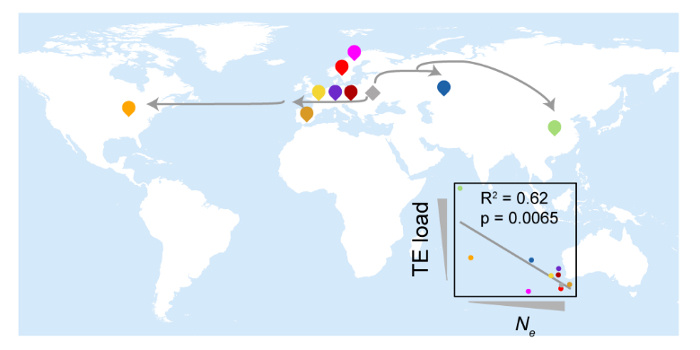
Mechanisms underlying transposable element load variation in Arabidopsis
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellJiang et al. explore the mechanisms underlying transposable element load variation in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad296
By Juan Jiang (Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences) and Ya-Long Guo (Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences)
Background:…

All in good time: Timing gene activation during early flower development
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellPelayo et al. explore the function of a biological timer that activates key genes for flowering.
Margaret Anne Pelayo, Nara Institute of Science and Technology
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad123
Background: For flowers to form, the floral meristem (floral stem cells) must irreversibly commit…
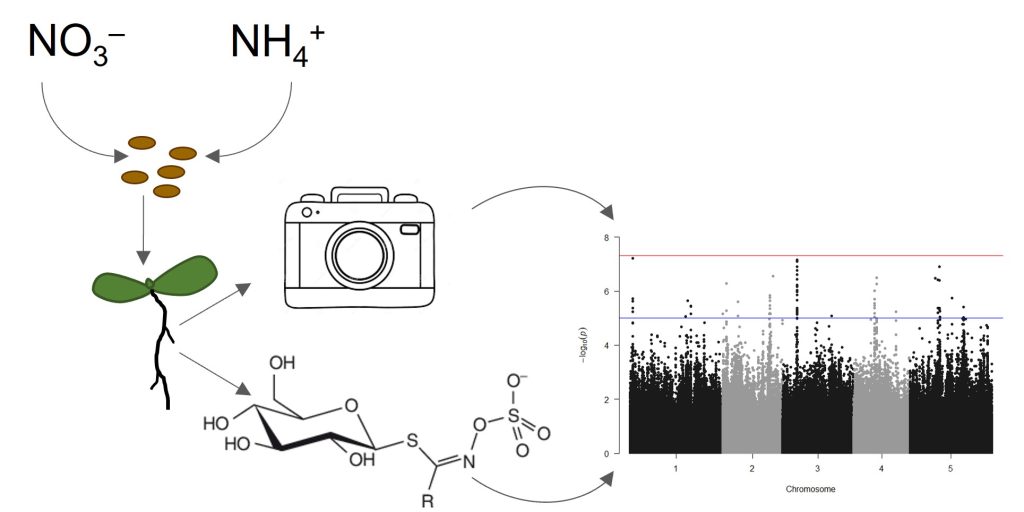
The genetic basis of nitrogen responses in Arabidopsis thaliana
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellElla Katz1 and Dan J. Kliebenstein1,2.
1Department of Plant Sciences, University of California Davis, Davis, CA, USA
2DynaMo Center of Excellence, University of Copenhagen, Denmark
Background: Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and development. Nitrogen availability and form…
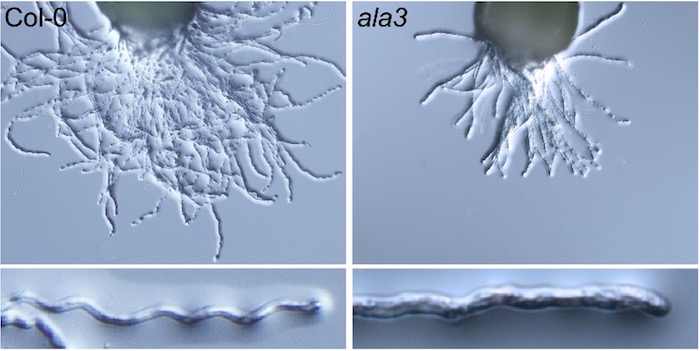
A mechanism that precisely guides pollen tube growth
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYang et al. investigate the role of the phospholipid flippase ALA3 in pollen tube guidance in Arabidopsis.
