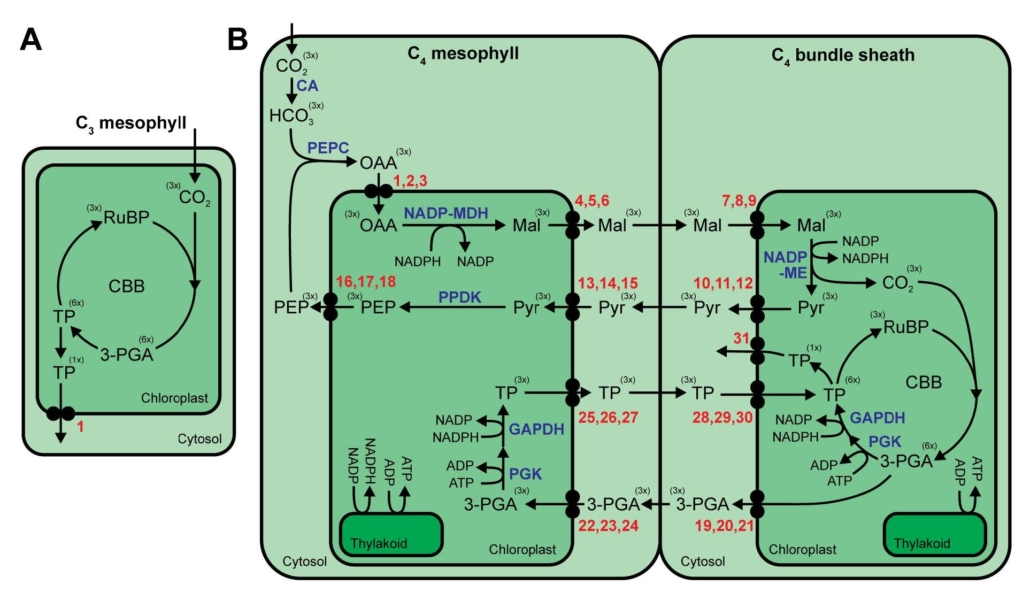
Review: The complexities of metabolite transport in C4 photosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 photosynthesis, an adaptive mechanism to spatially concentrate CO2 around Rubisco to enhance carbon fixation, has evolved independently at least 60 times in plants. This process spatially separates the initial carbon fixation by PEPC and carbon reduction by Rubisco, which requires that compounds move…
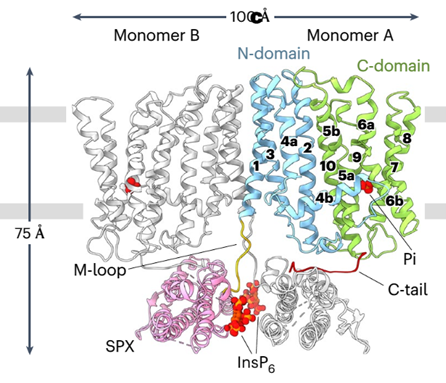
Structural insights into PHO1: A key regulator of phosphate translocation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient required for plant growth, development, and reproduction. It is primarily absorbed by plant roots in the form of orthophosphate (Pi). The root-to-shoot translocation of Pi depends on a crucial xylem-loading process mediated by PHOSPHATE 1 (PHO1), a Pi efflux…
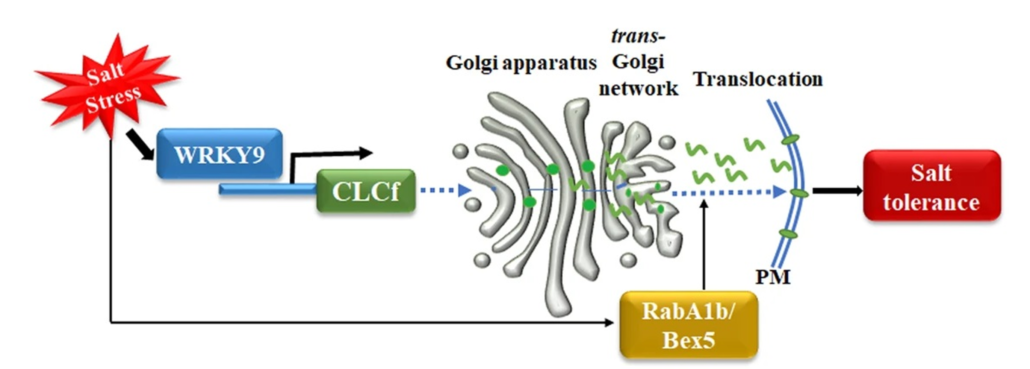
Translocation of a chloride channel from the Golgi to the plasma membrane helps plants adapt to salt stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants adapt to salt stress by maintaining ion balance using ion transporters. While much is known about cation transporters, the role of anion transporters is less clear. Rajappa et al. focus on the chloride channel gene AtCLCf in Arabidopsis thaliana, controlled by the transcription factor WRKY9 under…
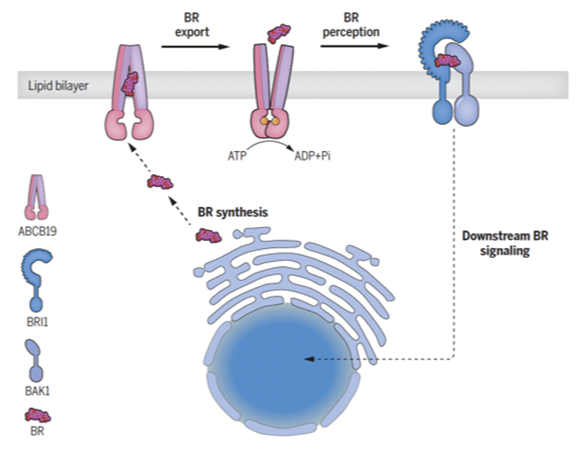
How do plants export brassinosteroids?
