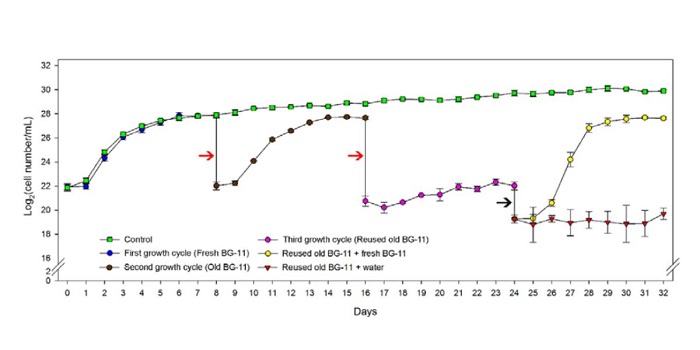
What Limits the Growth of Cyanobacteria?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
The commercialization of cyanobacteria-based biomass and biomolecules requires optimization for sustainable economic viability. Many studies identified growth-limiting factors in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis (e.g. nutrients and light). Understanding the factors controlling the limitation…
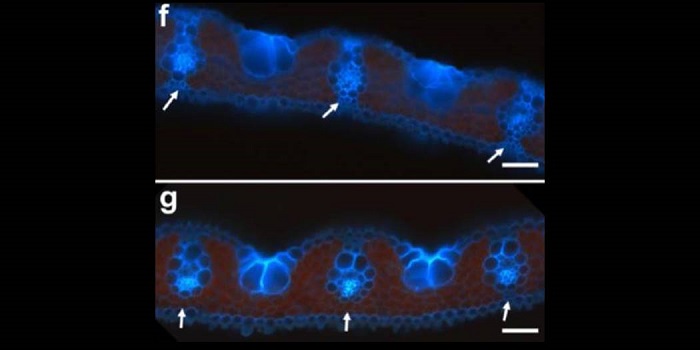
Expression of Kranz-anatomy candidate genes from maize in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost plants that use the more efficient C4 form of photosynthesis also exhibit Kranz anatomy, in which the PEPC and Rubisco carboxylases reside in distinct cells. Key genes that control the development of Kranz anatomy have been hard to find. In this report, Wang et al. analysed the effects of constitutively…
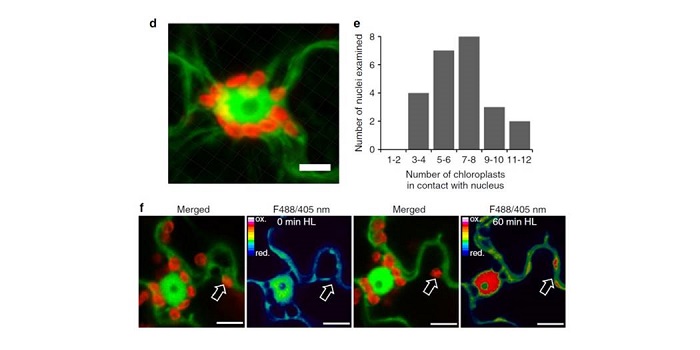
Photosynthesis-dependent H2O2 transfer from chloroplasts to nuclei provides a high-light signalling mechanism
Plant Science Research WeeklyBecause most chloroplast proteins are encoded in the nuclear genome, there must be ways for signals from the chloroplast to inform the nucleus and direct changes in gene expression. Several candidates have been proposed as chloroplast-to-nucleus (retrograde) signals. Using hydrogen-peroxide (H2O2) specific…
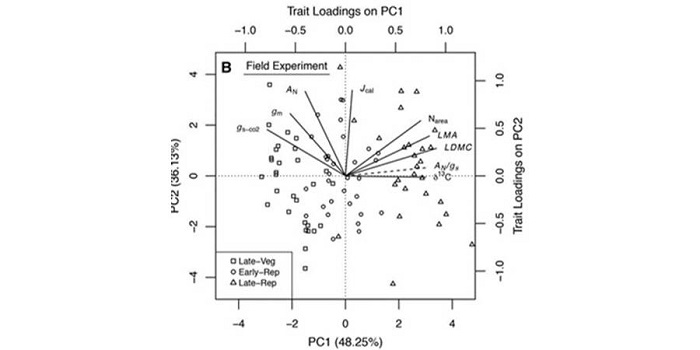
Variable mesophyll conductance among soybean cultivars sets a tradeoff between photosynthesis and water-use-efficiency
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAn experimental study by Tomeo and Rosenthal with soybean cultivars demonstrated that there exists genotypic differences in mesophyll conductance (gm), and that the potential exploitation of this trait may increase crop productivity. It was found that there exists a proper coordination mechanism…
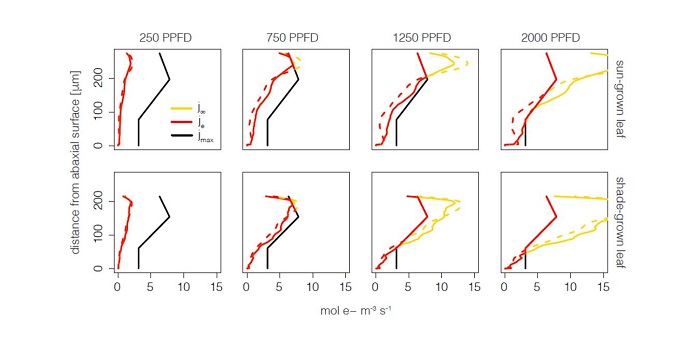
Light Direction, Absorption, and Photosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchPlant photosynthesis generally increases with irradiance until light saturation occurs. The directional quality of light, however, can affect its penetration and absorption within a leaf. For example, increasing the angle of incidence (from perpendicular) at which light intersects the leaf surface decreases…
