Part of the Stack; How Does a Protein Know its Place?
Research, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellParsons et al. successfully separate early to late Golgi cisternae to reveal the sequential localization of resident proteins and the sequence features that guide transmembrane proteins within the Golgi stack. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00081
By Harriet T. Parsons (University of Cambridge)…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Kevin Goslin
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesKevin Goslin, first author of Differential N-end rule degradation of RIN4/NOI fragments generated by the AvrRpt2 effector protease
Current Position: Postdoctoral researcher, Plant Developmental Genetics, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland
Education: PhD in Maynooth University, MSc in Trinity College,…
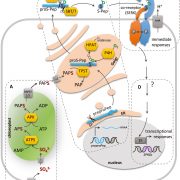
Review: Sulfated plant peptide hormones (J. Exp. Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s hard to believe that when I was a student we were taught that “plants don’t have peptide hormones”. Since then we’ve discovered many diverse families of plant peptide hormones (see the Teaching Tool on peptide hormones for an excellent overview). Here, Kaufmann and Sauter review one family,…

Perspective: Grazing animals drove domestication of grain crops (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHere’s an interesting question: Without human intervention, why would one find a dense stand of plants, growing in rather nutrient-rich soil? Perhaps you recognized that these conditions suggest seed dispersal by endozoochory, which involves passage through an animal's digestive tract. Spengler and…

COP1 can be hijacked by photoreceptors via their VP motifs (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant development is characterized by a high degree of plasticity in response to light. Light‐activated plant photoreceptors bind and inhibit the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1, thus protecting downstream transcription factors from degradation. However, the detailed mechanisms of how COP1 can function between…
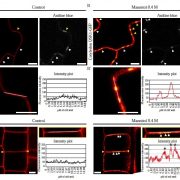
Plasma membrane-associated receptor like kinases relocalize to plasmodesmata in response to osmotic stress (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are channels through the cell wall that allow molecules and substances to move back and forth as needed; they also play a central role in growth, development and defence of all higher plants. In this study, Grison et al. describe the rapid relocation to the plasmodesmata pores of two plasma…
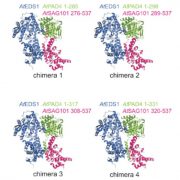
Reconstituting an NLR cell death branch (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArabidopsis genetics has identified numerous genes required for pathogen perception and defense response activation. Some of these genes are functionally conserved across plants and others are not. Toll-Interleukin1-Receptor (TIR)-domain NLRs (TNLs) are immune receptors that function upstream of EDS1…
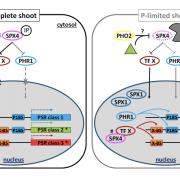
SPX4 acts on PHR1-dependent and -independent regulation of shoot phosphorus status (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant phosphorus homeostasis is important to understand as humans seek to increase food production while also reducing the amount of agricultural inputs and environmental pollution. In their recent paper, Osorio and colleagues expand our current understanding of phosphorus homeostasis in Arabidopsis…
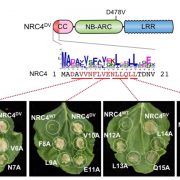
An N- terminal motif in NLR immune receptors is functionally conserved across distantly related plant species (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have robust NLR (nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat proteins) immune signaling networks consisting of sensor NLRs and helper NLRs that counteract diverse plant pathogens by inducing cell death at sites of pathogen infection. A recent preprint by Adachi et al. has defined an N terminal motif…

