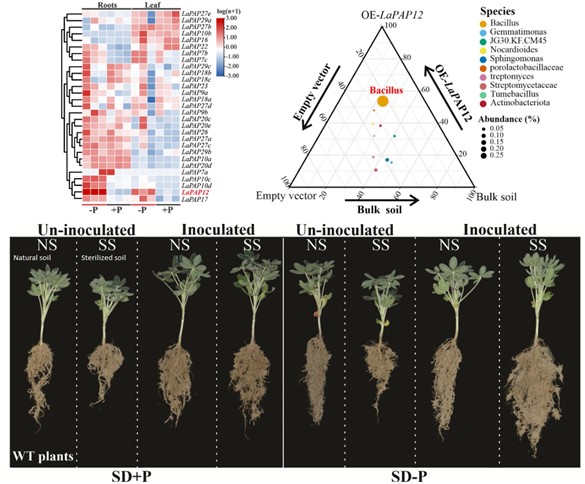
Root acid phosphatases and rhizobacteria synergistically enhance white lupin and rice phosphorus acquisition (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P, Pi in the form of inorganic orthophosphate) is crucial for plant homeostasis because it is a plant growth-limiting factor. White lupin is an excellent crop model to study Pi changes due to the development of cluster roots (CR). CR are composed of rootlets that allow a more efficient Pi…
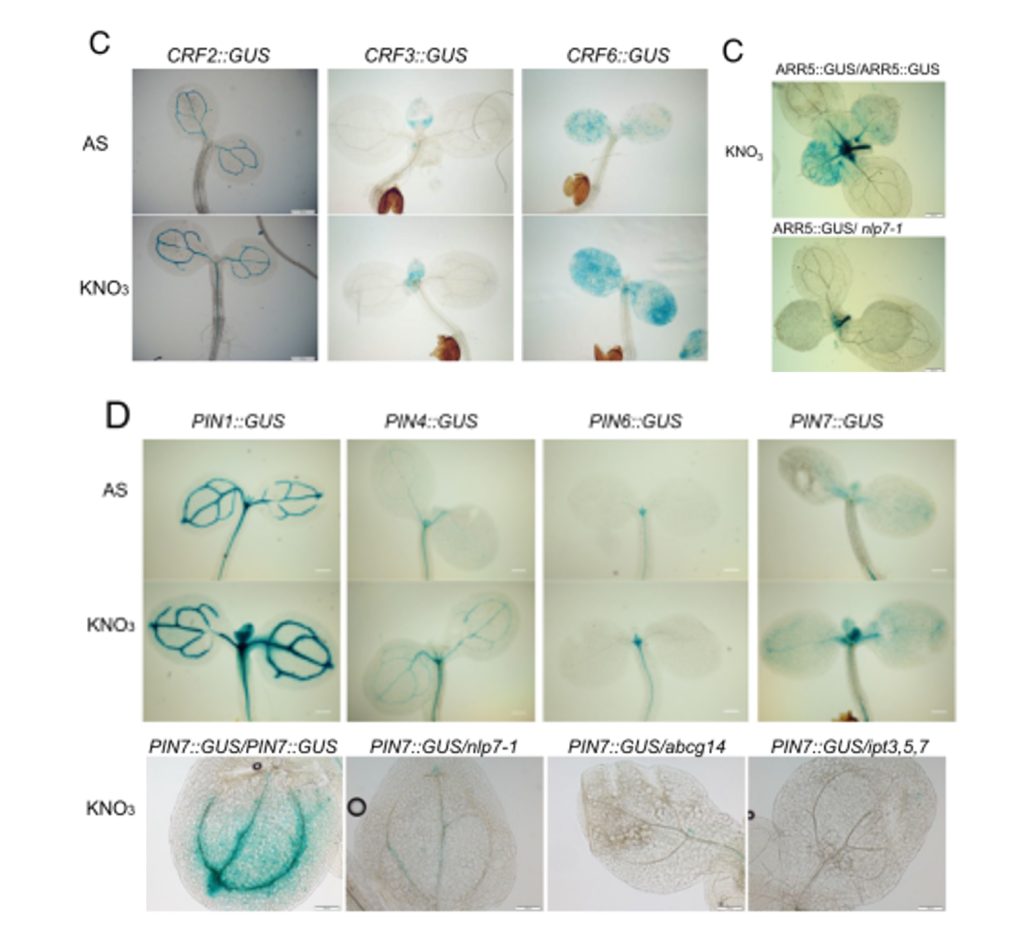
NLP7-CRF-PIN, the nitrate-cytokinin-auxin crosstalk module, conveys root nitrate signals and regulates shoot growth adaptive responses (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrate, the prominent form of nitrogen used by most land plants, is a signal regulating plant growth and development. Nitrate sensing by roots not only regulates root development to facilitate nutrient foraging, but also the growth of distant plant organs. Cytokinin is a mobile signal coordinating nitrate…
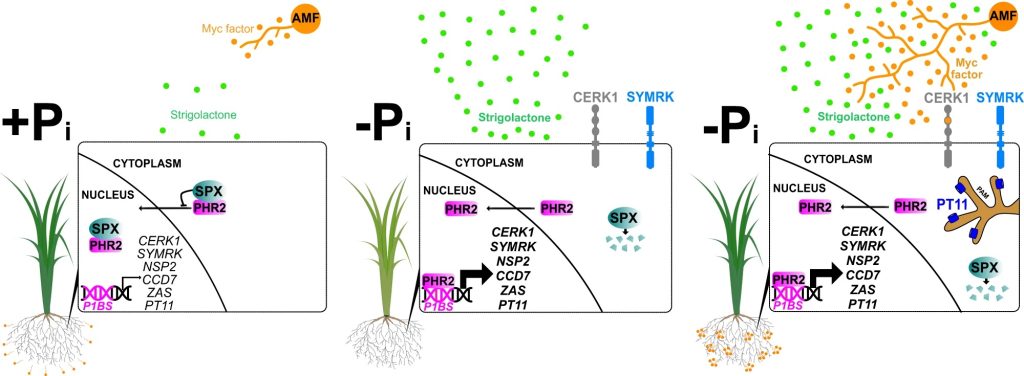
