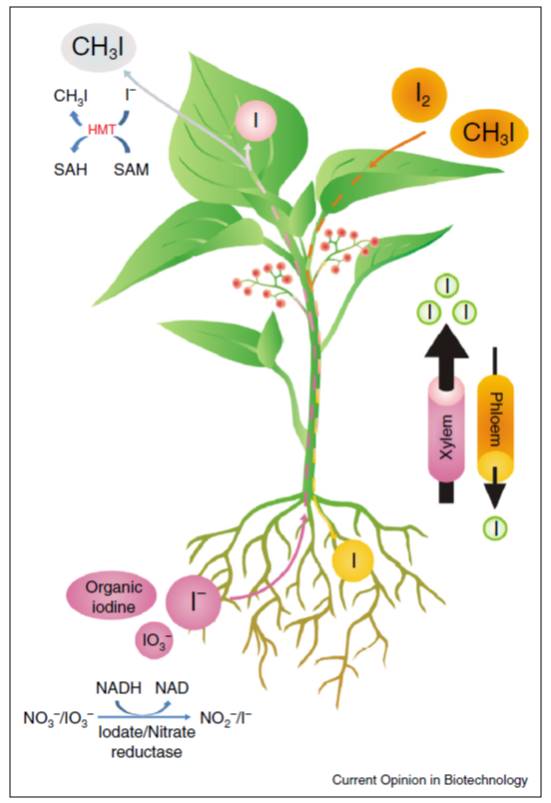
Biofortification of plants: New Reviews ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Biofortification is the nutritional enhancement (using conventional or genetic engineering approaches) of food with vitamins or micronutrients with the goal of improving the human diet. A set of new reviews in Current Opinion in Biotechnology summarizes progress towards biofortification of plants to…
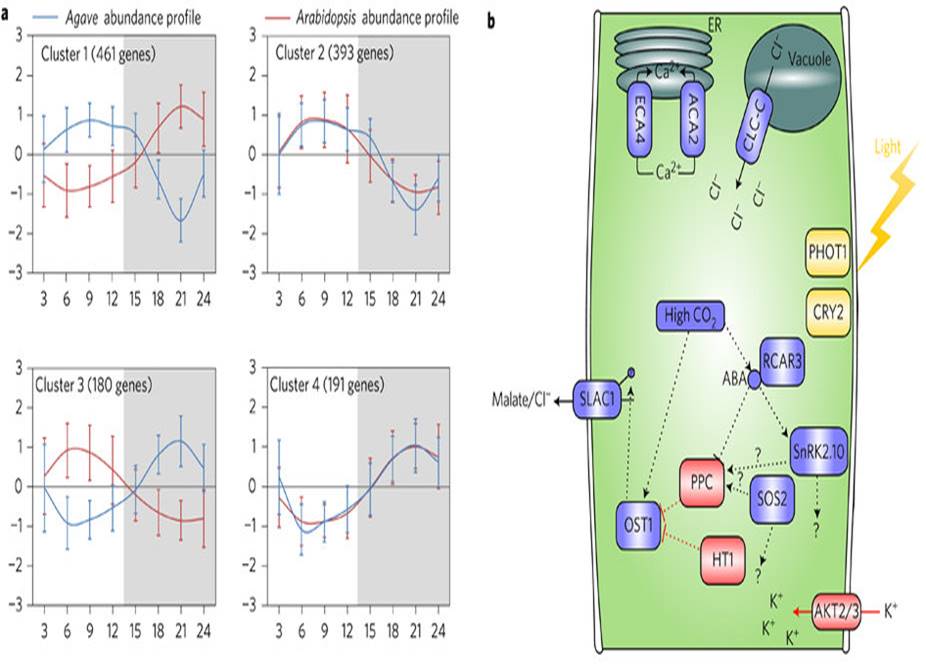
Transcript, protein and metabolite dynamics in CAM-plant Agave ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is a specialized form of photosynthesis that greatly increases water-use efficiency by taking up CO2 through stomata that are open at night (when evapotranspiration is low). Engineering plants that can switch to CAM during periods of drought is a key goal towards…
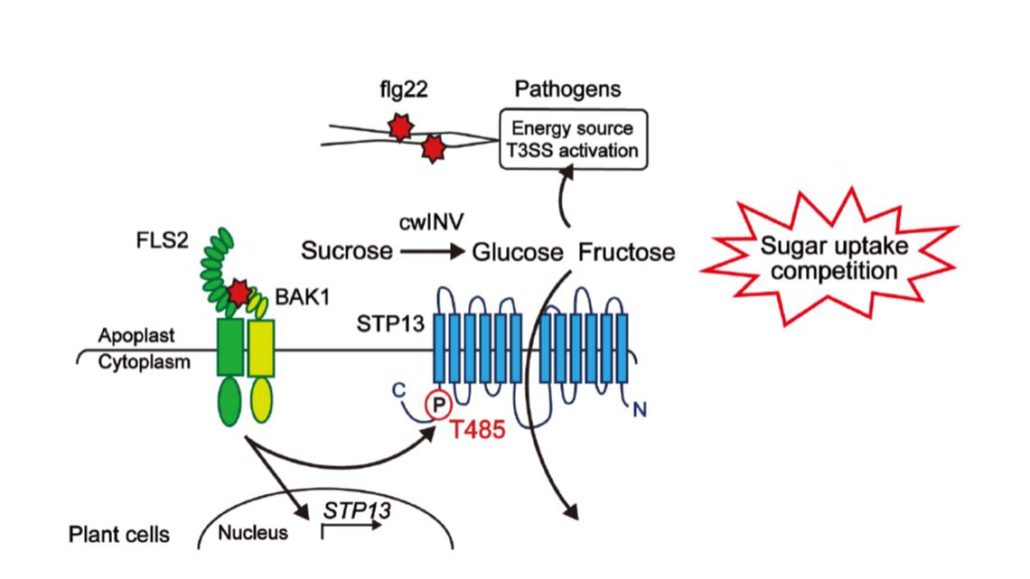
Stimulation of sugar import for antibacterial defense ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
When villagers see the marauding hordes approaching, they secure their food sources. Similarly, when the cell-surface FLS2 receptor detects a bacterial pathogen, it (through its co-receptor BAK1) phosphorylates and stimulates the activity of a cell-surface sugar transporter (STP13), leading to the…

Molecular basis for plant growth responses in shade and under competition for light ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
The wavelenghts of light perceived by a plant are information-rich, and plants integrate information from photoreceptors tuned to different wavelenghts to optimize their growth and development. Because plants absorb red light but not far-red light, a low ratio of red to far-red light indicates vegetative…
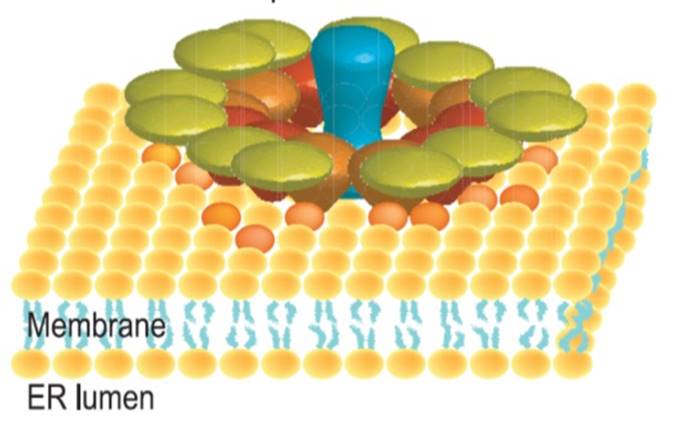
Clustering of sorghum defense-compound dhurrin proteins into a metabolon ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
