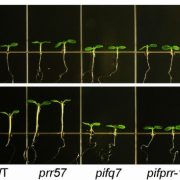
Central clock components modulate plant shade avoidance by directly repressing transcriptional activation activity of PIF proteins ($) (PNAS)
PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORs (PIFs) are transcriptional factors that relay light signals from the phytochrome photoreceptors to regulate the expression of light-sensitive genes, but there is not a direct correlation between PIF binding and expression of the target genes. In this paper, Zhang Y et…
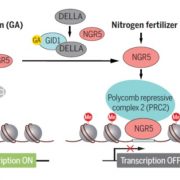
Enhanced sustainable green revolution yield via nitrogen-responsive chromatin modulation in rice ($) (Science)
The well-known success of the green-revolution was accomplished through the development of semi-dwarf grasses (rice and wheat), which led to decreased losses to lodging and higher yields; however, the benefits of these improved varieties depends on the application of nitrogen-rich fertilizer. As N-rich…
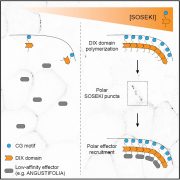
DIX domain polymerization drives assembly of plant cell polarity complexes (Cell)
In multicellular organisms like plants, asymmetric cell division can arise from cell polarity. The signals that establish cell polarity relative to the body axis are unknown in plants. In Arabidopsis, SOSEK1 was previously identified as having a polar distribution. SOSEK1 has a DIX domain similar to…
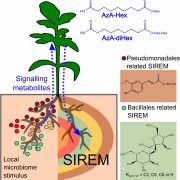
Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation ($) (PNAS)
Roots exude metabolites that affect the composition and activities of their microbiome. Korenblum et al. show that the microbiome in turn affects metabolite exudation, not only locally but also systemically (shown using a split-root system). They call this response SIREM: systemically induced root exudation…
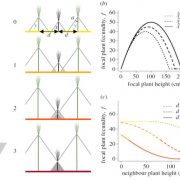
Farming plant cooperation in crops (Proc. R. Soc. B.)
If you want a great plant, select for a strong, vigorous, high-yielding individual; this is also the outcome of natural selection. But if you want a great field of plants, these traits may not be as suitable, because the plants will expend energy competing between themselves. When seeds from many plants…
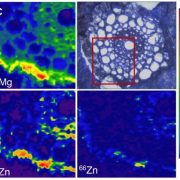
Plant Science Research Weekly: February 14
Review: Deep learning for plant genomics and crop improvement
One of the goals of plant science is to use the molecular phenotype (genome, transcriptome, proteome) to predict the whole-plant phenotype. Deep learning approaches can potentially begin to do this, starting with a training dataset, and…
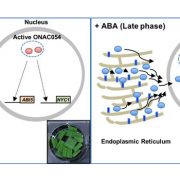
Multilayered Regulation in Senescence
Sakuraba et al. show the existence of multilayered regulation systems for the rice ONAC054 transcription factor, which is involved in abscisic acid-induced leaf senescence in rice. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00569
By Nam-Chon Paek, Department of Plant Science, Seoul National University,…
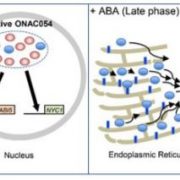
Make, Modify, Move: Multilayered Regulation of ONAC054 During ABA-Induced Leaf Senescence
‘Senescence’ originates from the Latin word senescere, to grow old. However, the process of leaf senescence is not simply the passive death of the leaf but instead represents an active and highly regulated process of nutrient remobilization from older leaves into developing parts of the plant to…
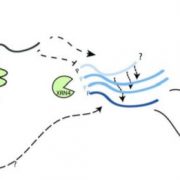
Rapid changes: ABA-independent SnRK2s target mRNA decay
Magda Julkowska
Magdalena.Julkowska@kaust.edu.sa
In response to stress, secondary messengers and rapid and reversible protein phosphorylation contribute to signaling cascades that generate unique signatures indicating stress type and severity. Activation of stress-induced signaling cascades…

