
Transposon-derived small RNAs triggered by miR845 mediate genome dosage response in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNat. Genet. Silencing of transposable elements (TEs) is mediated epigenetically by DNA methylation, relying partially on RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM). RdDM-induced DNA methylation undergoes a global reprogramming in the male germline, allowing expression of imprinted genes regulating fertility…
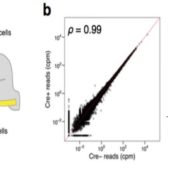
SLAM-ITseq: Sequencing cell type-specific transcriptomes without cell sorting
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogBioRxiv. Transcriptomic changes at the cellular level are of key importance in specialized cellular types. Therefore, transcriptome analysis at a cell-specific resolution is a powerful tool to learn about biological processes. This analysis is however limited by technological boundaries of microdissection…
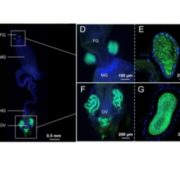
Drastic genome reduction in an herbivore’s pectinolytic symbiont
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCell. In a very interesting report, Salem et al., showed evidence of an alternative mechanism supporting how the degradation of pectin, a very hard to metabolize component of the cell wall, has directed the evolution of herbivory in insects and arthropods. Recent reports have indicated that horizontally…
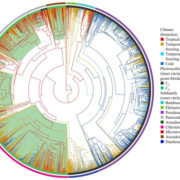
C4 photosynthesis evolved in warm climates but promoted migration to cooler ones
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogEcol. Lett. C4 photosynthesis represents a biochemical CO2-concentrating mechanism that increases Rubisco-mediated carboxylation of RuBP and reduces photorespiration. However, there is an energy cost associated with C4 photosynthesis, and so it is presumed to become advantageous over C3 photosynthesis…
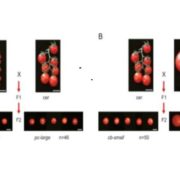
Rewiring of the fruit metabolome in tomato breeding
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCell. The tomato plant has been of keen interest to mankind for centuries, and its domestication led to delicious fruits much larger than their wild, bitter-tasting ancestors. Domestication of tomato had many intended outcomes (increased fruit size, less bitter taste), and several unintended consequences.…
Hidden shift of the ionome of plants exposed to elevated CO2 depletes minerals at the base of human nutrition
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogeLife. Free air CO2 enrichment (FACE) has been used to surround plants with an elevated concentration of CO2 (eCO2) during growth, and has consistently conferred an increase in carbon assimilation and plant productivity. However, the effect of eCO2 on nutrient status of the plant is unclear due to…
The G protein β subunit, AGB1, interacts with FERONIA in RALF1-regulated stomatal movement
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant Physiol. Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins participate in numerous processes including the regulation of hormonal responses and environmental stress. G proteins are composed of three subunits: Gα, Gβ, and Gγ. AGB1, a Gβ protein, forms a non-covalent dimer with a Gγ subunit,…

An extracellular network of Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNature. Through the activity of hundreds of membrane receptors, plants can sense the extracellular environment and tune their growth and responses to abiotic and biotic stimuli in an elegant and complex way. Despite their pivotal role, only a dozen of receptors have been characterized in plants and very…

Regulation of lateral root development via the HY5 Transcription Factor
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant Cell. Plants sense competitors through phytochromes. Phytochromes detect the reflection of far-red light from nearby plants, resulting in a reduced red:far-red (R:FR) ratio. The reduced ratio causes shade avoidance responses which modify shoot and root system architecture. This paper by van Gelderen…

