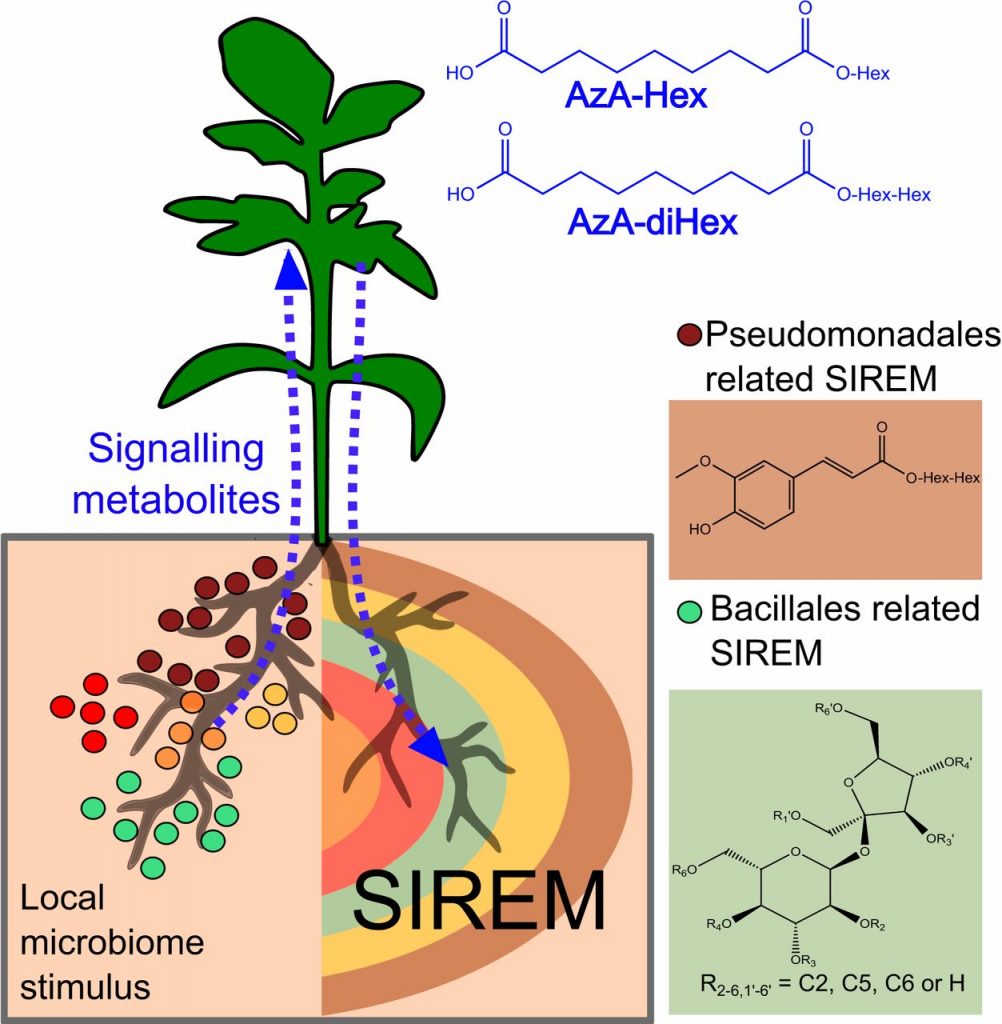
Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots exude metabolites that affect the composition and activities of their microbiome. Korenblum et al. show that the microbiome in turn affects metabolite exudation, not only locally but also systemically (shown using a split-root system). They call this response SIREM: systemically induced root exudation…
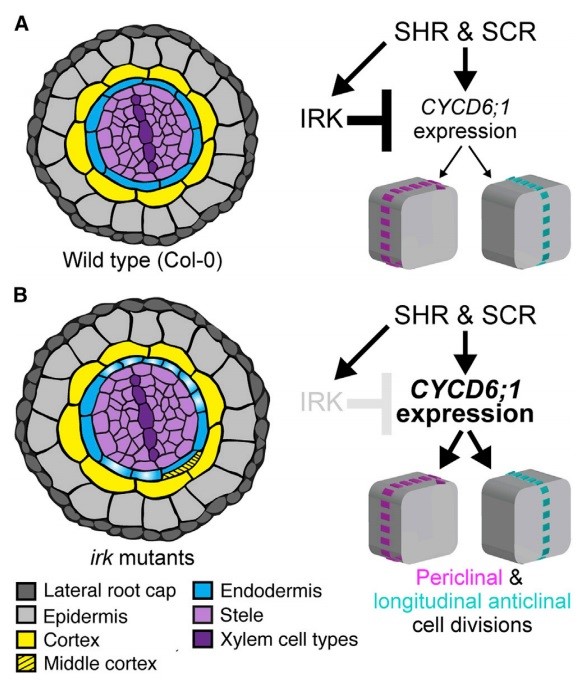
The Arabidopsis receptor kinase IRK is polarized and represses specific cell division (Devel. Cell) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrientation of cell division decides daughter cell fate and is fundamentally important for tissue patterning and morphology. For instance, asymmetric cell division leads to the generation of new cell types; in contrast, symmetric division produces cells with similar identity in a proliferative manner.…
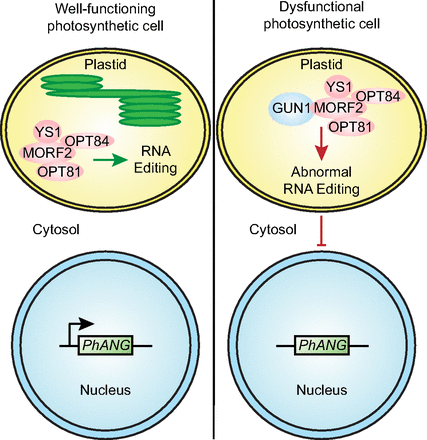
Research update: GUN1 hit the mark in 2019
Plant Science Research Weekly
Chloroplasts are able to sense and respond to environmental signals. They send retrograde signals that inform the nucleus about their developmental stage and integrity. In response, the nucleus adjusts gene expression to optimize chloroplast recovery and adaptation. Back in 1993, a screen for genotypes…