A metabolon is a physical clustering of metabolic pathway proteins. Until now, evidence for metabolons has been patchy, but Laursen et al. convincingly demonstrate the physical association of several enzymes involved in the production of dhurrin, a defense compound of sorghum. They use a method involving…
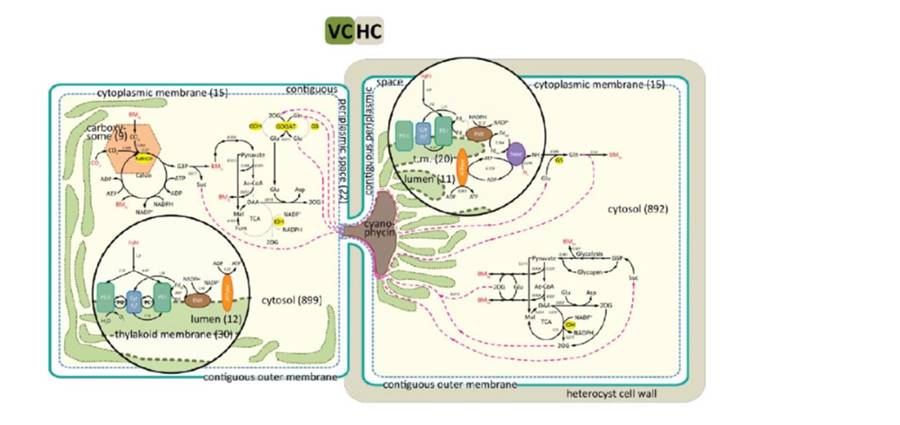
Two-cell metabolism in multicellular cyanobacteria ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
Nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria such as Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 have the challenge of supporting nitrogenase, an enzyme that is highly sensitive to oxygen, and simultaneously photosynthesis, an oxygen-producing set of reactions. They accomplish this by segregating these reactions into two cells, heterocysts…
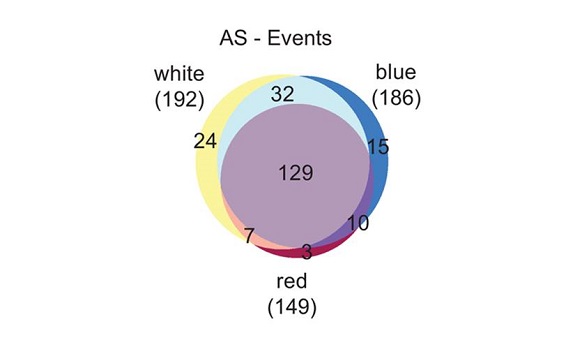
Metabolic Signaling Regulates Alternative Splicing during Photomorphogenesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Kathleen L. Farquharson [email protected]
Alternative splicing (AS) regulates gene expression and greatly expands the coding capacity of complex genomes. By regulating which elements of an mRNA transcript are removed or retained, AS produces multiple transcripts from a single gene. Some…
Do Phytochromes and Phytochrome-Interacting Factors Need to Interact?
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Nancy R. Hofmann [email protected]
A new study calls into question whether phytochrome B (phyB) must directly interact with phytochrome-interacting factors (PIFs) to promote light responses. Phytochrome photoreceptors mediate responses to red light in part by inducing the degradation of…

RNA Degradome Studies Give Insights into Ribosome Dynamics
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Gregory Bertoni [email protected]
RNA metabolism is key to a number of crucial processes in the cell, including transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and gene regulation. For efficient translation, mature mRNAs must have a 7-methylguanosine cap on the 5′ end to help recruit the translation…