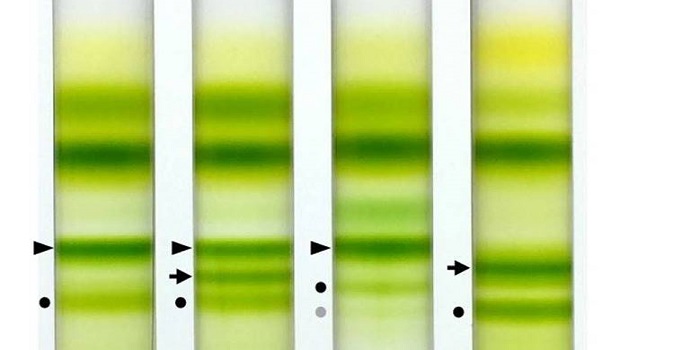
Review: Light-harvesting antenna complexes in Physcomitrella patens: implications for evolutionary transition from green algae to land plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe ancestors of land plants were aquatic. Myriad changes accompanied the transition from aquatic to terrestrial life, including changes necessitated by the difference in light intensity and quality. Bryophytes, the earliest diverging land plants, have some characteristics that reveal how plants transitioned…
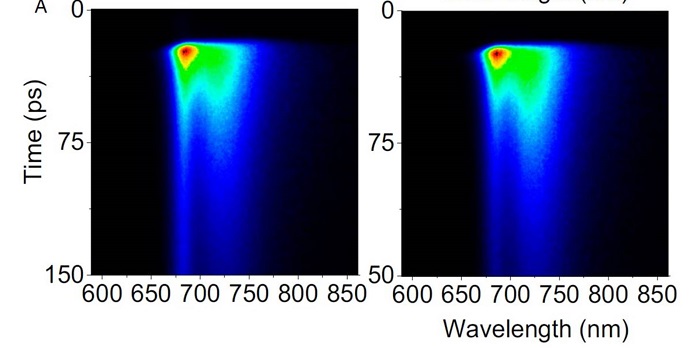
Zeaxanthin-dependent nonphotochemical quenching does not occur in photosystem I in Arabidopsis thaliana
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPhotosynthesis in plants involves two photosystems acting in series, Photosystem I (PSI) and PSII. Each photosystem is a massive complex consisting of numerous proteins and pigments. The photosystems are efficient at light harvesting but also sensitive to high-light induced photooxidative damage. Photosynthetic…

LIL3, a light-harvesting complex protein, links terpenoid and tetrapyrrole biosynthesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe final step in the synthesis of chlorophyll is the joining of chlorophyllide, (a tetrapyrrole with planar structure similar to heme) to a linear lipid (a product of the terpenoid pathway) that provides an attachment point for the resulting chlorophyll to pigment-binding proteins of the light-harvesting…
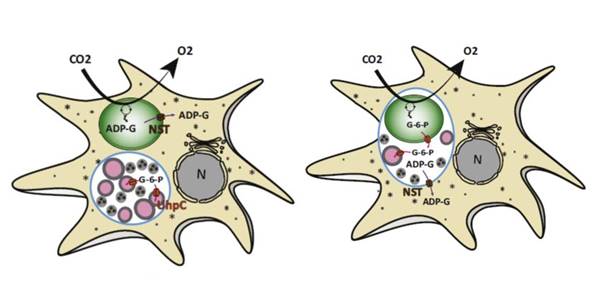
Opinion: Ménage-à-trois hypothesis of plastid endosymbiosis ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIt is well established that plastids are derived from the primary endosymbiosis of an ancient cyanobacterium into a eukaryotic host cell, but this understanding does not explain all of the evidence, nor does it explain how the nascent endosymbiont evaded the host cell's defense mechanisms. Recently,…