Review: The role of peptides cleaved from protein precursors in eliciting plant stress reactions (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough the first signaling peptide identified in plants, systemin, is involved in stress responses, developmentally important peptide signals have largely occupied the limelight. This Tansley Review by Chen et al. summarizes recent insights into peptides with a role in stress responses: wounding, pathogen…

Arabidopsis PP6 phosphatases dephosphorylate PIF proteins to repress photomorphogenesis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the absence of light, plants undergo skotomorphogenesis, characterized by longer hypocotyls, closed and yellowish cotyledons, and apical hooks. in the presence of light, they undergo photomorphogenesis, with inhibited hypocotyl elongation, and open and expanded green cotyledons. Light also modulates…
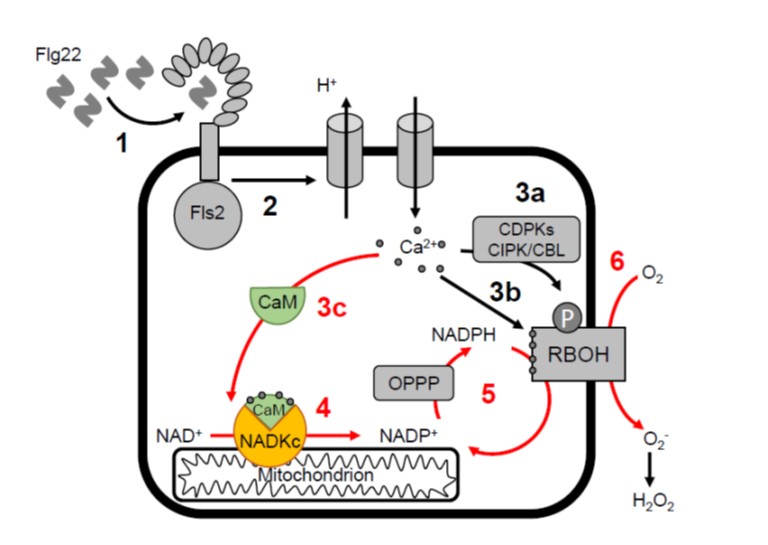
Identification of calmodulin-dependent NAD+ kinase that sustains the elicitor-induced oxidative burst (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen pathogens attack, one line of defense is the production of a burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which triggers additional defences. ROS is produced by the action of NADPH oxidases, which require NADPH as a substrate; NADPH is derived from NADP+, but where does this come from? Previous studies…
