
A plant-specific protein, COST1, mediates autophagy to promote drought tolerance (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch remains to be learned about the sensing and signaling mechanisms controlling growth in response to drought. To dissect how plants control drought via autophagy, Bao et al. found a plant-specific protein, COST1 (CONSTITUTIVELY STRESSED 1) containing a DUF641 (domain of unknown function 641) domain,…
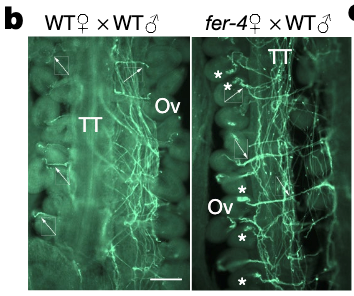
FERONIA controls pectin- and nitric oxide-mediated male–female interaction (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn flowering plants, fertilization occurs when a pollen tube, growing down the transmitting tissue, arrives at the ovule, ruptures, and releases its content of sperm cells. The pollen tube is guided towards the ovule by LUREs, small cysteine-rich secreted peptides. Timely rupturing and sperm release…
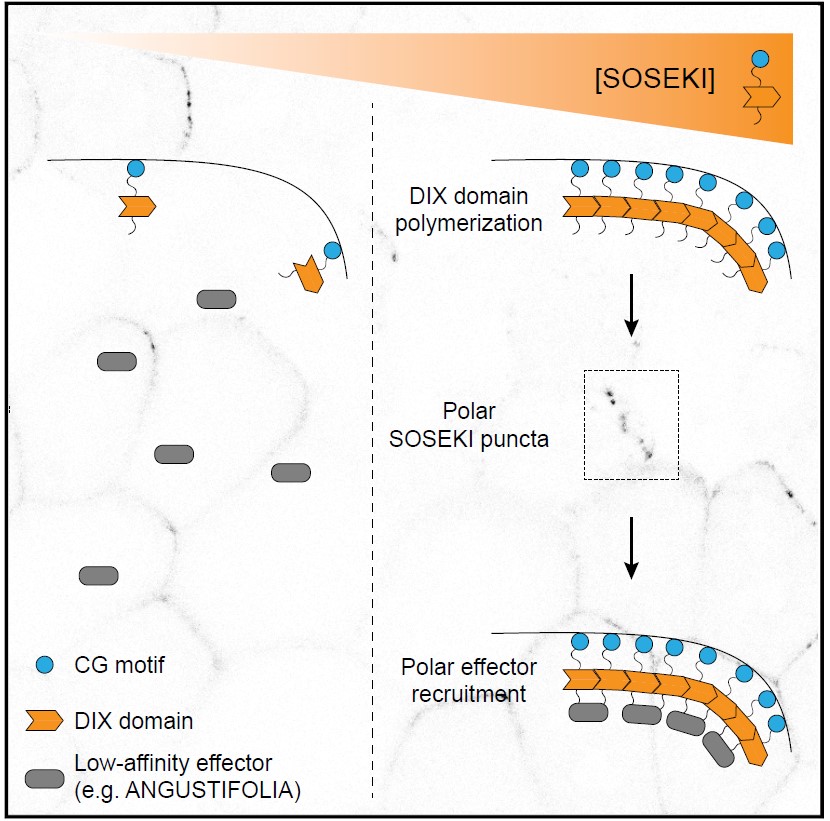
DIX domain polymerization drives assembly of plant cell polarity complexes (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn multicellular organisms like plants, asymmetric cell division can arise from cell polarity. The signals that establish cell polarity relative to the body axis are unknown in plants. In Arabidopsis, SOSEK1 was previously identified as having a polar distribution. SOSEK1 has a DIX domain similar to…
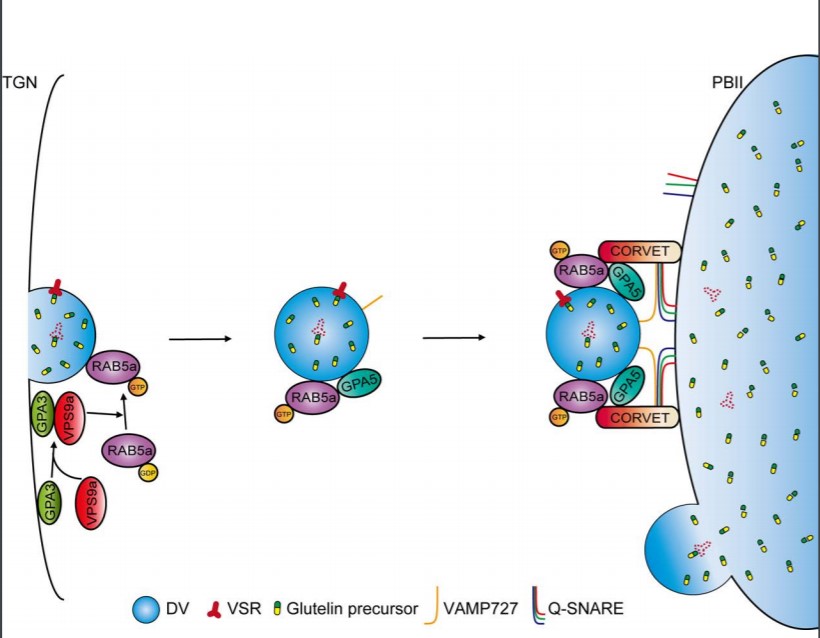
