
Recognizing featured Plant Cell first authors, July 2016
0 Comments
/
Recently, we’ve been profiling first authors of Plant Cell papers that are selected for In Brief summaries. Here are the first-author profiles from the July issue of The Plant Cell.
Fangwei Gu, featured first author of Arabidopsis CSLD5 functions in cell plate formation in a cell cycle-dependent manner
Current…
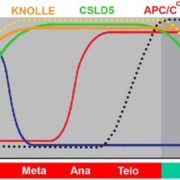
Divide and Conquer: Introducing a Novel Player in Cell Plate Formation
IN BRIEF by Kathleen L. Farquharson kfarquharson@aspb.org
Polysaccharide-rich cell walls are a distinguishing feature of plants that influence many aspects of growth and development, including cell division. Whereas contractile rings pinch dividing cells into two daughter cells in other eukaryotes,…
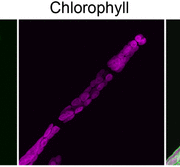
Invisible No Longer: Peptidoglycan in Moss Chloroplasts
IN BRIEF by Nancy Hofmann nhofmann@aspb.org
Most bacteria have a peptidoglycan layer between the inner and outer membranes (reviewed in Typas et al., 2012). The cyanobacterial endosymbiont that gave rise to plastids would have contained such a peptidoglycan wall including d-amino acids. Indeed, peptidoglycan…
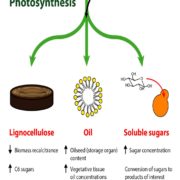
Review: Biotechnology and synthetic biology approaches for metabolic engineering of bioenergy crops
Shih et al. review how the many and diverse tools of plant synthetic biology can be applied towards bioenergy crops, focusing on traits related to lignocellulose, oil, and soluble sugars. Tools include those that edit genes, those that alter protein activities, and those that enable gene stacking in…

Shape-Shifters: How Strigolactone Signaling Helps Shape the Shoot
IN BRIEF by Jennifer Lockhart jlockhart@aspb.org
When a deer eats the primary shoot of a plant, this can activate a nearby dormant axillary bud, causing it to form a secondary shoot. Genetic and environmental factors also affect shoot architecture, which strongly influences crop productivity. Changes…
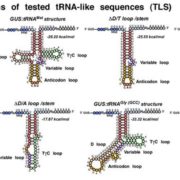
Ticket to Ride: tRNA-Related Sequences and Systemic Movement of mRNAs
IN BRIEF by Jennifer Mach jmach@aspb.org
Movement of macromolecules through the plant phloem provides a mechanism for long-distance signaling that plants use in development, disease resistance, and other adaptive responses (reviewed in Spiegelman et al., 2013). For example, full-length RNAs, such…

Thinking Outside the Plant: Exploring Phloem Development Using VISUAL
IN BRIEF by Jennifer Lockhart jlockhart@aspb.org
Investigating how plants grow and develop often requires a bit of creativity. For example, deep within the plant, the vascular cambium, a layer of embryonic, highly cytoplasmic cells, gives rise to xylem and phloem tissue, which must expand throughout…
Review: Plant synthetic biology for molecular engineering of signalling and development
Nemhauser and Torii define synthetic biology as “an engineering approach to design, build and analyize dynamic molecular devices and/or pathways from biological components to produce cells and organisms with customized functionality.” In their review, they describe several plant synthetic biology…
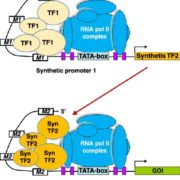
Review: Plant synthetic promoters and transcription factors
Many plant traits are multigenic, so engineering them requires modulating the expression of several genes simultaneously. Synthetic promoters and transcription factors offer such a possibility. For example, a cis-element can be introduced into the promoter of each gene of interest, and a synthetic transcription…

