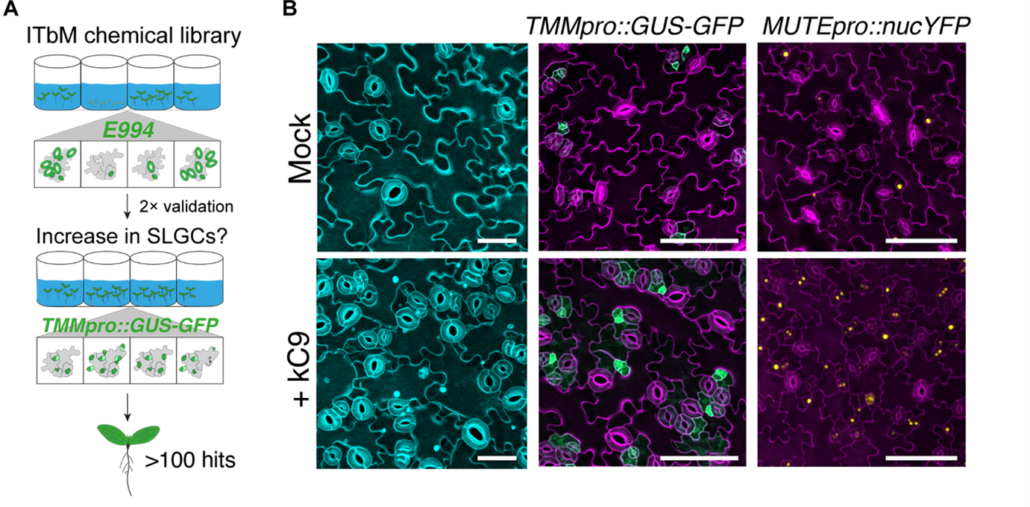
Finding balance: How plants achieve signal specificity in stomatal development and defense
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to develop and grow within their environment whilst defending themselves against potential external threats. There are limited resources for these energy-intensive processes and so cross-talk is common between the signalling pathways to find balance between growth and defence. Hermann et…
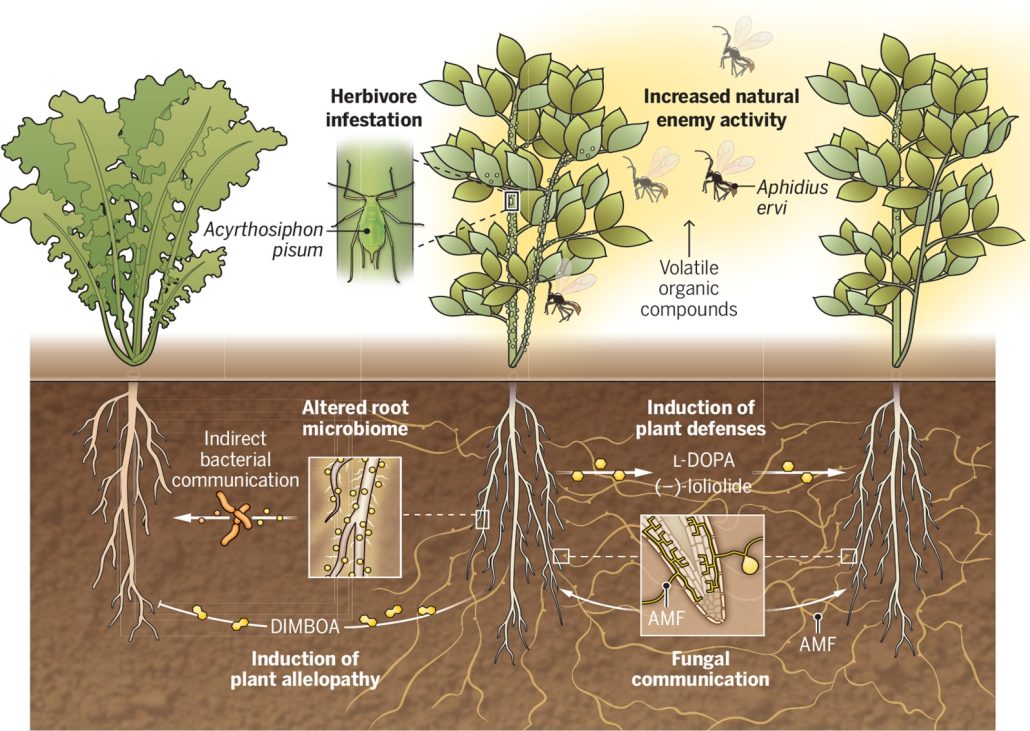
Perspective: Exposing belowground plant communication
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess a fascinating ability to communicate with each other through a complex system of chemical signals. Aboveground, they use airborne volatile signals to attract predatory insects, prime defenses in neighbors, facilitate nutrient transfer, and promote plant interactions. However, less is known…
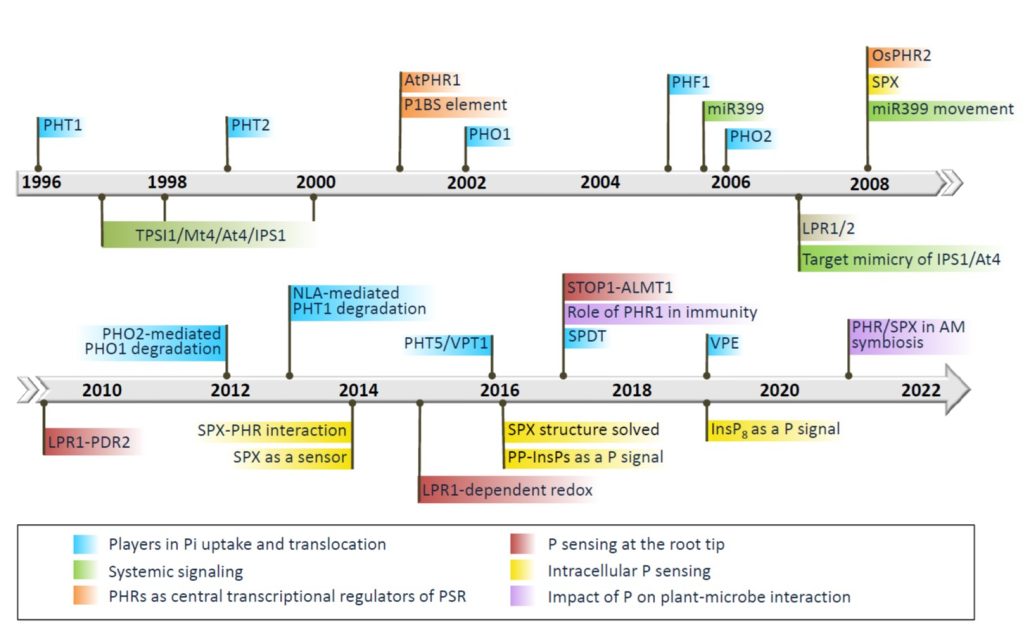
Review. Milestones in understanding phosphorus uptake, transport, sensing, use, and signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient and critical component of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and other molecules. Yang et al. provide a historical (since 1996) overview of the processes controlling its uptake and use. Plants take up P from the rhizosphere primarily in the form of orthophosphate (Pi).…
