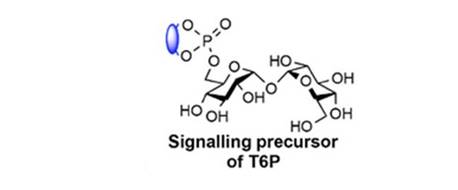
Plant-permeable trehalose 6-phosphate analogues increase yield and resilience ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) is a sugar signaling molecule that regulates how plants allocate and use sucrose, which in turn affects stress resilience and yields. Griffiths et al. designed a plant-permeable, photo-activated T6P analogue that is converted to T6P in planta. Spraying this compound onto plants…
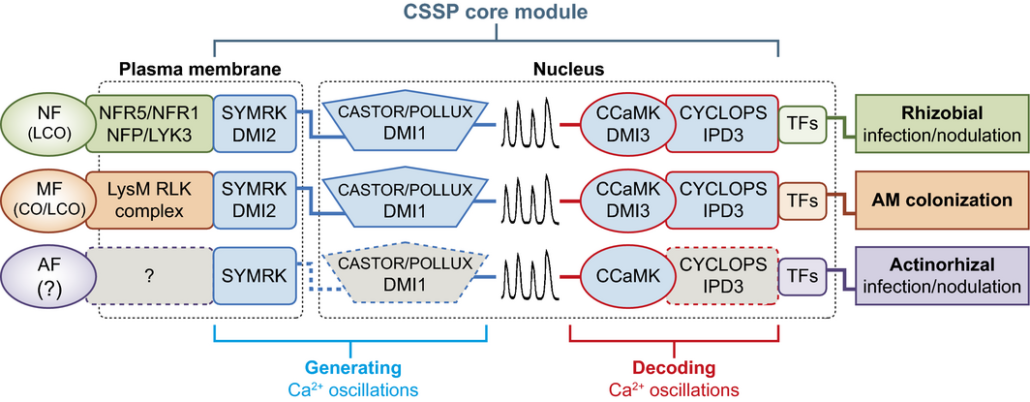
Review: Nuclear Ca2+ signaling in endosymbiosis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe Common Symbiosis Signaling Pathway (CSSP) conveys the perception of endosymbionts (rhizobia or mycorrhizal fungi) at the plasma membrane to the nucleus to initiate transcriptional responses. Calcium oscillations are core to the CSSP, whether the endosymbiont is fungal or bacterial. Barker et al.…
Previewing Pollen Biology special issue of Plant Physiology
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIn Plant Physiology Preview you can get a head start on reading the excellent set of articles from a forthcoming special issue on Pollen Biology. Updates and research articles cover all aspects of this crucial part of reproductive biology, from the complex cell biology that underpins polar growth of…
Best of 2016: Top Topics in The Plant Cell journal
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant CellWe’ve highlighted some of the Plant Cell papers that were widely shared, liked, blogged, retweeted and otherwise garnered high-levels of attention this year. Perhaps you can use some holiday-season quiet time to catch up on those you missed.
Reviews and Perspectives
Creating order from chaos: epigenome…

Best of 2016: Top Topics in Plant Physiology jounal
Blog, Research, Research Blog
We’ve highlighted some of the Plant Physiology papers that were widely shared, liked, blogged, retweeted and otherwise garnered high-levels of attention this year. Perhaps you can use some of that holiday-season quiet time to catch up on those you missed.
