Structural analysis of HTL and D14 proteins reveals the basis for ligand selectivity in Striga (Nature Comm.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStrigolactones induce germination of parasitic plant Striga, which causes more crop loss in Africa than any other parasite. Karrakins are structurally related to strigolactones, yet they do not induce Striga germination. By studying the structure and substrate recognition of strigolactone and karrakin-binding…

De novo domestication of wild tomato using genome editing (Nature Biotech - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBreeding of crops typically focuses on yield increase, and is accompanied with the loss the genetic diversity, reduced nutritional value as well as susceptibility to environmental stress. As many domestication traits exhibit simple Mendelian inheritance patterns, Zsögön et al. targeted known domestication…
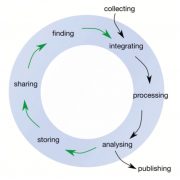
Opinion: Best practice data life cycle approaches for the life sciences (F1000 Res)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProducing data is costly, and with advances in technology, we are producing data with revolutionary capacity. However, we are also losing data at an astonishing rate, with around 80% of data being unavailable 20 years after publication. Griffin et al. provide guidelines, repositories and other resources…
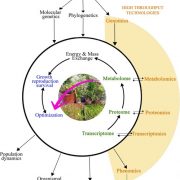
Focused Review: A role for ecophysiology in the ’omics’ era (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEcophysiology is the study of plant functioning as modulated by the environment (or, as described by one author, “outdoors physiology“). Flexas and Gago ask whether research (and training) in ecophysiology has been left behind somewhat by successes in -omics approaches, and from a Web of Science…
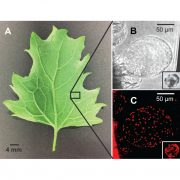
Molecular basis of salt sequestration in epidermal bladder cells of Chenopodium quinoa
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe recent focus on quinoa is a result of not only its high nutritional value, but also its astonishing salt stress tolerance. Epidermal bladder cells (EBC) are suspected to be a cause of salinity tolerance by serving as salt dumping place. In order to identify molecular mechanisms underlying salt sequestration,…
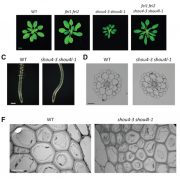
SHOU4 proteins regulate trafficking of cellulose synthase complexes to the plasma membrane (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant cell walls provide mechanical support and define the extent and direction of cell expansion. Regulation of cellulose synthase determines cell wall load bearing and involves the receptor like kinases FEI1/FEI2. To gain further understanding of cell wall integrity regulation Polko et al. performed…
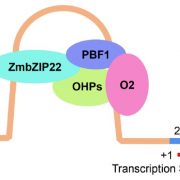
ZmbZIP22 regulates 27-kD γ-zein transcription during maize endosperm development (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyZeins are maize seed storage proteins, but are notoriously low in the amino acids lycine and tryptophan. Therefore, to improve maize's nutritional properties, efforts have been made to decrease zein levels. However, such efforts often lead to abnormal (opague) kernels. Previous work has demonstrated…
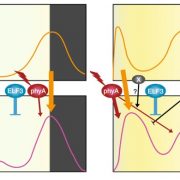
Flowering time in the real world (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere are pros and cons to growing plants in controlled conditions. On the one hand, controlling light, temperature, humidity and other environmental factors should aid reproducibility between experiments and labs. But what if the conditions used profoundly and unexpectedly affect the process you are…

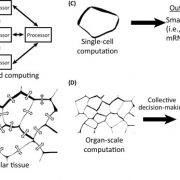
Opinion: Information processing and distributed computation in plant organs ($) (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe great strides we’ve made in understanding how plants perceive their environment, from light to pathogens to nutrients, haven't been matched with an understanding of what they do with all that information; how do so many inputs get integrated into a single or few responses? And how does the information…