Plants’ PHR2-controlled phosphate starvation response regulates fungal symbiosis in rice (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants’ interaction with microbes in the rhizosphere affects their health and productivity. Plant-arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) fungi symbiosis is associated with almost 80% of land plants. The fungi provide phosphate, stress tolerance, and firmness to the soil in exchange for carbon. While low phosphate…
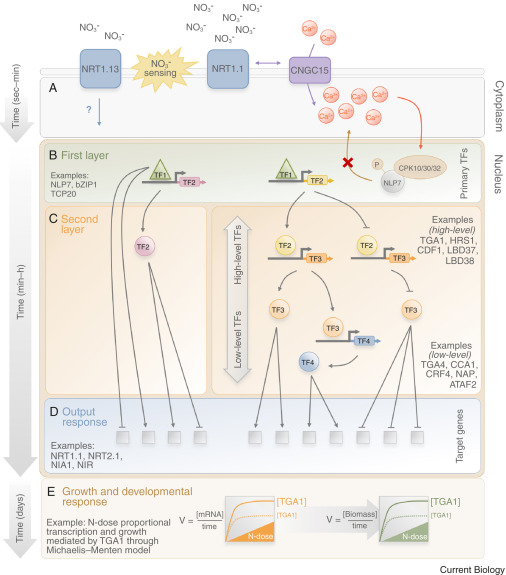
Review: Molecular regulators of nitrate response in plants (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrate is the major form of nitrogen used by plants in an aerobic crop cultivation scenario. Lamig et al. review recent additions to the already vast knowledge of nitrate signaling. A first line of regulation concerns nitrate uptake through post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation of nitrate…

Review: Protein phosphorylation “toggle switch” for plant iron balance (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProtein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation act as a switch regulating a multitude of protein properties, be it their activity, interaction with other proteins, stability, or even cellular localization. This review by Li et al. describs the many ways that protein phosphorylation contributes to iron…