Background: In flowering plants, pollen tube guidance regulates the rapid growth and timely targeting of the pollen tube to the ovule in the pistil during sexual reproduction, when signaling…
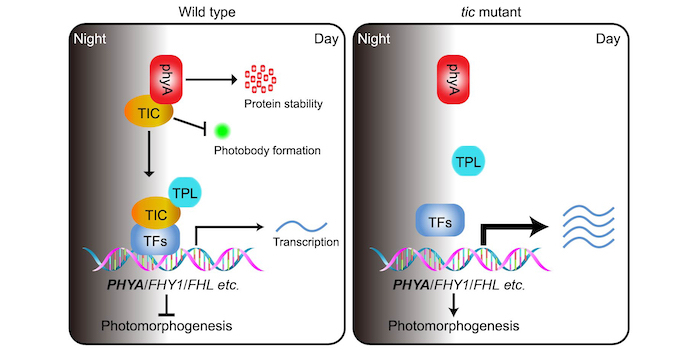
Tick tock: TIME FOR COFFEE regulates far-red light inhibited hypocotyl growth
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. explore how the circadian clock regulates phytochrome A abundance and activity to mediate far-red light inhibited hypocotyl growth.
Background: To enhance plant adaptability to natural conditions, the circadian clock is synchronized and entrained by light via photoreceptors. Intriguingly,…
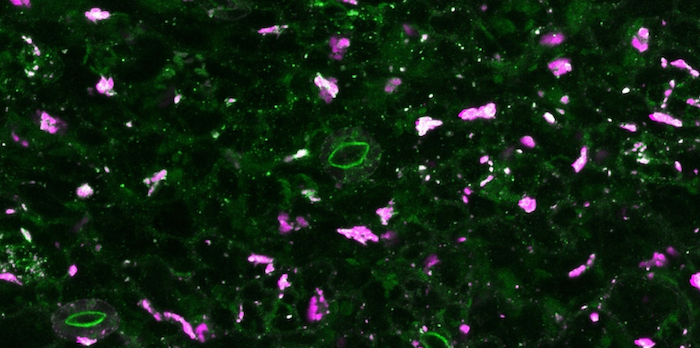
Cauliflower mosaic virus uses Arabidopsis RNA processing body components to its advantage
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHoffmann et al. discover how Arabidopsis RNA processing body components are co-opted by Cauliflower mosaic virus to evade translational repression.
By Gesa Hoffmann and Anders Hafrén, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
Background: Viruses are unique in their ability to reuse and recycle…
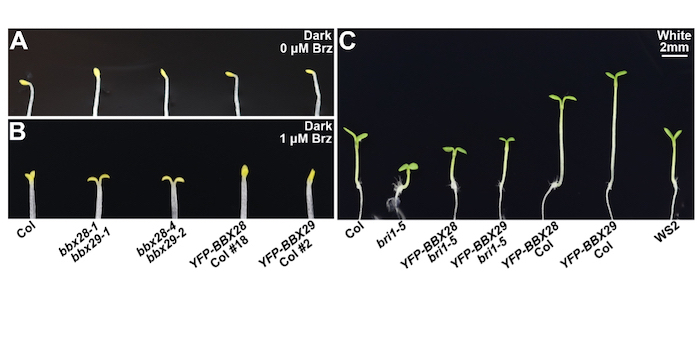
A new link between light and brassinosteroid signaling
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellCao et al. demonstrate that the photomorphogenic repressors BBX28 and BBX29 enhance brassinosteroid signaling to promote hypocotyl elongation and cotyledon closure.
By Jing Cao and Fang Lin
Background: Light signals and brassinosteroids (BRs) are external stimuli and internal cues, respectively,…
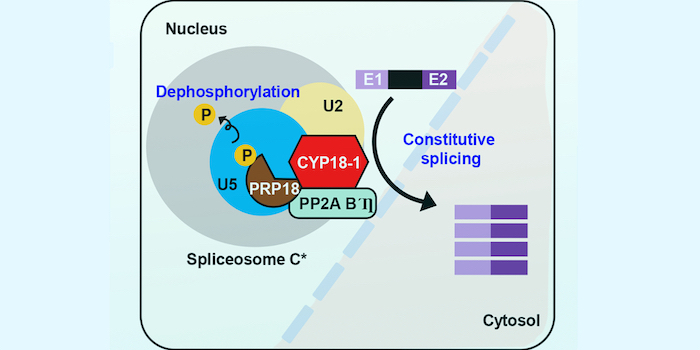
A spliceophilin helps Arabidopsis adapt to heat stress
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellJo et al. uncover the role of a spliceosome component in removing retained introns in Arabidopsis in response to heat stress https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac084
Background: Alternative splicing plays a key role in abiotic stress responses in plants, especially responses to heat stress. The spliceosome…

Lower oil content leads to wrinkled, immature seeds
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHuang et al. elucidate the relationship between fatty acid biosynthesis and seed maturation in Arabidopsis.
By Ruihua Huang and Shengchun Zhang
Background: Storage substances such as starch, protein, and oil in crop seeds are major sources of food for humans. These substances mainly accumulate…