GPA5 encodes a Rab5a effector required for post-Golgi trafficking of rice storage proteins ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStorage proteins secreted into vacuoles during seed development serve as precursors for germination and plant growth. In this paper, Ren et al. identified a regulator, GLUTELIN PRECURSOR ACCUMULATION 5 (GPA5) that is involved in protein trafficking into the vacuoles during seed development. The loss…
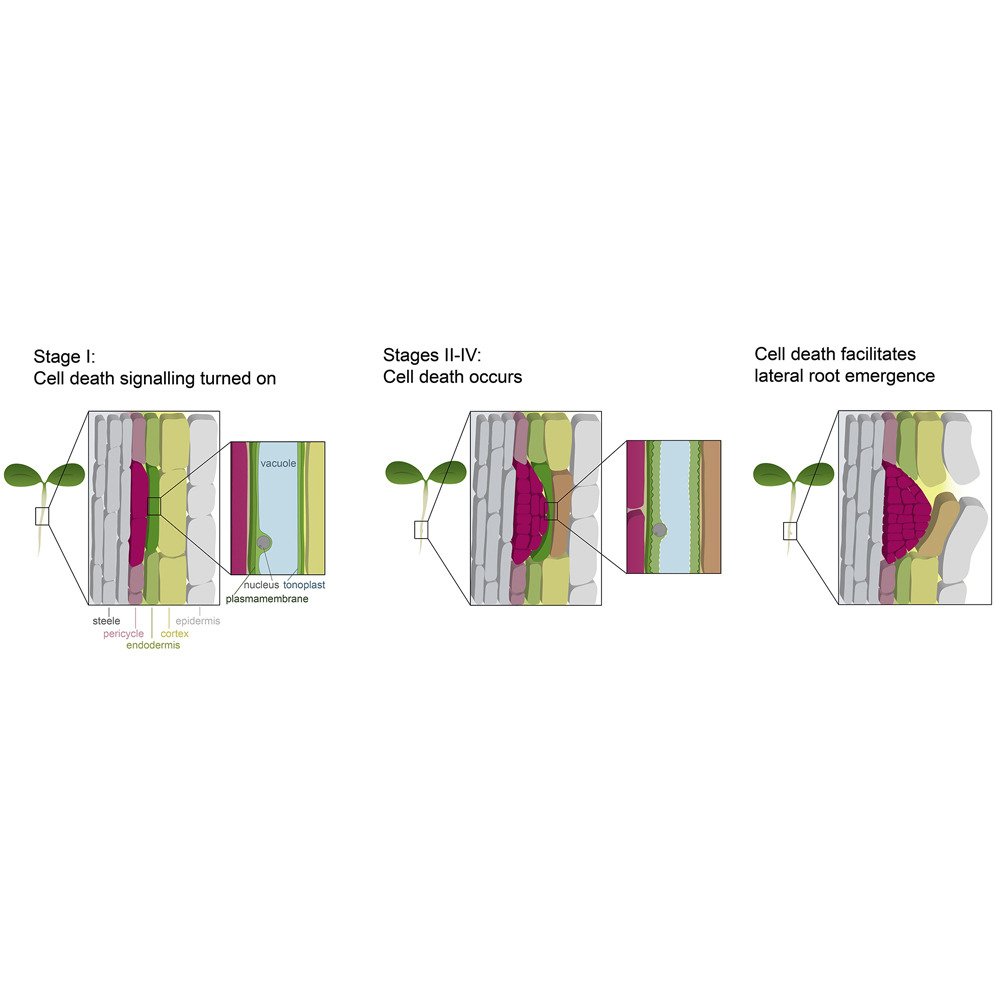
Death in cells overlying lateral root primordia facilitates organ growth in Arabidopsis (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhile cell division and cell expansion are known to be determinants of plant organ growth, little is known about the role of cell elimination and death in this process. Cell death indicators such as cell death- and autolysis-associated cysteine proteases have been observed in cells overlying the site…
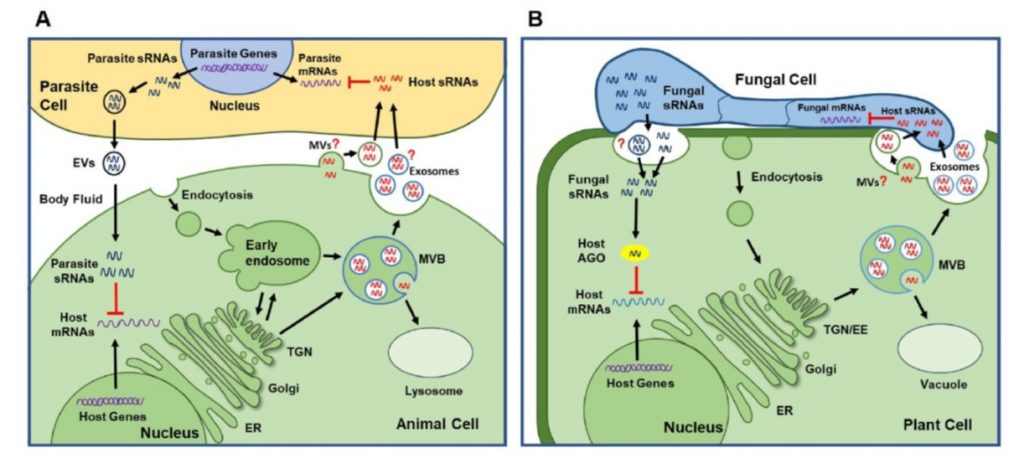
Review. Small RNAs and extracellular vesicles: New mechanisms of cross-species communication and innovative tools for disease control (PLOS Pathogens)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe have only recently begun to appreciate the phenomenon of cross-species or cross-kingdom small RNA transfer, and its applications. Using examples from plants and animals, Cai et al. summarize how some pathogens have evolved the capacity to introduce small RNAs into their host to suppress host defense…

