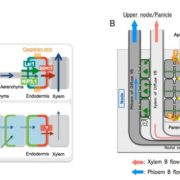
Boron Transport in Rice
Boron (B) is an essential micronutrient for plant growth and development. Its major physiological function is to maintain the structure of the cell wall by crosslinking pectic polysaccharides through borate-diol bonding of two rhamnogalacturonan II molecules. B is immobile in most plant species. Therefore,…
Epigenetic Divergence Associated with Heterosis
Heterosis refers to the tendency of a crossbred individual to show qualities superior to those of both parents. The phenomenon has been exploited extensively in agricultural breeding for decades and has improved crop performance enormously. Despite its commercial impact, knowledge of the molecular basis…

Mineral Deposits in Ficus Leaves
Mineral deposits occur in many, but not all plant leaves. In those leaves that do have minerals, the mineral type, morphology and the distributions within the leaves are under strict control. In fact, mineralization in certain leaves is a well-preserved trait throughout evolution, indicating that such…

Anthocyanins on Demand
Anthocyanins are vacuolar pigments derived from the phenylpropanoid pathway that are produced in many different plant species. The role of anthocyanin accumulation under stress in vegetative tissues is probably linked to the scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Anthocyanins are powerful antioxidants…

Laccase Confers Biotic Stress Tolerance in Cotton
Cotton (Gossypium spp.) is a globally cultivated globally crop of vast economic importance. Pathogens and pests are major limitations to cotton yield and quality. Verticillium wilt, caused by the fungus Verticillium dahliae, is the disease most detrimental to cotton production. Cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa…
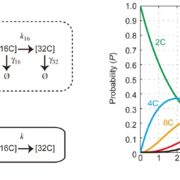
Probing the stochastic property of endoreduplication in cell size determination of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf epidermal tissue
PLOS One. Endoreduplicated cells grow in size as their DNA content increases. The distribution of size was observed to be Poisson. This allowed the authors to create a mathematical model with a single parameter which describes the probability of exiting endoreduplication. The model recovers cell size…
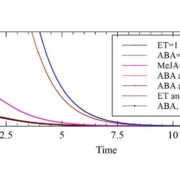
A mathematical model of the interaction of abscisic acid, ethylene and methyl jasmonate on stomatal closure in plants
PLOS One. Plant stomatal opening is controlled by phytohormones, among other factors. This article models the phytohormone signaling response in guard cells using ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Sixteen components in this system were analyzed by constructing 16 different models and determining…
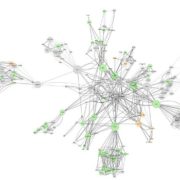
Predicting gene regulatory networks by combining spatial and temporal gene expression data in Arabidopsis root stem cells
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. GENIST (gene regulatory network inference from spatiotemporal data) is a new algorithm developed by de Luis Balaguer et al to predict new gene interactions and transcriptional regulators (available at https://github.com/madeluis/GENIST). The algorithm combines inference of…
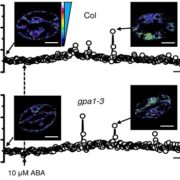
A new discrete dynamic model of ABA-induced stomatal closure predicts key feedback loops
PLOS Biol. This article describes a stochastic mathematical model of the stomatal closure network responding to abscisic acid (ABA). The Boolean network is constructed from a comprehensive literature review of the components’ dependencies. The model’s predictions agree with experimental data 90%…

