Special Issue: Long-distance signaling ($) (Plant Cell Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOf course plants need to communicate between their different parts, and our understanding of these crucial signals has been advancing rapidly. This issue of Plant Cell Physiology includes a set of papers highlighting recent findings. A meeting report by Kiba on the Integrative Graduate Education and…
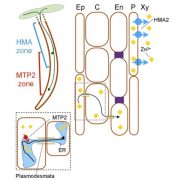
Systemic upregulation of Zn partitioning to the shoot supplements local Zn-deficiency responses (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyZinc is an important micronutrient for plants and people. To better understand Zn uptake and homeostasis, Sinclair et al. used a transcriptomic approach to identify genes abnormally expressed in zinc-transporter mutants (hma2 hma4). In these mutants, Zn accumulates in roots but isn’t effectively transported…
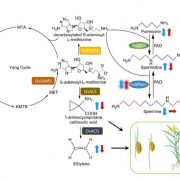
The spermine synthase OsSPMS1 regulates seed germination, grain size, and yield (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPolyamines including spermine and spermidine are present in all eukaryotes and have diverse roles. In plants they have been implicated in responses ranging from abiotic and biotic stresses to grain filling. Tao et al. examined the function of OsPMS1, encoding a spermine synthase, through genetic methods…

FLOWERING LOCUS T3 controls spikelet initiation but not floral development (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFT encodes a mobile protein that carries a flower-promoting signal to the shoot apical meristem. In most plants, the FT gene has duplicated and diversified. Mulki et al. investigated the function of FT3 (HvFT3) in barley. Prior work showed that overexpression of HvFT1 accellerated the initiation and…

Molecular events marking the onset of berry ripening in grapevine (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDo you know the difference between a wine made from Pinot noir grapes and one made from Cabernet Sauvignon grapes? Most people can taste a difference, but to really understand the wines you might want to go a bit deeper through metabolomic and transcriptomic approaches, as done by Fasoli et al. (in a…
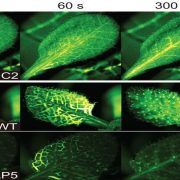
Glutamate is a wound-induced signal that activates long-distance calcium signaling (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeveral years of intensive research have revealed a suite of mobile signals that travel long-distances to inform meristems on developmental phase transitions or to protect distal plant tissues from abiotic or biotic stressors. In a new article published in Science, Toyota et al. (2018) identify a role…

A shoot-derived miRNA ensures susceptibility to beneficial rhizobacteria in legumes (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen-fixing rhizobacteria and leguminous plants engage in a tightly controlled root symbiosis resulting from bacteria-to-plant as well as (plant) shoot-to-root communication. This interplay controls the initiation and maintenance of root nodule development while preventing the over-production of…
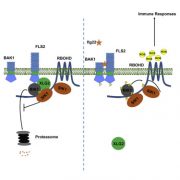
MAP4 kinase SIK1 promotes ROS burst and antibacterial immunity in plants (Cell Host Microbe)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCell surface pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) such as FLS2 that recognize conserved pathogen features are important contributors to plant defenses against pathogens, triggering the so-called Pattern-Triggered Immunity (PTI) response. Pattern recognition by PRRs triggers the production of extracellular…

Wheat microbiome bacteria reduce virulence of pathogenic fungus by altering fungal histone acetylation (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklySometimes the plant is a relatively passive host upon which other organisms engage in dynamic interactions. Chen et al. showed that a wheat head-associated bacterium, Pseudomonas piscium, produces antifungal compounds that inhibit the growth of a plant pathogenic fungus, Fusarium graminearum. The authors…

