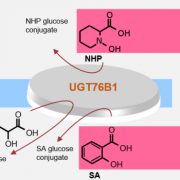
Interactive glucose attachment to multiple signaling molecules as an immune-suppressive platform to contain plant pathogen defense
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBauer et al. characterize UGT76B1 as a metabolic suppressor of the Arabidopsis immune response. The Plant Cell (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koaa044
By Dereje W. Mekonnen1, Jürgen Zeier2, Anton R. Schäffner1
1Institute of Biochemical Plant Pathology, Department of Environmental Sciences,…
Review: Plant evolution driven by interactions with symbiotic and pathogenic microbes (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the great questions in plant science has been, “How do plants recognize friend from foe?” Like most great questions, this one benefits from a historical perspective. In their new review, Delaux and Schornack look at plant evolution through the lens of plant interactions with symbiotic and…
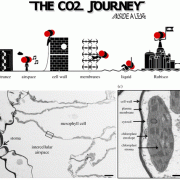
CO2 diffusion in tobacco: a link between mesophyll conductance and leaf anatomy (Interface Focus)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThree key factors affect a plant’s ability to fix carbon: enzymatic activity of Rubisco, stomatal conductance, and the journey from sub-stomatal cavity to Rubisco, also known as mesophyll conductance (gm). This latter is the focus of this new work by Clarke et al. They delightfully compare this journey…
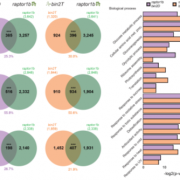
Multi-omics analysis reveals interplay between BR and TORC signaling (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have evolved well-coordinated crosstalk between different signaling pathways to respond and adapt to various environmental stresses. Brassinosteriods (BRs) and Target of Rapamycin Complex (TORC) have multiple roles, through transcription, translation and autophagy, to control the balance between…
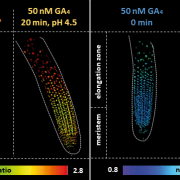
Differential biosynthesis and cellular permeability explain longitudinal gibberellin gradients in growing roots (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGibberellin (GA) controls multiple developmental processes throughout the plant life cycle, from seed germination to flowering. In Arabidopsis, GA also regulates division of meristematic cells at the tip of the root and cell elongation in the growing zone. Despite its importance, little is known about…
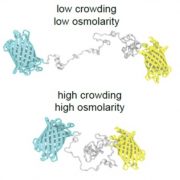
Measuring the physical-chemical effects of osmotic stress in living cells (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe osmotic state of a cell is affected by internal (metabolite content) and external (water availability) factors. Recent work by Cuevas-Velazquez and colleagues describes the design of a FRET-based biosensor that allows dynamic monitoring of osmotic stress in living cells. They exploited features of…
Evolution and ecology of seed internal morphology in relation to germination characteristics in Amaranthaceae ($) (Ann. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed germination, a critical life stage in a plant's life cycle, can be affected by internal seed morphology. In this exciting research, Vandelook and colleagues investigated the evolution of embryo and nutritive tissue characteristics and their relationship with the germination traits of 84 species…

Plant Science Research Weekly: Feb 26, 2021
Blog, WWR Full PostReview: Plant evolution driven by interactions with symbiotic and pathogenic microbes
One of the great questions in plant science has been, “How do plants recognize friend from foe?” Like most great questions, this one benefits from a historical perspective. In their new review, Delaux and Schornack…

Recognizing Plant Physiology author Masaru Nakayasu
Plant Physiology: Author Profiles
Masaru Nakayasu, first author of Tomato roots secrete tomatine to modulate the bacterial assemblage of the rhizosphere
Current Position: Specially appointed assistant professor, Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Japan
Education: BA, MS, and Ph.D., Kobe University,…

