
Finding balance: How plants achieve signal specificity in stomatal development and defense
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to develop and grow within their environment whilst defending themselves against potential external threats. There are limited resources for these energy-intensive processes and so cross-talk is common between the signalling pathways to find balance between growth and defence. Hermann et…
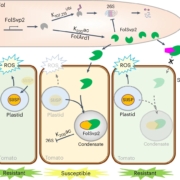
Tomato PR1 protein prevents the fungal effector FolSvp2 from suppressing SlISP-mediated ROS production
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and pathogens are locked in a co-evolutionary arms race. Pathogens secrete effectors into plants, leading to effector-triggered susceptibility. Plants in turn respond through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the expression of defence-related genes to defend themselves, which…
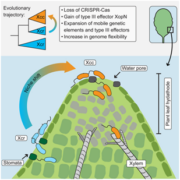
Shaping pathogenicity: How CRISPR-Cas loss fuels Xanthomonas evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens have evolved diverse infection strategies governed by virulence factors, often targeting specific host organs or tissues. Genome fluidity plays a crucial role in enabling microbial pathogens to adapt to the dynamic selection pressures imposed by co-evolution with their hosts. In a recent study,…
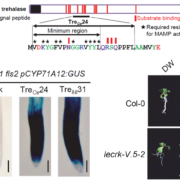
LecRK-V and trehalose-associated immunity: a conserved defense mechanism across kingdoms
Plant Science Research WeeklyMembrane-localized receptor-like kinases (RLKs) are essential for perceiving diverse signaling molecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, hormones, reactive oxygen species, ions, and damage-associated molecular patterns. Among the well-characterized RLKs, FLS2, EFR, and CERK1 are known to recognize…

Plant Science Research Weekly: February 21, 2025
WWR Full PostPerspective: How should the advancement of large language models affect the practice of science?
In this thought-provoking Perspective, four sets of authors express their opinions about the use of Large Language Models (such as ChatGPT) in the practice of science. Each essay is well reasoned, and…
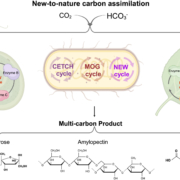
Review: Genetic engineering for carbon assimilation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (Ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the central enzyme for photosynthesis, This enzyme poorly discriminates between CO2 and O2, which limits its efficiency. To work around this and make carbon assimilation more efficient, scientists have been employing different engineering…
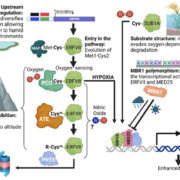
Review: Geography, altitude, agriculture, and hypoxia
Plant Science Research WeeklyHypoxia, or reduced oxygen availability, is a double-edged sword: while it disrupts metabolism and can cause cell death, it also plays a vital role in regulating development in animals and plants. With extreme flooding increasing due to climate change, understanding how genetic variation enhances hypoxia…
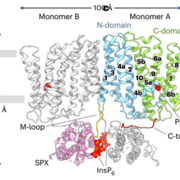
Structural insights into PHO1: A key regulator of phosphate translocation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient required for plant growth, development, and reproduction. It is primarily absorbed by plant roots in the form of orthophosphate (Pi). The root-to-shoot translocation of Pi depends on a crucial xylem-loading process mediated by PHOSPHATE 1 (PHO1), a Pi efflux…
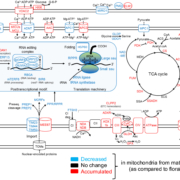
High-energy requiring pollen grains have specialized mitochondria
Plant Science Research WeeklyImagine you’re on a quest to deliver a package, racing against the competition. How do you prepare? Pollen grains and the pollen tubes that they form are essentially package-delivery systems. Their purpose is to deliver genetic information (sperm cell nuclei) to the ovule. Once the task is completed,…

