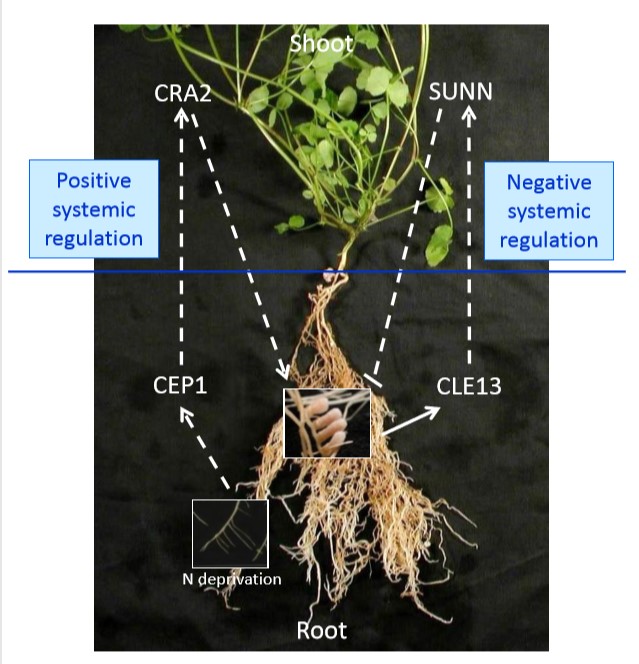
Independent regulation of symbiotic nodulation by the SUNN negative and CRA2 positive systemic pathways (Plant Physiol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAutoregulation of nodule development (AON) is a process by which leguminous plants control nodule development. SUNN, a LRR-RLK, and a systemic CLE peptide play a negative role in nodulation through systemic signaling. In this paper Laffont et al. showed the another systemic regulation of nodulation in…

Cell type specific transcriptional reprogramming during Ustilago maydis and maize interaction (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Ustilago maydis is a model biotrophic fungus which causes smut disesase in maize, characterized by tumorous symptoms on all aerial parts. Tumor formation in leaves of the host is a result of massive reprogramming by modulation of two processes, hypertrophy (cell expansion) and hyperplasia (cell division).…

Two opposing pathways independently regulate symbiotic nodulation in Medicago truncatula ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo optimize usage of nutrient, legumes utilize multiple strategies to regulate root nitrogen-fixing symbiotic nodulation. Excessive nodulation may hamper plant’s normal growth, so fine-tuning it is important for plant survival. Laffont et al. report that there are two independent pathways systematically…
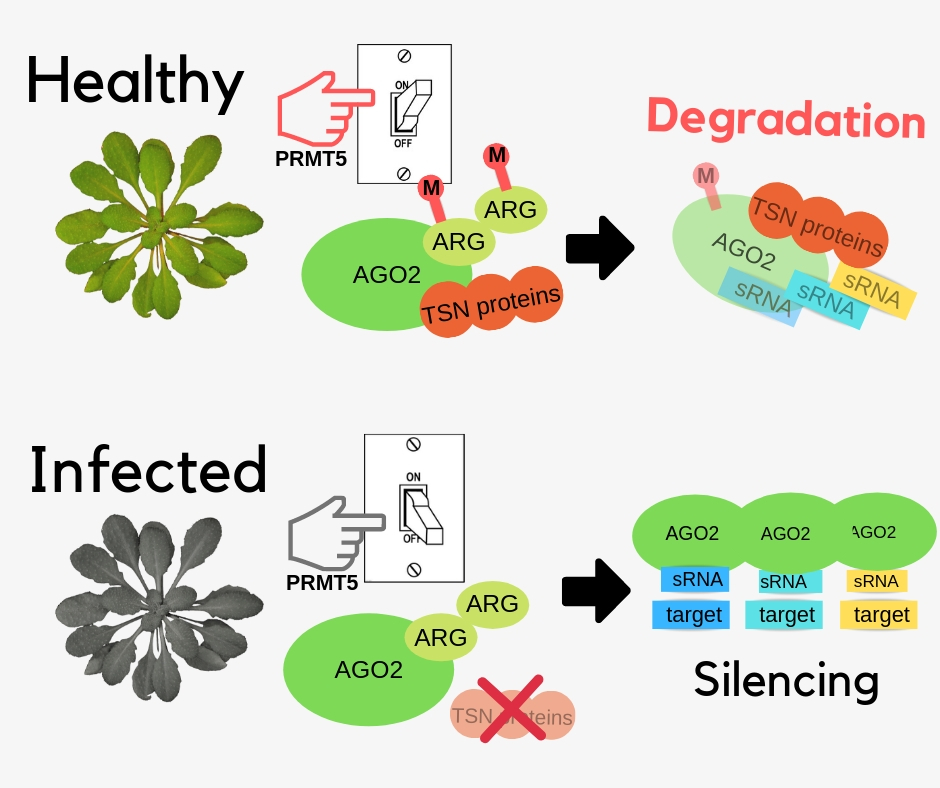
Dual regulation of Arabidopsis AGO2 by arginine methylation (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have natural mechanisms against pathogen infections. Post-translational modifications (PTMs) on key proteins involved in RNAi pathways are needed to control these immune responses. Argonaute (AGO) proteins are targets of PTMs to direct the silencing of genes. Here, Hu et al. identified the role…

The volatile indole primes rice defense against caterpillar attack (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHerbivore-induced volatiles have been shown to prime plant defense response in multiple species. A new study by Ye et al. unveils some of the early signaling events in volatile-mediated defense priming in rice. The authors show that rice plants release increased amounts of the volatile indole when attacked…
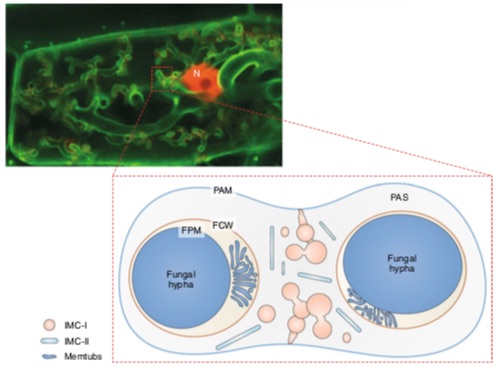
Membrane systems at the host-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus interface (Nature Plants) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal interaction with plants, the fungal partner promotes nutrient acquisition in exchange for some sugar and fatty acids from host plants. This exchange occurs at the symbiotic interface in the plant cortical cells where fungal hyphae form special branched structure called…
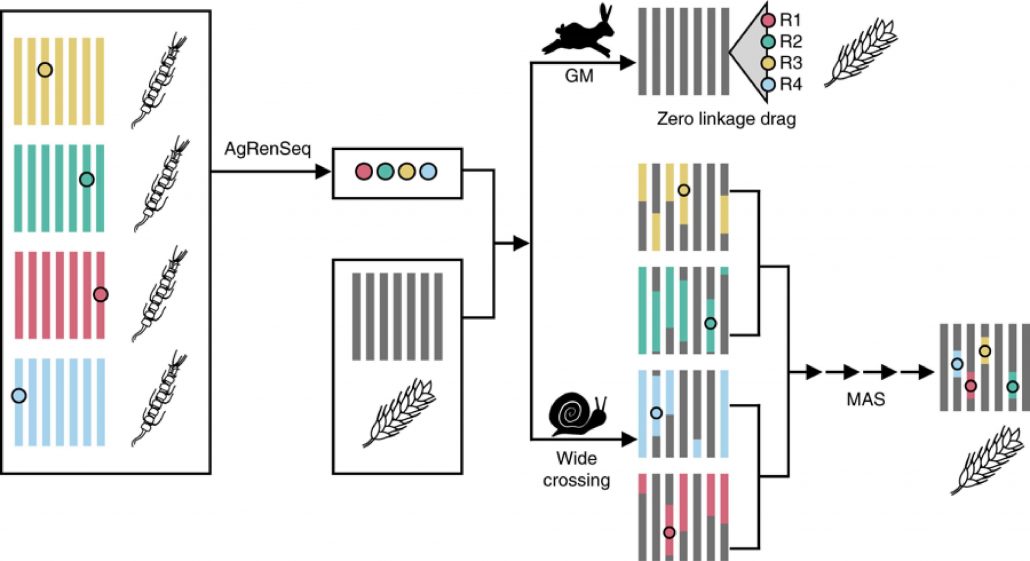
Tapping into the genetic diversity of wild crops for engineering disease resistance (Nature Biotech)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLack of sequence information makes harnessing the diversity of disease resistance (R) genes in wild crops highly challenging. Arora and Steuernagel et al. report AgRenSeq, a reference genome-free technique, for rapid cloning of nucleotide binding/Leucine-rich repeat (NLR) resistance genes from wild…

The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops (Nature Ecol Evol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens and pests are bad, but just how bad? And how do different regions of the world compare in terms of crop losses to pathogens and pests? Savary et al. surveyed crop experts from across the globe to address these questions, focusing on five major food crops (wheat, rice, maize, potato and soybean).…
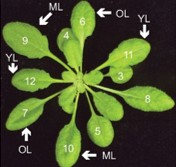
Leaf age dictates abiotic versus biotic stress signalling in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants sense and respond to various external stimuli throughout their lifespan. During stress responses brought forth by abiotic or biotic factors, molecular and physiological adjustments mediated by distinct yet interconnected hormone pathways play critical roles in plant survival. Berens et al. investigate…

