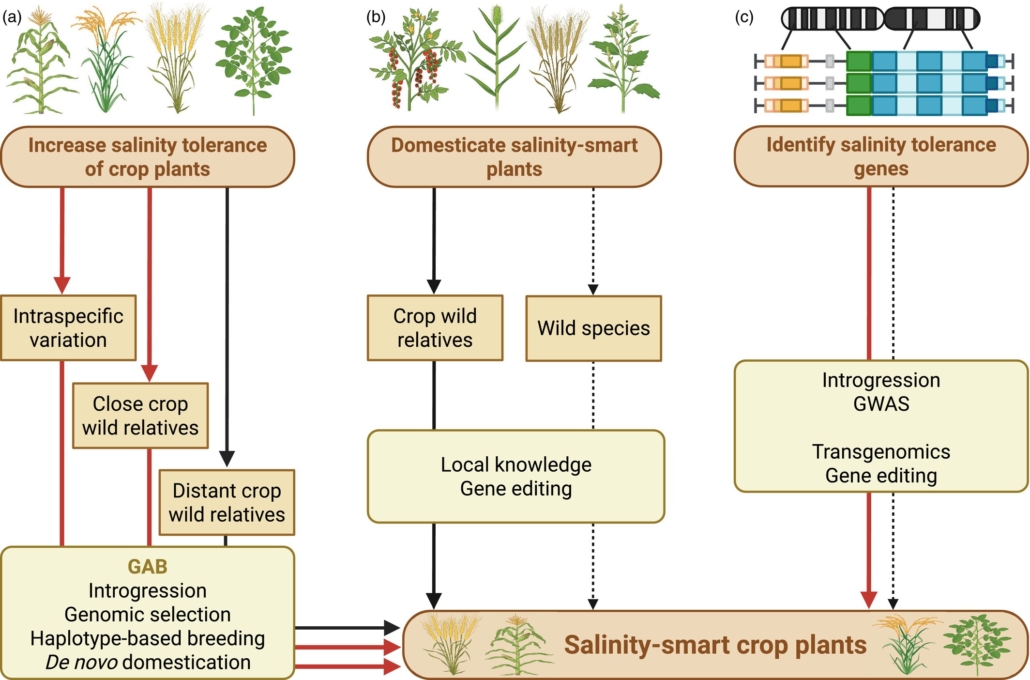
Review: Genomic tools and breeding tools to design salinity-smart food crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost food crops are relatively intolerant to soil salinity, yet globally soils are becoming increasingly salinized. This excellent review by Raza et al. pulls together the myriad approaches that are being used to develop salinity-smart crops. It starts with an overview of how soil salinity affects crops…
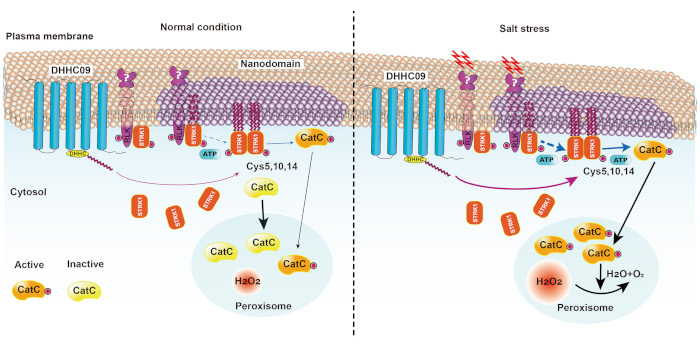
A zinc finger protein promotes salt signaling in rice via transphosphorylation
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellTian et al. identify the zinc finger protein DHHC09 as a regulator of rice salt tolerance.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae001
By Ye Tian, Xuan-Ming Liu, and Jian-Zhong Lin
Background: Soil salinity results in oxidative stress and heavy losses to crop production. S-acylation of proteins…
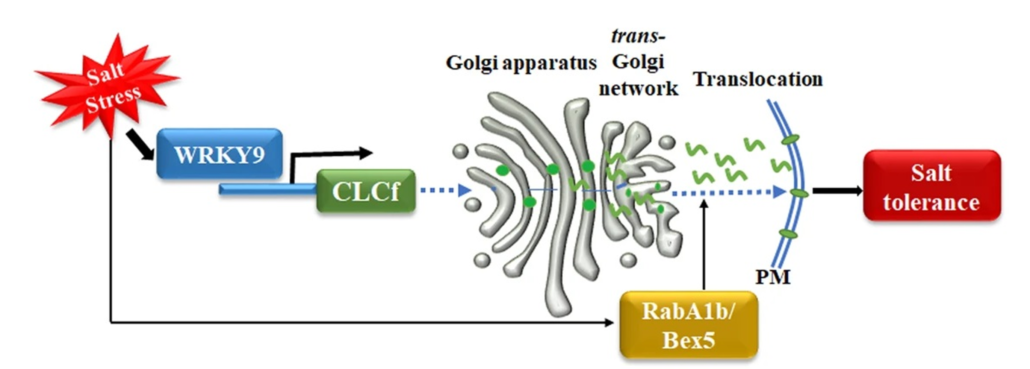
Translocation of a chloride channel from the Golgi to the plasma membrane helps plants adapt to salt stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants adapt to salt stress by maintaining ion balance using ion transporters. While much is known about cation transporters, the role of anion transporters is less clear. Rajappa et al. focus on the chloride channel gene AtCLCf in Arabidopsis thaliana, controlled by the transcription factor WRKY9 under…
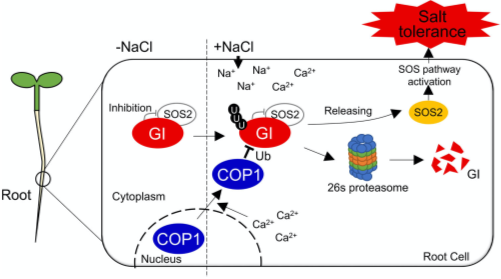
COP1 regulates salt tolerance via GIGANTEA degradation in roots
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlobal climate change affects weather patterns, and excess soil salinity harms plant growth. Previous studies have shown interaction between the circadian clock and salt responses. In normal conditions, the core circadian clock oscillator GIGANTEA (GI) sequesters the SOS2 kinase, part of the salt-overly…

The phosphatase PC1 switches off catalase to balance salt tolerance and growth
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellCong Liu, Jianzhong Lin, and Xuanming Liu and colleagues show that the protein phosphatase PC1 dephosphorylates and deactivates CatC to negatively regulate H2O2 homeostasis and salt tolerance in rice.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad167
By Cong Liu, Jianzhong Lin, and Xuanming Liu
Background:…