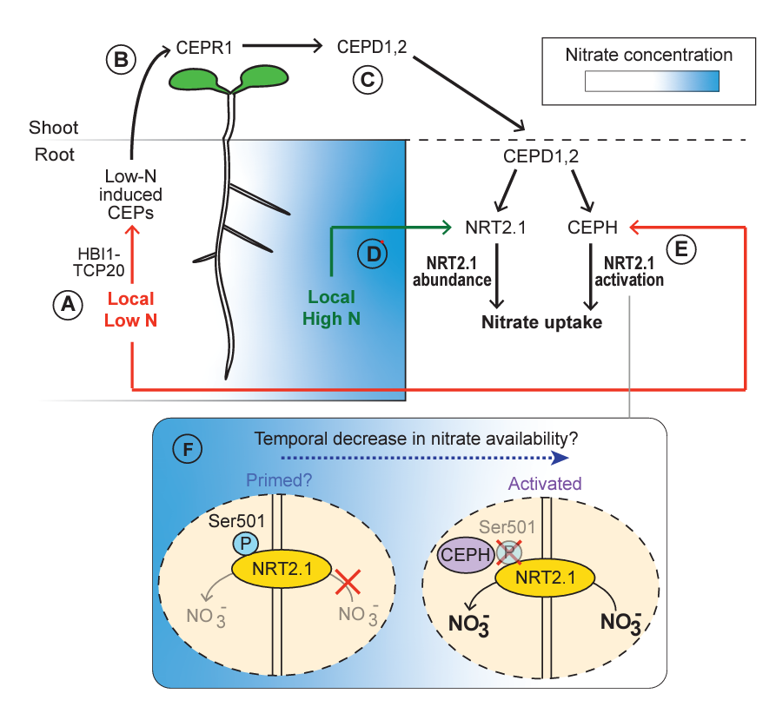
Review: CEP hormones at the nexus of nutrient acquisition and allocation, root development, and plant–microbe interactions
Plant Science Research WeeklyC-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) is a multigene family of peptide hormones originally described as systemic long-distance signals in response to nitrogen limitation. Over the years since the discovery of these peptide hormones, the literature on CEP biology has expanded the repertoire of developmental…
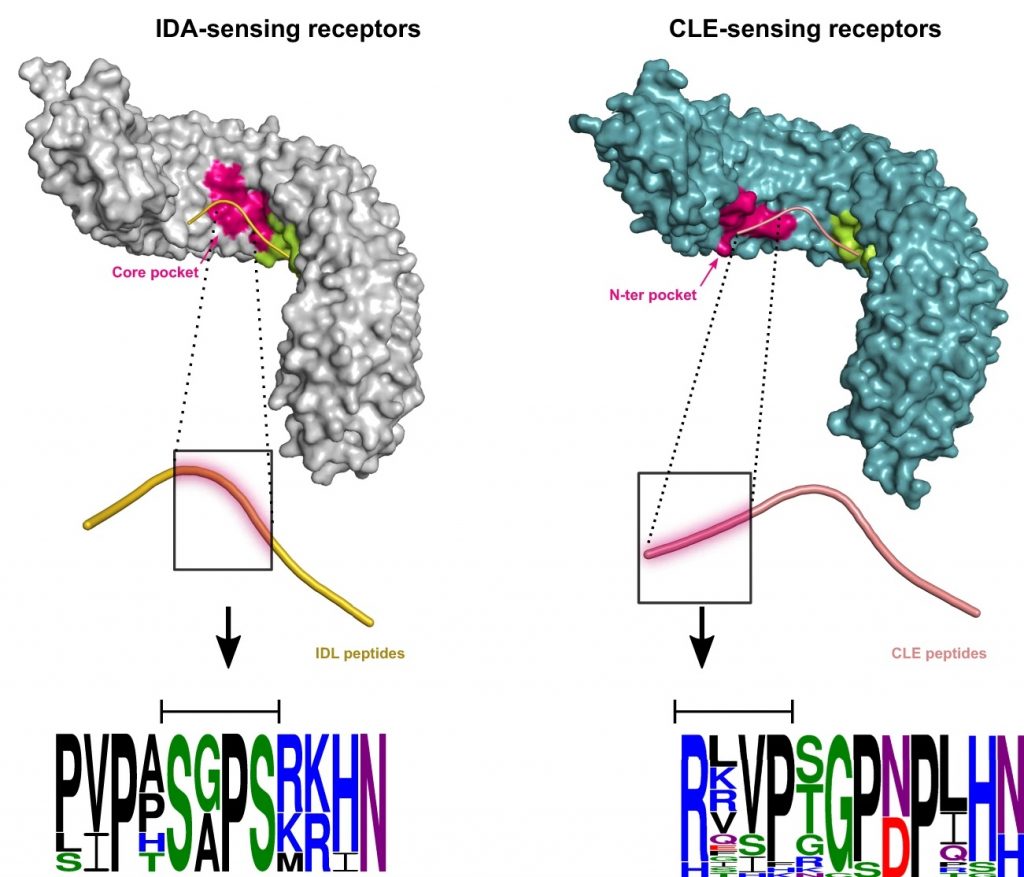
HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCell-to-cell communication is crucial for coordinating plant immunity, development, and environmental adaptations. The main players in sensing signaling molecules are membrane receptor kinases such as Leucine Rich Repeat Receptor Kinases (LRR-RKs). In some cases these receptors detect peptide signals.…

GABA signalling modulates stomatal opening to enhance plant water use efficiency and drought resilience (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a non-protein amino acid produced by animals and plants, but is its function conserved across kingdoms? In mammals, GABA acts as chemical messenger in the central nervous system by inhibiting neurotransmission. In plants, GABA accumulates in response to stress but its…
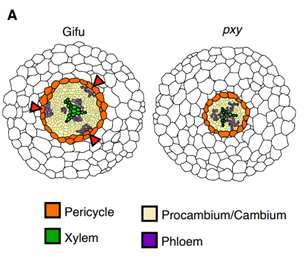
