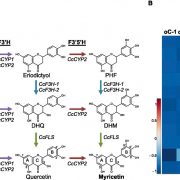
Synthesis of a Plant-Based Drug for the Potential Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideType 2 diabetes, which is characterized by high blood glucose (Glc) levels, afflicts ~6% of the population of the western world. A major goal in treating diabetes is reducing high levels of blood Glc, which is a particular problem in patients whose diets are rich in starch and other sugars. The main…
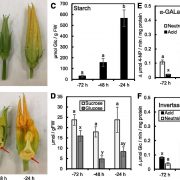
Sugar Metabolism in Squash Nectaries and Nectar
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideFloral nectar is a sugar-rich solution produced by plants to attract animal pollinators. The best-elucidated model of nectar secretion, based on studies of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), involves the build-up and degradation of nectary starch, the resynthesis of Suc from starch-derived hexoses,…
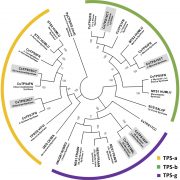
Coregulation of Cannabinoid and Terpenoid Pathways
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideMany governments have recently enacted laws that allow for the legalization of cannabis for medical and/or recreational purposes. Unfortunately, specific labeling regulations with regard to the composition of active ingredients, serving sizes, and recommended doses are woefully lacking. The capitate-stalked…
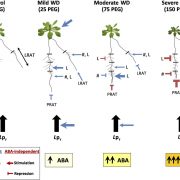
Abscisic Acid Mediates Root Responses to Water Deficit
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideOf all abiotic stresses faced by plants, water deficit (WD) is the one that most profoundly affects crop productivity. When exposed to WD, plants first respond by restricting stomatal aperture and by rapid changes in root hydraulic conductivity (Lpr). Over a longer term, plants change both shoot growth…

Energy Costs of Root Growth
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe energy costs of root growth are particularly high in dry and compacted soil because soil penetration resistance increases under these conditions. As a result, more photosynthate is needed for root system expansion, leaving less carbon available for aboveground plant growth. Furthermore, the growth…
Role of Polysaccharide Synthesis in Diatoms
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDiatoms are a type of phytoplankton that account for ~20% of global primary production. Like all phytoplankton, they produce and store copious amounts of polysaccharides. More specifically, diatoms produce significant amounts of b-1,3 glucans, particularly chrysolaminarin. Mutualistic associations…
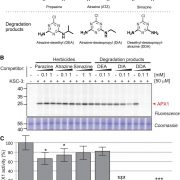
Triazine Probes for Ascorbate Peroxidases
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideMolecules based on 1,3,5-triazine are rare in nature. Most 1,3,5-triazine compounds are anthropogenic and have only existed in the last 150 years. Because it is easy to synthesize, 1,3,5-triazine is often employed as a modular scaffold in industrial applications, including the synthesis of medicines,…
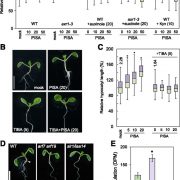
Pinstatic Acid: a Novel Modulator of PIN Trafficking
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe polar subcellular localization of the auxin efflux machinery determines the directionality of auxin flow in plants. In particular, the dynamics of polar localization of PIN proteins regulates the rate and direction of cellular auxin export and this ultimately determines auxin gradients in the tissue.…

A Role for Mitochondrial Fission in Pollen Growth
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe tapetum is the innermost layer of the anther and encloses the locule wherein pollen develops. In addition to supplying nutrients for pollen growth, the tapetum synthesizes and transfers pollen outer wall precursors for the formation of the pollen outer wall. To synthesize, secrete, and transfer materials…