Gene duplication accelerates the pace of protein gain and loss from plant organelles (Mol. Biol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrganelles, such as the chloroplast and nucleus, are structures with specific functions within a plant cell. It has been reported that many related, or homologous, proteins function in different organelles. However, how and why organellar proteins have diverged over evolutionary time remains unclear.…

A single light-responsive sizer can control multiple-fission cycles in Chlamydomonas (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow do cells know when it is time to divide? Helt et al. explore this question using the single-celled alga Chlamydomonas. Unlike most animal and fungal cells, which tend to maintain a relatively consistent size by dividing after their size has doubled, Chlamydomonas cells can undergo several rounds…
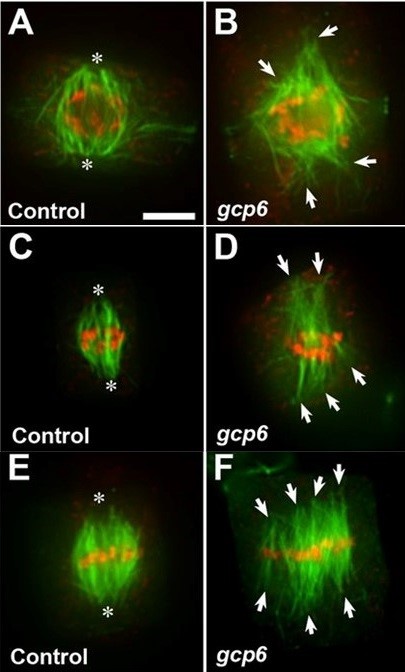
The γ-tubulin complex protein GCP6 in crucial for spindle morphogenesis but not essential for microtubule reorganization in Arabidopsis (OA)
Plant Science Research Weekly
During cell division, cells require to form mitotic spindle and these mitotic spindles are basically newly formed microtubules. The formation of new microtubules depends on γ-tubulin. Along with 5 GPCs (γ-tubulin protein complex), γ-tubulin form γTuRC (γ-tubulin ring complex) and it facilitates…

