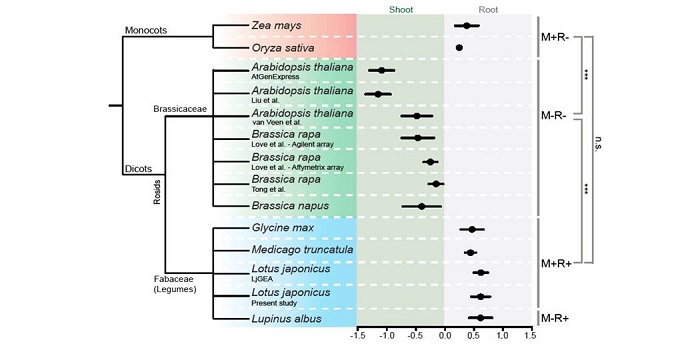
The Brassicaceae family displays divergent, shoot-skewed NLR resistance gene expression
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNLR (Nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat resistance) genes help plants recognize pathogens. Munch et al. looked at expression pattern data of 1,235 NLRs from nine plant species. The distribution of NLR gene expression between shoot and root is relatively constant within a species, and for most…

The rust fungus Melampsora larici-populina expresses distinct sets of secreted protein genes during infection of its two host plants, larch and poplar
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRust fungi represent an important group of plant pathogens, many of which have heteroecious lifestyles (meaning that they require two alternate hosts). However, the molecular mechanisms used by these pathogens for suppression and colonization of multiple hosts are poorly understood. Lorrain et al.…

Plant extracellular vesicles are incorporated by a fungal pathogen and inhibit its growth ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogExtracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-released structures that play a role in cell-to-cell communication. These vesicles in plants have been poorly studied although they are predicted to have a role in defense upon pathogen infection. Regente et al. have characterized EVs from sunflower by transmission…

Actin and Aphid Feeding
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogRemodeling of the actin network in plant cells involves the severing, depolymerization and polymerization of F-actin. A variety of actin-binding proteins are involved in remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton, including the actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF) family of proteins. As a result of their ability…

LYS12 LysM receptor decelerates Phytophthora palmivora disease progression in Lotus japonicus
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIt might sound odd, but so far it was hard to find a nice pathogen infecting model legume plants. Fuechtbauer and colleagues showed the capacity of an oomycete (Phytophtora palmivora) to infect Lotus japonicus and describe how a LysM receptor, LYS12, is partly mediating this plant-microbe interaction.…

Sequestration and activation of plant toxins protect the western corn rootworm from enemies at multiple trophic levels
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants are attacked by diverse herbivores but have also evolved strategies to resist them. However, highly adapted herbivores exist, including those that have evolved the ability to stabilize, sequester and reactivate plant toxins. This evolved trait has contributed to herbivore defense against higher…
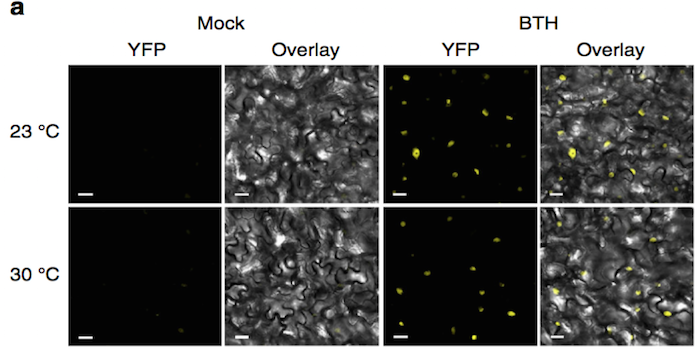
Dual impact of elevated temperature on plant defense and bacterial virulence in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHuot et al. describe how elevated temperature (30 °C) enhances Arabidopsis thaliana disease susceptibility to the bacteria Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000): this includes an increase of bacterial type III secretion suggesting that increased Pst DC3000 virulence at 30°C is linked…

Review: Plasmodesmal regulation during plant- pathogen interactions
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlasmodesmata are plasma membrane-enclosed pores between cells that were initially described by Tangl in 1879 as ‘open communications’ between protoplasts of endosperm cells. These structures are regulated by callose deposition from the apoplast and play an important regulatory role in stress and…

An Arabidopsis glycine-rich plasma membrane protein enhances disease resistance in soybean
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPreviously, the authors identified an Arabidopsis mutant that shows resistance to a widespread oomycete pathogen. In this new work, Wang et al. identified the Phytophthora sojae susceptible gene locus, PSS1, which encodes a plasma-membrane localized glycine-rich protein. When introduced into soybean…