Plant Science Research WeeklyIf you’ve ever wondered how plants grow, survive, and adapt to their dynamic environment, the secret lies in their vast array of chemical messengers, also called phytohormones. Brassinosteroids are important hormones that are crucial for plant development and defense against environmental stresses.…
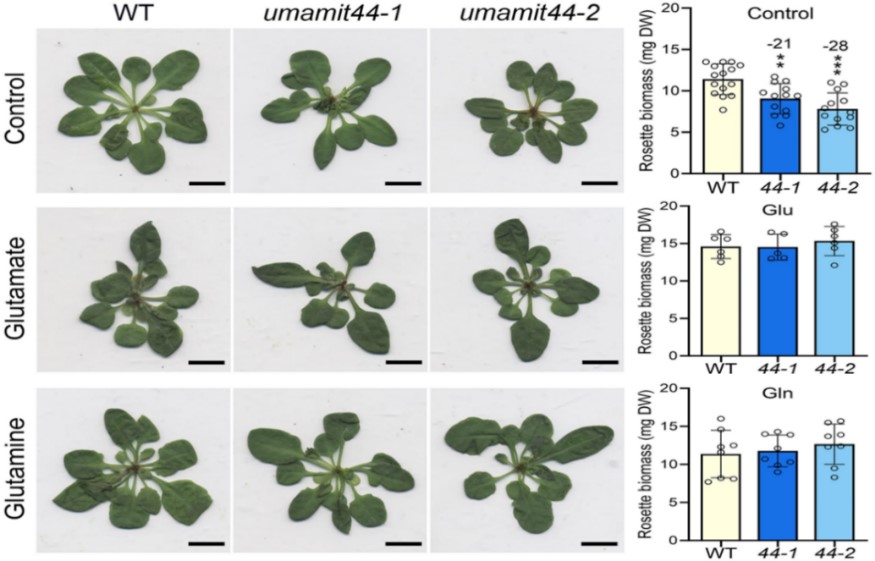

UMAMIT44 exports plastidial glutamate and is essential for plant growth
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmino acids (AA) are fundamental components of peptides, proteins, and enzymes that play a critical role in plant growth, cellular metabolism, and stress response. Plants synthesize most AA within chloroplasts and require membrane transporters to transfer them from stroma to cytosol. Cytosolic AA are…

Increading Fe and Zn concentrations in wheat flour
Plant Science Research WeeklyHuman malnutrition results from the lack of essential mineral micronutrients. In particular, iron deficiency might cause anaemia and stunted development in children, while zinc deficiency might reduce immunity to infectious diseases. In bread wheat, iron and zinc are located in the embryo and aleurone.…
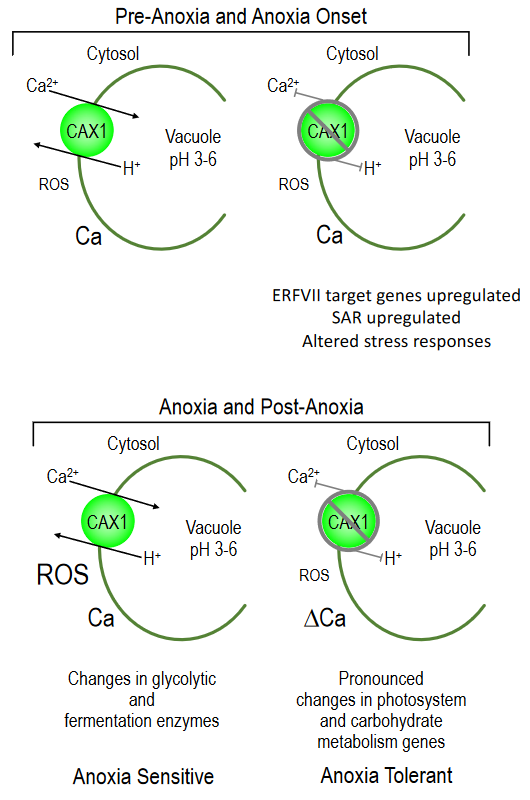
