
Redox regulation of NADP-malate dehydrogenase is vital under fluctuating light environment (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRedox switches regulate photosynthetic reactions and are mediated by conserved cysteine pairs, activated by reduction under light and deactivated by oxidation in the dark. Those reactions are mediated by thioredoxins (Trx). Usually, only plastidic and not cytosolic isozymes show these redox switches.…
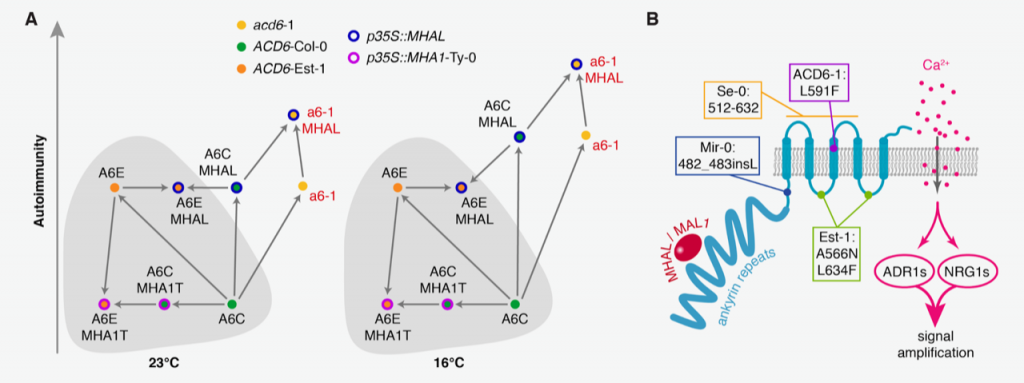
Regulation of ACD6 ion channel-like protein by small peptides (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyACCELERATED CELL DEATH 6 (ACD6) positively regulates the signaling of the plant defense hormone salicylic acid (SA). It was originally identified by the study of natural variation in defense responses of Arabidopsis thaliana. The naturally hyperactive ACD6-Est-I allele confers broad-spectrum disease…
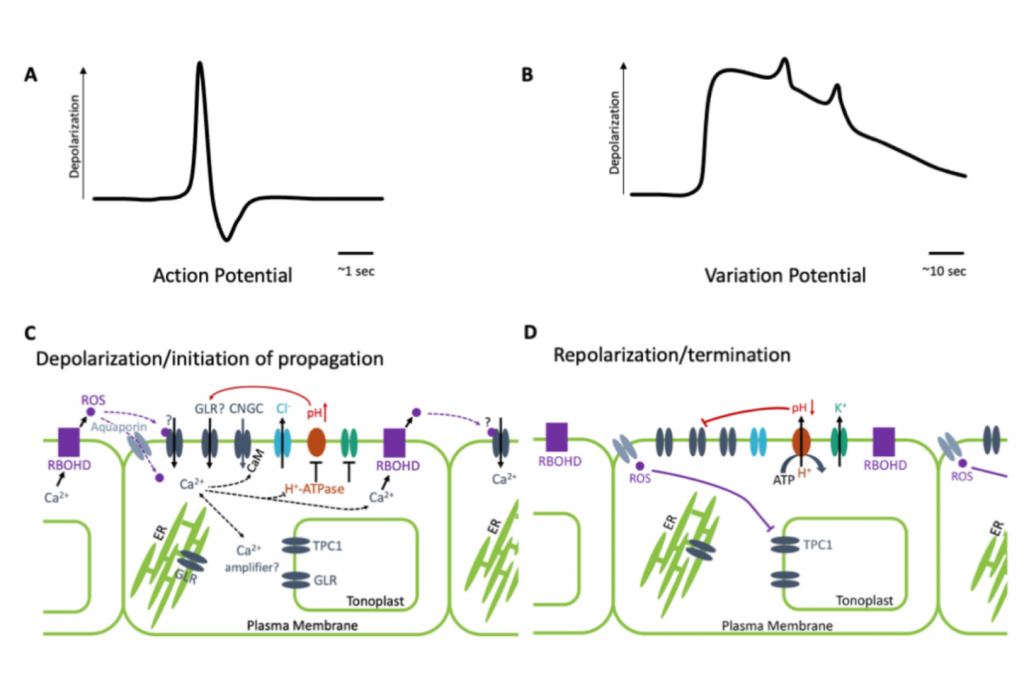
Review. The Fast and The Furious: Rapid long-range signaling in plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess a complex series of local and systemic signaling networks driven by multiple stimuli. They translate this information into plant-wide response to coordinate their physiology and development. Here, Johns et al. review these communication pathways, which function across different scales…

