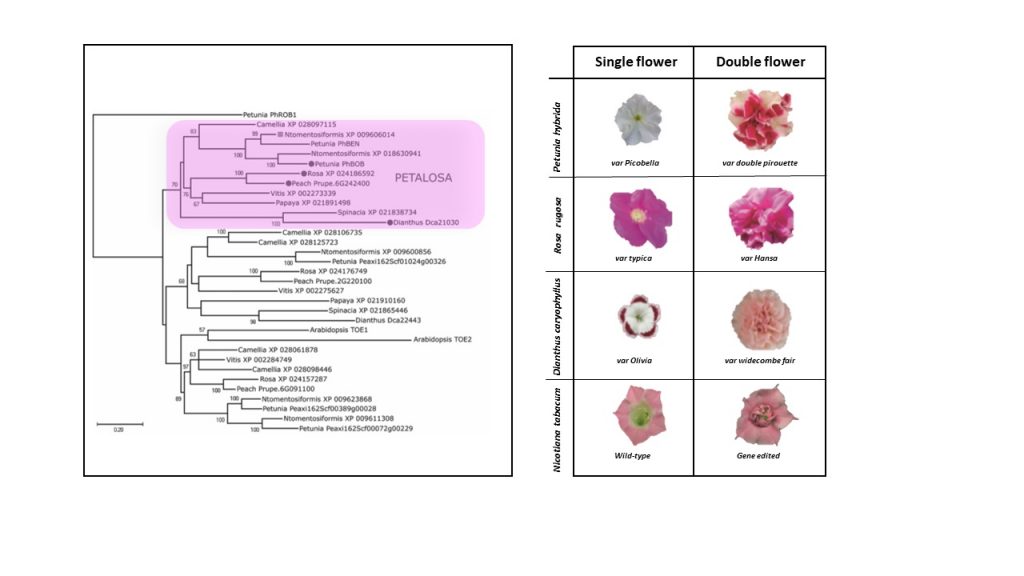
Mutations PETALOSA cause a dominant double-flower phenotype (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlower development has always been a fascinating field of research in plant biology. While molecular studies in the past focused on regulatory genes involved in the formation of floral organs in model species, current investigations are addressing the genetic determinants underlying the huge variety…