The vacuolar H+/Ca transporter CAX1 participates in submergence and anoxia stress responses (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium (Ca) signaling is one of the primary plant responses to confront abiotic stresses. To coordinate Ca levels in the different compartments of the cell, several transporters are needed including the H+/Ca exchangers (CAXs) in the tonoplast (vacuolar membrane). While the role of calcium signaling…
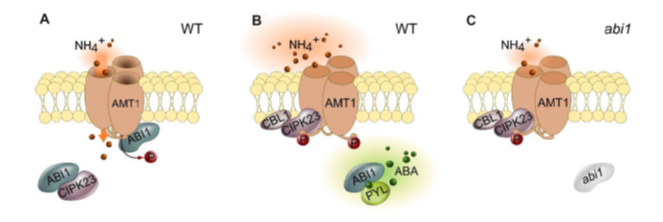
ABA-INSENSITIVE1 activates ammonium transporter AMT1 in an ABA dependent manner (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo avoid ammonium toxicity, the ammonium transporters (AMTs) are tightly regulated by phosphorylation-dependent inactivation. The multifunctional kinase CIPK23 inactivates the AMT1s by phosphorylating conserved threonine residues (T460 in AMT1;1 and T472 in AMT1;2). ABA-INSENSITIVE1 (ABI1) and ABI2…
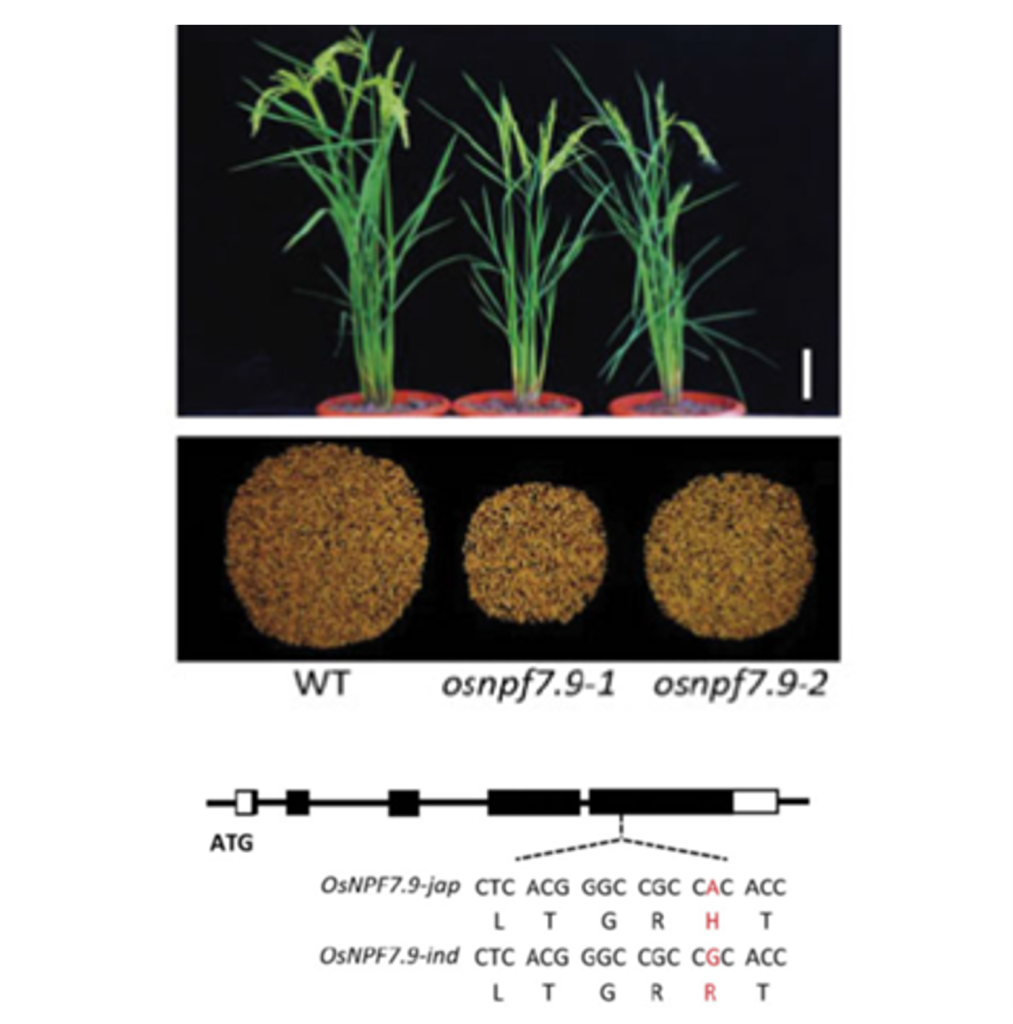
Nitrate transporter NPF7.9 is a regulator nitrogen use efficiency and stress-induced nitrate allocation to roots in rice (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn addition to its role as a nutrient and a developmental signal, nitrate regulates stress responses in plants. By homology to nitrate transporters previously identified in Arabidopsis as contributing to stress induced-nitrate allocation to roots (SINAR) and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), Guan et al.…