Microbiota-root-shoot axis modulation by MYC2 favors Arabidopsis growth over defense under suboptimal light (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicrobiota-root-shoot axis modulation by MYC2 favors Arabidopsis growth over defense under suboptimal light
Below- and aboveground plant organs experience distinct biotic and abiotic environments. Thus, coordination between root and shoot responses are likely crucial for plant survival. Given that…

CAMEL in the canal: Regulation of PIN proteins during canalization (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin transport during development or wound regeneration is known to require auxin-induced channel or ‘canal’ formation that includes polar localization of PIN auxin transport proteins. Hajný and colleagues have characterized a receptor-like kinase (RLK) complex involved in auxin-induced pattern…
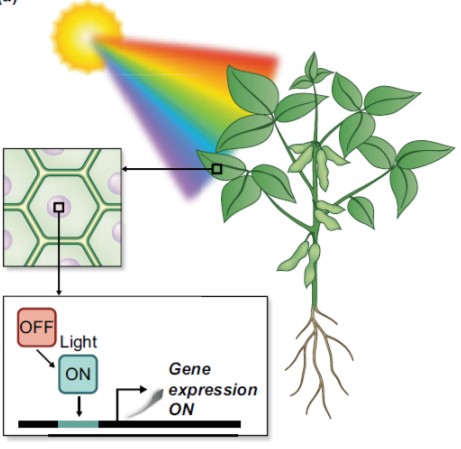
Review: Optogenetics in plants (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Optogenetics is the process by which light can modify cellular behavior, through the action of light-sensitive proteins or other molecules. In many respects, optogenetics seems more like science fiction than reality; the realization that neural activity in the brain can be altered through pulses…