The breakaway attention-getter from Plant…
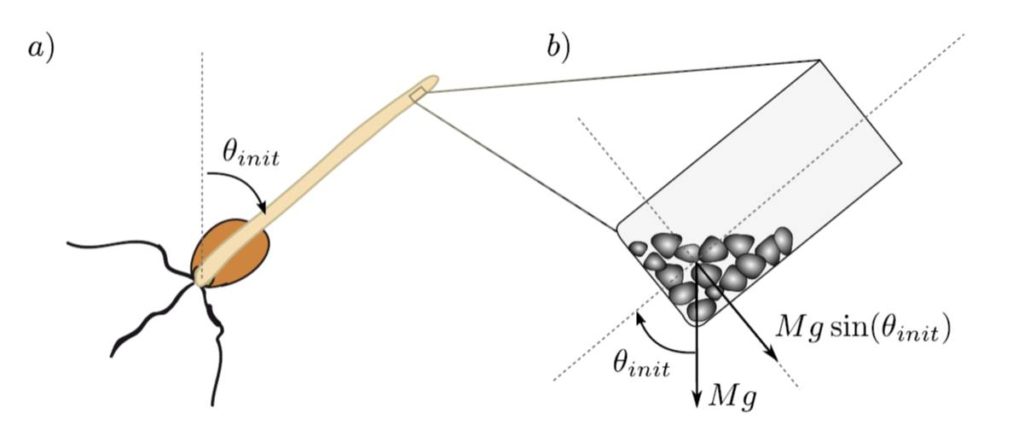
Inclination, not force, is detected in shoot gravitropism
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant cells detect gravity as a consequence of the movement of dense starch granules called statoliths when the statoctyte, the cell that encompasses, them reorients. An open question has been whether the position of the statoliths within the statocyte or the force exerted by them is the primary gravisensing…
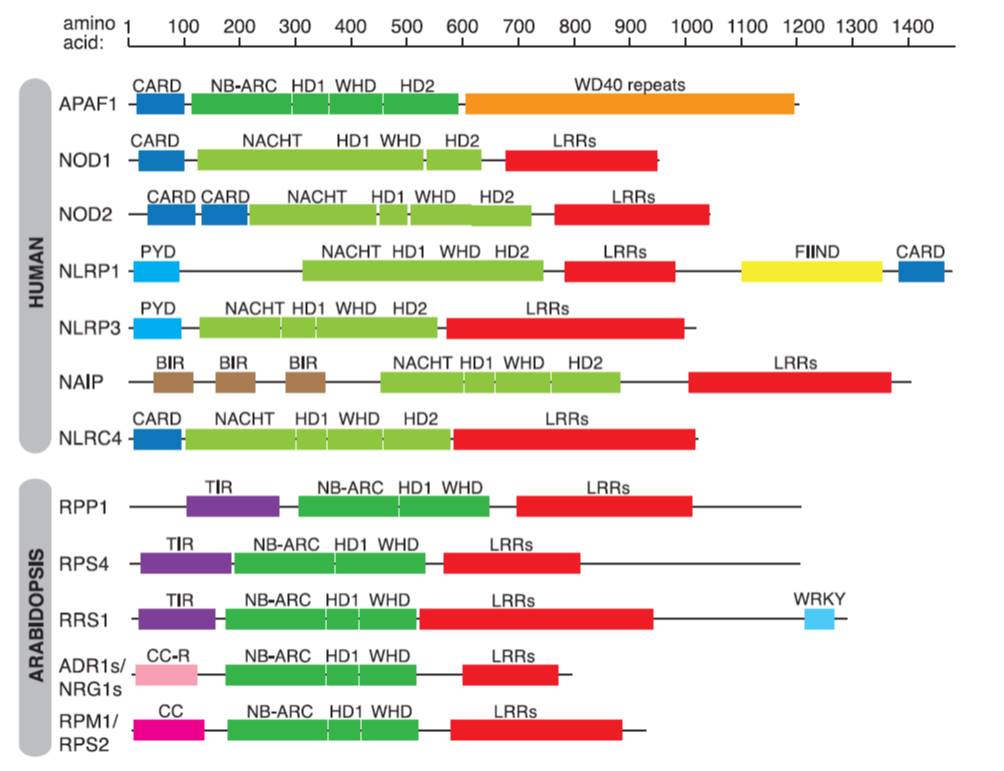
Review: Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCells recognize invaders through both cell-surface receptors and intracellular receptors, the latter of which can recognize the invader directly or indirectly, for example through its effects on host proteins. Intracellular surveillance proteins in animals and plants share a core domain, the nucleotide…

Molecular basis for plant growth responses in shade and under competition for light ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
The wavelenghts of light perceived by a plant are information-rich, and plants integrate information from photoreceptors tuned to different wavelenghts to optimize their growth and development. Because plants absorb red light but not far-red light, a low ratio of red to far-red light indicates vegetative…
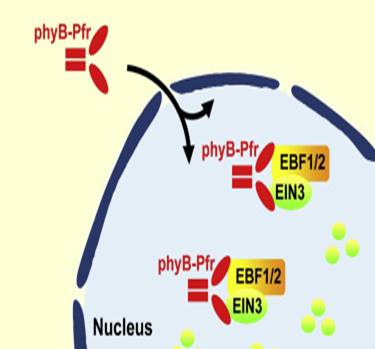
Light suppresses ethylene response by direct interaction between phyB and EIN3
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research
A seedling in the dark produces ethylene, which in a dicot such as Arabidopsis leads to apical hook formation that protects the cotyledons from damage as the seedling pushes through the soil. The emergence of the seedling into the soil causes a rapid transition to photomorphogenesis and a suppression…

