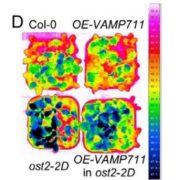
A SNARE Protein that Regulates Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase activity
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays an important role in plant drought responses. Previous studies have indicated that ABA inhibits plasma membrane H+-ATPase (PM H+-ATPase) activity, and the resultant decrease in PM H+-ATPase activity promotes stomatal closure under drought stress, thereby reducing…

Chloroplast Accumulation Enhances Photosynthesis and Biomass Production
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideLight-induced chloroplast movement is one of the most important responses for utilization of photosynthetic light. Chloroplasts move toward weak light-irradiated areas to efficiently absorb light (the accumulation response), whereas they move away from excess light to avoid photodamage (the avoidance…

A Tapetal Boric Acid Channel Involved in Pollen Cell Wall Formation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideBoron (B) is an essential plant micronutrient that plays a major role in cell wall structure and function by providing cross-linking of the rhamnogalacturonan II (RG-II) pectin component of the cell wall. Under normal pH conditions, B is found principally as boric acid. Although boric acid permeates…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Maurizio Camagna
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesMaurizio Camagna, first author of Enzyme fusion removes competition for geranylgeranyl diphosphate in carotenogenesis
Current Position: PhD Student at Nagoya University
Non-scientific Interests: Traveling, gardening, programming, learning languages, drinking and brewing beer, magnets
Brief Bio:…

Sweet and Juicy: Identification and Origins of the Dry Alleles in Sorghum
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSorghum (Sorghum bicolor) is the fifth most important cereal crop globally and is considered to be the “camel among crops” due to its ability to flourish in low-nutrient soils and to withstand prolonged drought. Cultivated varieties are phenotypically and morphological diverse. Consequently, sorghum…

Digital imaging combined with genome-wide association mapping links loci to plant-pathogen interaction traits (Plant Phys.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResistance to plant pathogens is often studied as a qualitative trait than quantitative, focusing on the lesion size and pathogen numbers. However, resistance to generalist plant pathogens, such as Botrytis cinerea, is known to involve multiple genes. Fordyce et al. used high-throughput phenotyping…
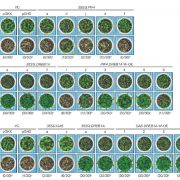
The xerobranching response represses lateral root formation when roots are not in contact with water (Curr. Biol. - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots navigate through the soil, foraging for water and nutrients. Orman-Ligeza et al. observed that lateral root development is repressed when the roots are growing through the soil air spaces. Exposure to water deficit induced transcriptome reprogramming in barley roots of genes involved in many hormone…
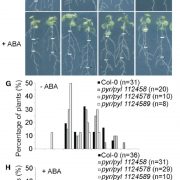
A gene‐stacking approach to overcome the trade‐off between drought stress tolerance and growth in Arabidopsis (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the face of increasing incidence of drought events, developing drought-tolerant plants becomes urgent matter. However, the increase in drought tolerance often coincides with the significant reduction of plant size, as in the case of overexpressing DEHYDRATION-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT-BINDING PROTEIN 1A…

A plant chitinase controls cortical infection thread progression and nitrogen-fixing symbiosis (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen-fixing bacteria produce species-specific chitin-like molecules, Nod factors, which induce nodule development and infection thread formation in the host plant, aiding microbial infection. Malolepszy et al. performed a detailed study of symbiotic defective mutants in lotus (chit5), where the nodule…