Natural variation identifies a Pxy gene controlling vascular organization and formation of nodules and lateral roots in Lotus japonicus (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiosis between legumes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria such as Mesorhizobium loti requires an exchange of signals. Plants recognize both specific nod factors (lipochitooligosaccharides) as well as cell-surface exopolysaccharides through distinct pathways. The M. loti exoU mutant fails to properly form…
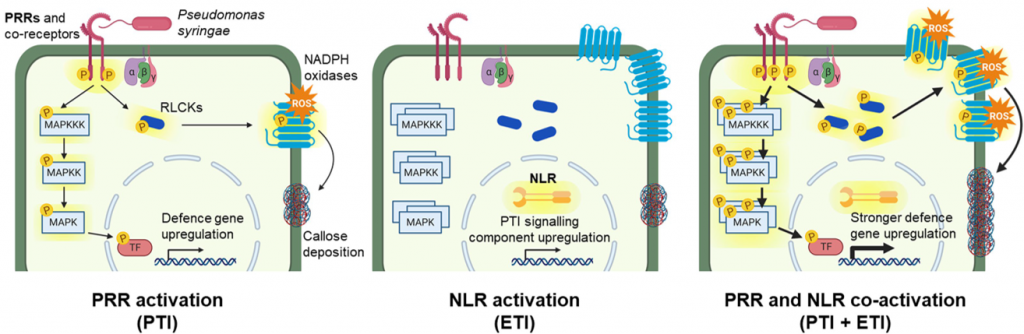
Not PTI or ETI: PTI and ETI (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTwo very exciting papers have come out this week in Nature that address a long-standing question about the relative contributions of two different plant immunity pathways. PTI (pathogen-triggered immunity) recognizes conserved pathogen signatures at the plant cell surface; a model system for PTI is the…

Redox regulation of NADP-malate dehydrogenase is vital under fluctuating light environment (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRedox switches regulate photosynthetic reactions and are mediated by conserved cysteine pairs, activated by reduction under light and deactivated by oxidation in the dark. Those reactions are mediated by thioredoxins (Trx). Usually, only plastidic and not cytosolic isozymes show these redox switches.…