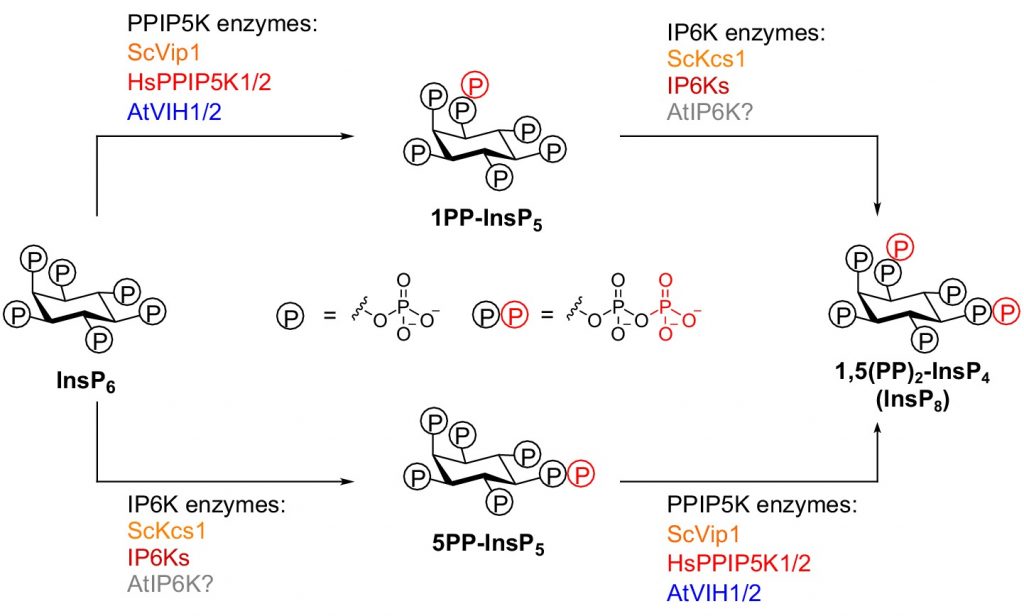
Two bifunctional inositol pyrophosphate kinases/phosphatases control plant phosphate homeostasis (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient for plant growth and development. P is predominantly absorbed by plants in its inorganic form, phosphate (Pi). Because Pi homeostasis is critical for balanced growth and development, plants like many other eukaryotic organisms have developed a complex system…
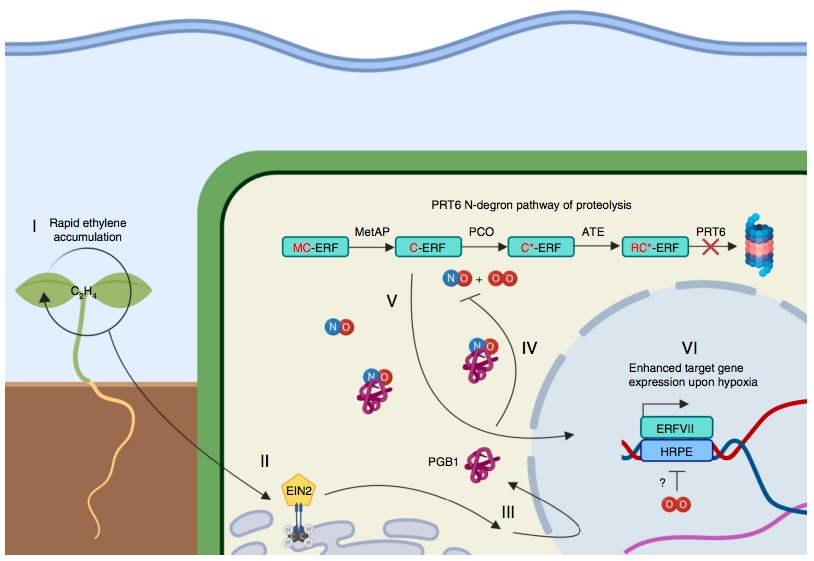
Ethylene-mediated nitric oxide depletion pre-adapts plants to hypoxia stress (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate projection models predict an increasingly wetter world with frequent and severe flooding events, causing loss of crops. As it is for other organisms, it is a challenge for plants to stay under water for long periods. However, how plants react to submergence is poorly understood. Environmental…

COP1 can be hijacked by photoreceptors via their VP motifs (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant development is characterized by a high degree of plasticity in response to light. Light‐activated plant photoreceptors bind and inhibit the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1, thus protecting downstream transcription factors from degradation. However, the detailed mechanisms of how COP1 can function between…

