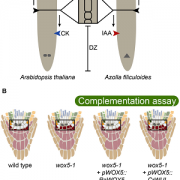
Review - Getting to the Roots: A Developmental Genetic View of Root Anatomy and Function From Arabidopsis to Lycophytes (Frontiers in Plant Sci)
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots are essential organs for water and nutrient uptake, and aboveground biomass support. While these organs are important for many plant functions, the evolutionary history of the root is still unclear. The fossil record suggests that roots evolved in both the lycophyte (clubmosses and their…

The Arabidopsis negative regulator of root hydraulics XND1 is involved in abiotic and biotic stress responses (Nature Comm.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProper uptake and management of water is essential for plant growth and adaptation to stress. However, there are gaps in the understanding of the genetics of root hydraulics, including the regulatory components. Tang et al. used a genome-wide associate analysis approach to identify XYLEM NAC DOMAIN 1 (XND1),…

ABA-mediated regulation of stomatal density is OST1-independent (Plant Direct)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata are not only important for CO2 uptake, but are also important in limiting water loss when the water availability is running low. Stress hormone ABA activates protein kinase OPEN STOMATA 1 (OST1) leading to opening of ion channels, water efflux and stomatal closure. Increased levels of ABA decrease…

Insights into the evolution of multicellularity from the sea lettuce genome (Current Biol. - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transition from unicellular to multicellular life forms occurred across multiple kingdoms, and in plants is correlated with the expansion of gene families involved in extracellular matrix formation and cell cycle regulation. Green seaweeds acquired their plant-like body independently of other lineages…

Magazine Feature: Can botanic gardens save all plants? (Current Biol. - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the past botanic gardens served many purposes ranging from providing tranquil environment, spreading crops to places far away from their natural environment and providing emerging botanists with live samples. Currently, botanic gardens provide entertainment and education for millions of visitors.…
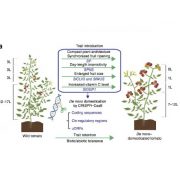
Domestication of wild tomato is accelerated by genome editing (Nature Biotech. - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWild tomato, Solanum pimpinellifolium, exhibits remarkable tolerance to salt stress and bacterial spot disease. Domestication of S.pimpinellifolium requires adjustment of day-length sensitivity, plant compactness, fruit size and the fruit could benefit from increased vitamin C content. Li et al. used…
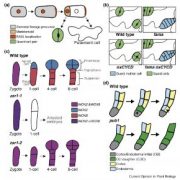
Review - A plane choice: coordinating timing and orientation of cell division during plant development (Current Opinion in Plant Bio)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAsymmetric cell division is instrumental to development of specialized cells, while symmetric cell division underlies proliferative growth. The defects in cell division plane arise when transition between the G1 to S stage is accelerated, suggesting that the signals leading to division plane position…

Rapid improvement of domestication traits in an orphan crop by genome editing (Nature Plants - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrphan crops, like groundcherry (Physalis pruinosa), are regionally important but are not grown on large commercial scale as they never went through a breeding cycle. Precision gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR/Cas9, can alter the most important agronomic traits in relatively short time. Lemmon…

Members of the Arabidopsis FORKED1-LIKE gene family act to localize PIN1 in developing veins (J Exp Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyVascular system is one of the adaptive features for terrestrial plants. Polar localization of PIN1 is essential for creating directional auxin flow, resulting in vein pattern formation. Mariyamma et al. propose that FORKED1 (FKD1) and its homologues control the PIN1 polar localization. The team identified…

