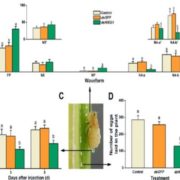
A salivary endo-β-1,4-glucanase acts as an effector that enables the brown planthopper to feed on rice
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
The rice brown plant hopper (BPH) Nilaparvata lugens is a damaging herbivorous insect that sucks nutrients from phloem. Previously, Ji et al. surveyed genes encoding putative secreted proteins from the BPH salivary gland and identified NlEIG1 as a putative endo-β-1,4-glucanase (cell-wall degrading…
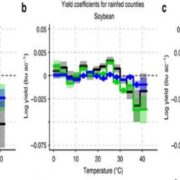
Response of US crops to elevated temperatures
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchClimate change could affect agricultural productivity by increasing the number of days with temperatures above 30°C that staple crops like soybean, maize and wheat will experience during a given growing season. Schauberger et al. used nine statistical models to assess future threats to US crops. They…
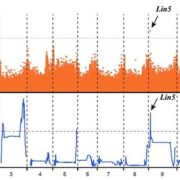
A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThey say that “chacun à son gout” (each has his own taste), but when it comes to tomatoes there is near universal agreement that they don’t taste as good as they used to: a fact that is borne out by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and the panel of taste-testers employed by Tieman et al. in…

ARF19 affects seed size in biofuel plant jatropha
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchJatropha curcas is a perennial woody plant with high seed oil content that has potential to be used in biofuel production. However, there is limited knowledge about the biology of seed oil production in Jatropha spp. Sun. et al., used a genetic approach to identify a J. curcas QTL that controls seed…
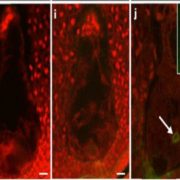
MATRILINEAL, a sperm-specific phospholipase, triggers maize haploid induction ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSexual reproduction, with all that recombination and independent assortment, is an excellent way to generate genetic diversity and increase the likelihood that some progeny will survive. However, the seed industry strives to produce genetically uniform seeds. Although there are various ways to circumvent…
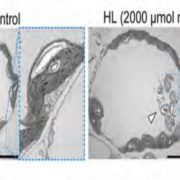
Entire photodamaged chloroplasts are transported to the central vacuole by autophagy
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAutophagy is the process by which macromolecules and organelles are recycled. Previously it was shown that during leaf senescence or energy starvation, chloroplasts are degraded piecemeal by autophagy. In this work, Izumi et al. examined the role of autophagy in UVB damaged chloroplasts, using wild-type…
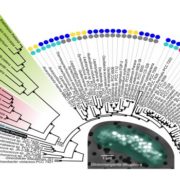
An early-branching freshwater cyanobacterium at the origin of plastids ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlastids are derived from an ancient endosymbiosis of a cyanobacterium, but which cyanobacteria are plastid’s nearest living relatives? Ponce-Toledo et al. generated an extensive phylogeny comprising numerous cyanobacteria and plastid-bearing eukaryotes (glaucophytes, red algae and green algae). Their…
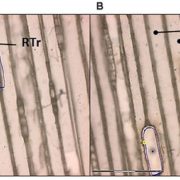
Protocol: Laser capture microdissection for woody tissues
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchLaser capture microdissection (LCM) was developed 20 years ago as a way to isolate single cells or clusters of cells for subsequent –omic analysis. In LCM, thin sections are generated, the cells of interest cut out using a focused laser, and the isolated cells collected for subsequent studies. Several…

Three Reviews: Phytochrome, shade avoidance and far-red light ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant Cell Environ. has a set of reviews on light responses. Ballaré and Pierik (10.1111/pce.12914) review The shade avoidance syndrome: Multiple signals and ecological consequences, Sheerin and Hiltbrunner (10.1111/pce.12915) review the Molecular mechanisms and ecological function of far-red light…

