Review: Mechanisms to mitigate the tradeoff between growth and defense ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
It is widely recognized that defense incurs a cost in terms of reduced growth. Karasov et al. explore the nature of this tradeoff. They observe that rather than tradeoff being driven directly by metabolic competition, it appears to occur upstream through regulatory processes including antagonism between…

Review: Wheat genomics comes of age
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchDue to its highly repetitive, polyploid genome, wheat genomics has lagged behind that of other cereals, but new tools promise to begin closing that gap. Uauy reviews these new tools, which include access to full genomes of several wheat varieties, gene expression data from hundreds of publicly available…
Update: Origins and evolution of stomatal development
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, ResearchThe fossil record suggests stomata-like pores were present on the surfaces of land plants over 400 million years ago. Whether stomata arose once or whether they arose independently across newly evolving land plant lineages has long been a matter of debate. In Arabidopsis, a genetic toolbox has been identified…

Signatures of local adaptation in lowland and highland teosintes from whole genome sequencing of pooled samples ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTeosinte, the ancestor of maize, grows in a range of environments in México. Teosinte parviglumis (Zea mays ssp parviglumis) is more prevalent in lowland regions while teosinte mexicana (Zea mays ssp mexicana) occupies highland territory (>2000 m above sea level). Admixture between parviglumis and…
Aflatoxin-free transgenic maize using host-induced gene silencing
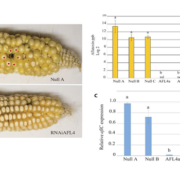
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAflatoxins are toxic metabolites produced by some species of Aspergillus fungi that can occur on numerous crop plants. When ingested by animals, aflatoxins cause health problems including liver cancer and stunted growth. Thakare et al. used host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) to block aflatoxin production…
Divergent evolution driven by pollinators
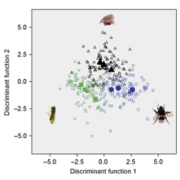
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA great variety of plants rely on pollinators to be fertilized successfully. This close relationship is thought to drive evolutionary diversification in plants, making the presence or absence of pollinators in response to climate change an increasingly relevant matter. Gervasi and Schiestl addressed…
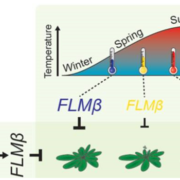
Natural haplotypes of FLM non-coding sequences fine-tune flowering time in two ambient spring temperatures in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchDelaying reproduction until conditions are favorable is a key to success. FLOWERING LOCUS C is a well-known regulator of flowering that delays flowering until after winter vernalization. In the spring, FLOWERING LOCUS M (FLM) fine-tunes flowering time in response to ambient temperatures between 5ºC…
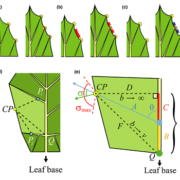
A common developmental program can produce diverse leaf shapes
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe plethora of diverse leaf shapes results from variations of shared molecular mechanisms that govern leaf growth and development. To better understand the molecular underpinnings of diverse leaf morphologies, Runions et al. constructed a computational model of leaf development that included multiple…
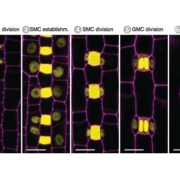
Mobile MUTE specifies subsidiary cells to build physiologically improved grass stomata ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants breathe through pores called stomata on leaf surfaces. Stomata are the point of contact with the outside world as they allow gas exchange (e.g., CO2 for photosynthesis) and transpiration. Grasses have evolved to form more efficient stomata in which the guard cells are flanked by additional subsidiary…

