A Phytophthora effector targets nuclear transcriptional complexes in plant immunity
By Xufang Qiu, Liang Kong and Yuanchao Wang
Background: To prevent infection, plants have evolved two layers of immunity, pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI). Activation of PTI and/or ETI triggers a series of plant immune responses, including massive transcriptional reprogramming of immune genes regulated by nuclear transcriptional complexes. Among them, BRI1-associated receptor kinase 1-3 (BAK1-3) and Pathogenesis-related protein 1 (PR1), which encode two key immune regulators in salicylic acid (SA) pathway and PTI, undergo transcriptional regulation. Pathogens deploy numerous effectors to suppress plant immunity and the Phytophthora effectors directly involved in regulating the function of this nuclear transcriptional complex remain elusive.
Question: We hoped to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of plant immune gene transcription by this nuclear transcriptional complex, and to investigate how Phytophthora effectors manipulate the expression of plant immune genes.
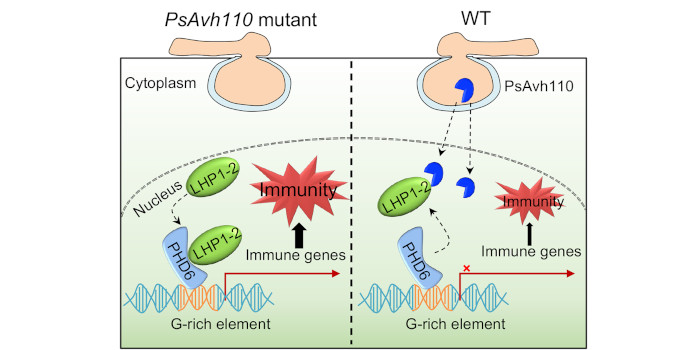
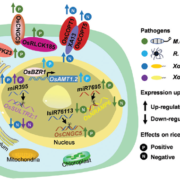
Findings: PsAvh110, a nuclear-localized effector from Phytophthora sojae, suppresses soybean (Glycine max) immunity to promote pathogen infection. By transcriptome analysis, we found that PsAvh110 suppressed a subset of soybean immune-related genes. PsAvh110 disrupts the assembly of a nuclear transcriptional complex containing Like-heterochromatin protein 1-2 (GmLHP1-2) and plant homeodomain finger protein 6 (GmPHD6) via binding to GmLHP1-2, thus inhibiting the complex’s transcriptional activity. Interestingly, GmLHP1-2/GmPHD6 binds to G-rich elements in the promoters of PsAvh110-suppressing immune genes, including GmBAK1-3 and GmPR1, to activate their expression. To counteract soybean immunity, P. sojae utilizes the effector PsAvh110 to compete with GmPHD6 for binding to GmLHP1-2, thereby interfering with the formation of GmLHP1-2/GmPHD6 complex. Therefore, we revealed that the nuclear complex plays a crucial role in regulating gene activation through binding to the G-rich elements, which could be targeted by Phytophthora effector for suppressing plant immunity.
Next steps: Since G-rich elements play important roles in regulating immune gene expression, our future work will investigate whether we can engineer durable disease-resistant crops by editing these elements in the promoters of immune genes using gene-editing technology.
Reference:
Xufang Qiu, Liang Kong, Han Chen, Yachun Lin, Siqun Tu, Lei Wang, Zhiyuan Chen, Mengzhu Zeng, Junhua Xiao, Peiguo Yuan, Min Qiu, Yan Wang, Wenwu Ye, Kaixuan Duan, Suomeng Dong, Yuanchao Wang (2022) The Phytophthora sojae nuclear effector PsAvh110 targets a host transcriptional complex to modulate plant immunity. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac300