Gene knock-down using gene editing
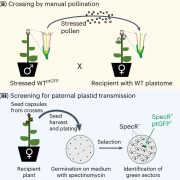
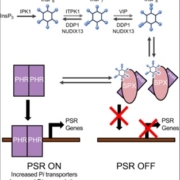
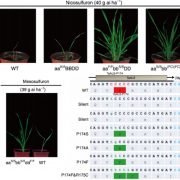
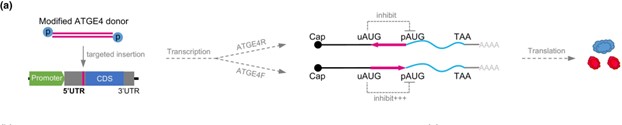 An efficient method of gene downregulation, where gene expression is reduced but not completely knocked out, is useful for crop improvement. Here, Shen et al. have developed a system to achieve this, by using CRISPR/Cas9 to insert an element containing a Kozak sequence and an ATG start codon just before the primary start codon of the gene they wish to silence. This new ATG site acts as a competitor to the primary start codon, and leads to a reduction in translation of the normal transcript. The was tested in dual luciferase assays in rice protoplasts and led to ~75% reduction in expression of target genes. They then applied it to a commercial rice variety to downregulate the amylose synthesis gene Waxy. Plants with the gene knock-down element inserted upstream of Waxy had lower Waxy expression and had a milky coloured endosperm, which is indicative of reduced amylose content. Thus, this approach has been shown to successfully decrease gene expression in crop plants. (Summary by Rose McNelly @Rose_McN) New Phytol. 10.1111/nph.19856
An efficient method of gene downregulation, where gene expression is reduced but not completely knocked out, is useful for crop improvement. Here, Shen et al. have developed a system to achieve this, by using CRISPR/Cas9 to insert an element containing a Kozak sequence and an ATG start codon just before the primary start codon of the gene they wish to silence. This new ATG site acts as a competitor to the primary start codon, and leads to a reduction in translation of the normal transcript. The was tested in dual luciferase assays in rice protoplasts and led to ~75% reduction in expression of target genes. They then applied it to a commercial rice variety to downregulate the amylose synthesis gene Waxy. Plants with the gene knock-down element inserted upstream of Waxy had lower Waxy expression and had a milky coloured endosperm, which is indicative of reduced amylose content. Thus, this approach has been shown to successfully decrease gene expression in crop plants. (Summary by Rose McNelly @Rose_McN) New Phytol. 10.1111/nph.19856