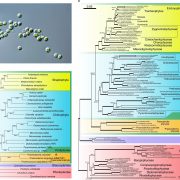
The genome of Prasinoderma coloniale unveils the existence of a third phylum within green plants (Nature Ecol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe green plant lineage (Viridiplantae) has long been described as having a single origin (starting with the engulfment of a cyanobacteria-like endosymbiont) that has led to two phyla: the Streptophyta, including embryophytes (land plants) and some algae such as chara and nitella, and the Chlorophyta,…
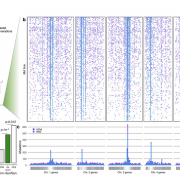
Mutation bias shapes gene evolution in Arabidopsis thaliana (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClassical evolutionary theory states that the probability of a mutation occurring is independent of fitness consequences. However, reassessment of traditional assumptions is warranted with recent discoveries showing that cytogenetic (DNA sequences and epigenetic) features can affect local mutation probabilities.…
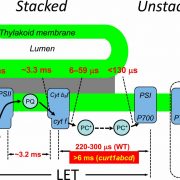
Plastocyanin is the long-range electron carrier between photosystem II and photosystem I in plants (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn linear electron transport (LET), electrons are passed from photosystem II to photosystem I, but it has not been clear which of two mobile electron carriers is responsible, plastocyanin (PC) or plastoquinone (PQ). PQ carries electrons from PSII to the cyt b6f complex and PC from there to PSI. Höhner…
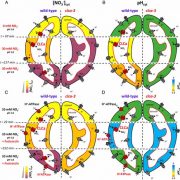
Vacuolar channel CLCa is involved in guard cell pH homeostasis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants, stomata are involved in a host of responses, controlled by ion homeostasis in guard cells. In an attempt to understand the function of a plant chloride channel (CLC), CLCa, which transports chloride (Cl-) and nitrate (NO3-) in guard cells, Demes and colleagues sought to establish a relationship…
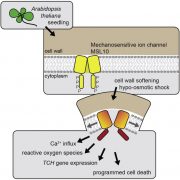
MscS-like 10 as a cell swelling sensor and promotes hypo-osmotic shock responses (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOptimal volume and turgor in the plant cell is important for metabolism, development and growth. Excessive diffusion of water into the cell will cause extreme swelling and a loss of cellular integrity. Members of the plasma membrane MscS-like (MSL) family of mechanosensitive (MS) ion channels play a…

Reprogramming of stem cell activity to convert thorns into branches (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThorns are modified axillary shoots with a sharp tip that helps in deterring herbivores and are found among several families of angiosperms. Thorns develop from their meristem-like tip to their base, but unlike branches they are determinate organs. The mechanism of their terminal differentiation into…
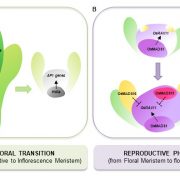
Genes of the RAV family control heading date and carpel development in rice (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed-bearing annual plants essentially get one shot at getting their reproductive timing right; too early and there won’t be enough stored nutrients to produce healthy seeds, and too late and the seeds might not mature fully before bad weather or rot sets in. Previously, the RAV (RELATED TO ABI3 AND…
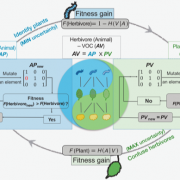
Plant-herbivore chemical communication decoded (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChemical communications between species are prevalent in nature. For instance, herbivorous insects can spot their host plants by sensing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by plants. Despite our knowledge about interactions between individual plant and herbivore species, little is known about…

Induced tolerance to abiotic and biotic stresses of broccoli and Arabidopsis after treatment with elicitor molecules (Sci. Rep.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant hormones such as jasmonates (JAs) and salicylic acid (SA) are known for their role in regulating plant growth under both abiotic and biotic stresses. These hormones, which are synthesized within the plant, can modulate cellular processes in targeted cells locally and can be moved to other parts…