Phosphorylation-dependent sub-functionalization of the calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium-dependent protein kinases (CPKs) form an important class of sensor-responder proteins that bind Ca2+ to ‘sense’ intracellular Ca2+ levels, and ‘respond’ by phosphorylating target proteins. CPK28 has distinct roles in growth and defense. To analyze the importance of Ca2+ in fine-tuning…
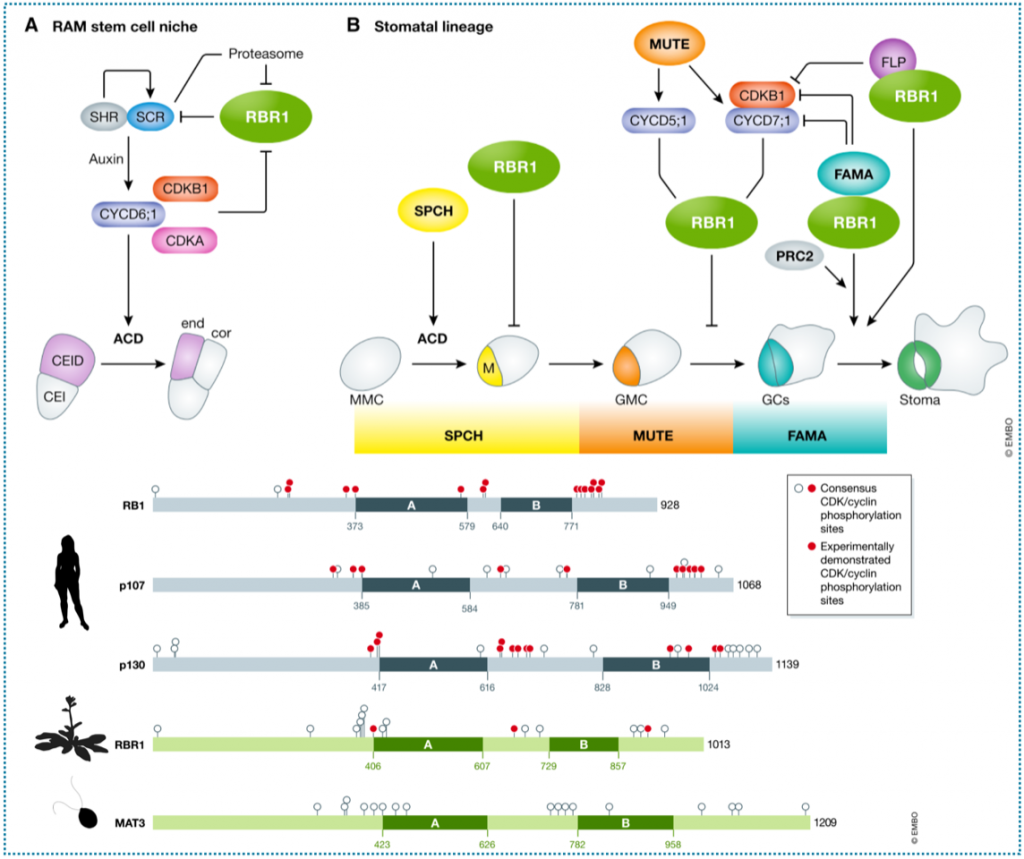
Review. Roles of plant retinoblastoma protein: cell cycle and beyond (EMBO J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cell cycle is at the heart of processes such as cell division, fate acquisition and cell cycle exit towards differentiation. Decades of cell cycle research in animals and yeast have outlined the main components that control the cycle’s transitions, such as cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, E2F…
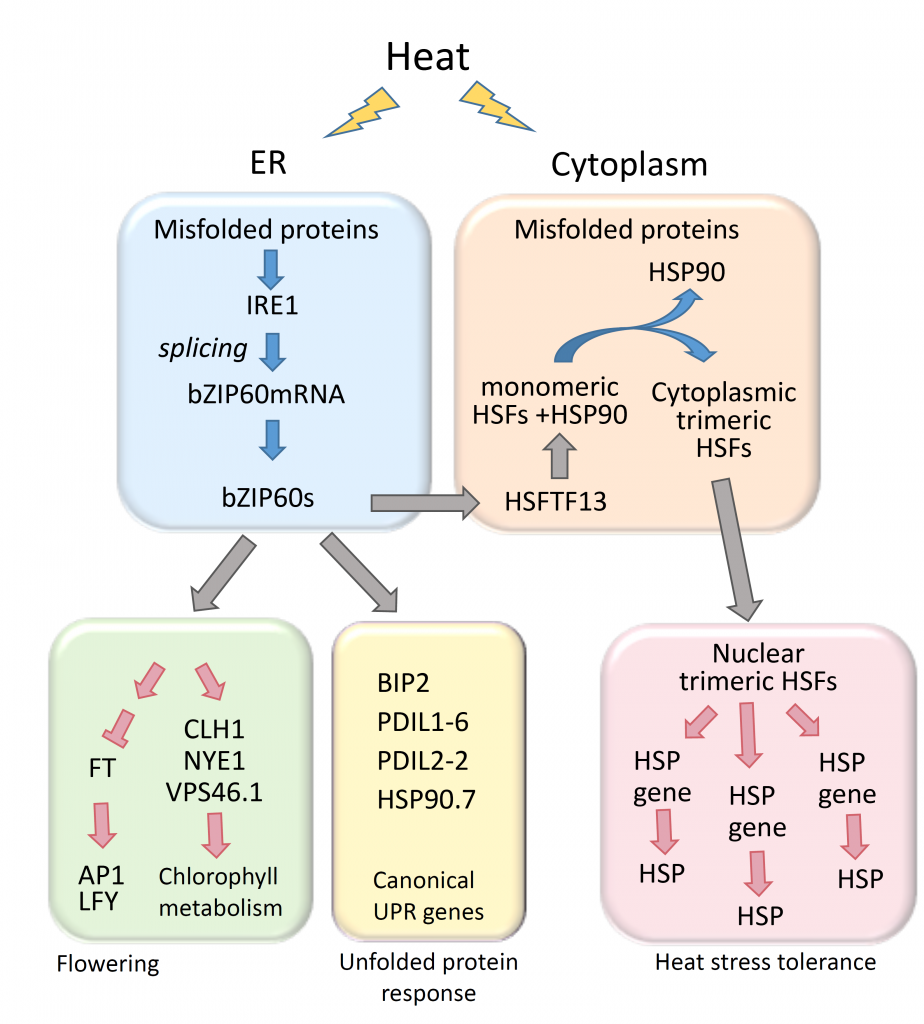
The transcription factor bZIP60 modulates the heat shock response in maize (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring heat stress, heat shock transcription factors upregulate heat shock protein genes and give rise to the heat shock response (HSR) that occurs in the cytoplasm, while in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the unfolded protein response (UPR) is also activated during heat stress. Both HSR and UPR cause…