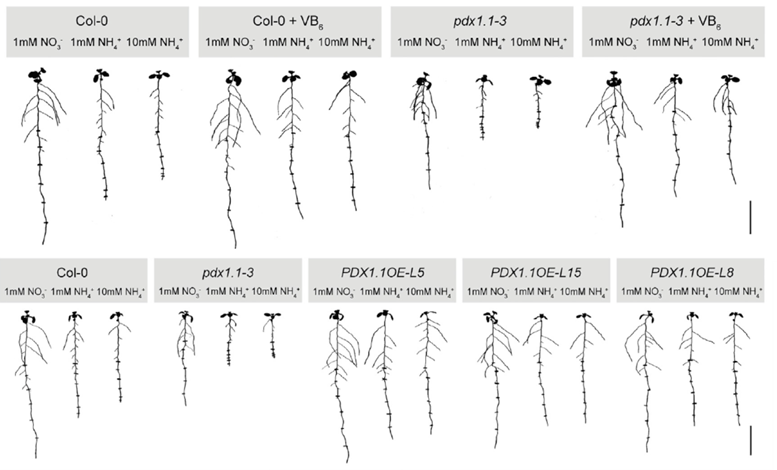
PDX1.1-dependent vitamin B6 synthesis alleviates ammonium toxicity-associated ROS production (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmmonium is a nitrogen form preferred by many plant species. However, high ammonium concentrations lead to decreased primary root elongation due to membrane depolarization and lower apoplastic pH. Liu et al. report that ammonium toxicity results in iron-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) production…
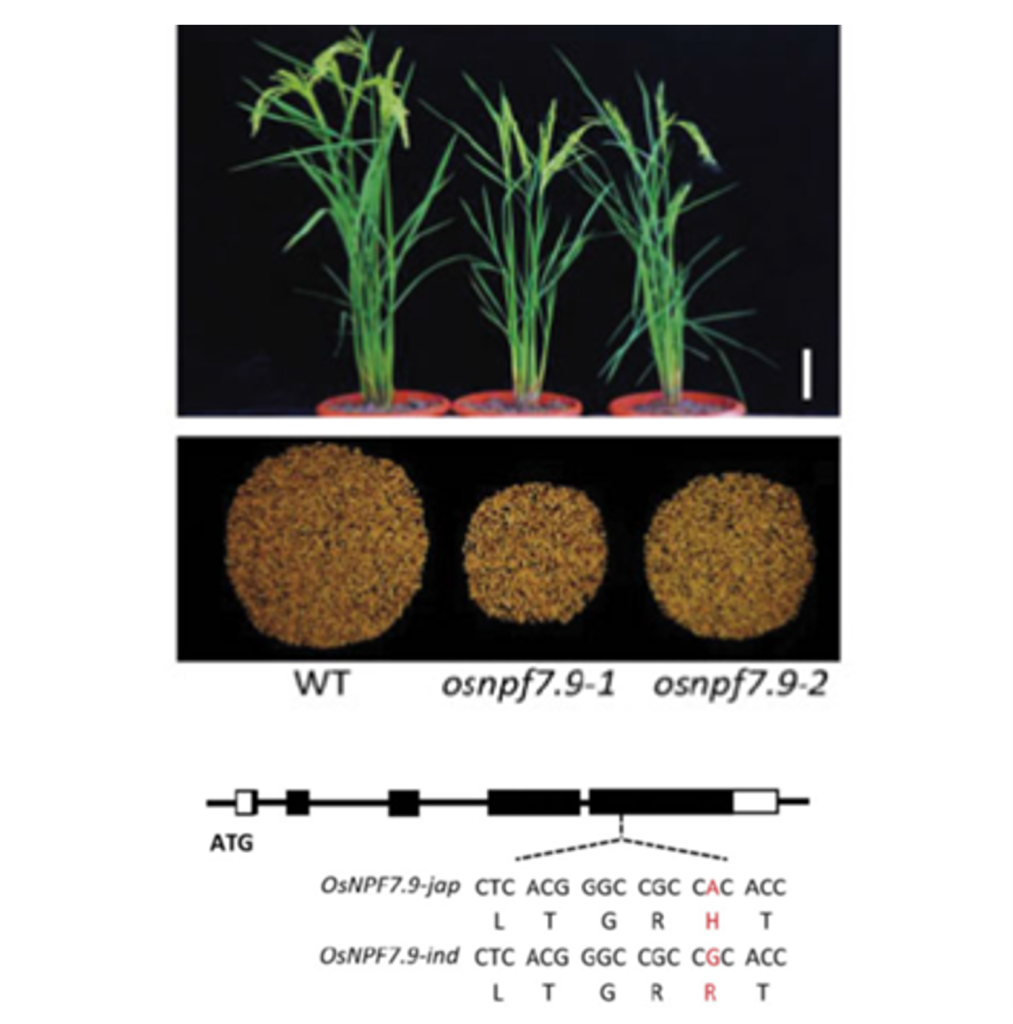
Nitrate transporter NPF7.9 is a regulator nitrogen use efficiency and stress-induced nitrate allocation to roots in rice (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn addition to its role as a nutrient and a developmental signal, nitrate regulates stress responses in plants. By homology to nitrate transporters previously identified in Arabidopsis as contributing to stress induced-nitrate allocation to roots (SINAR) and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), Guan et al.…
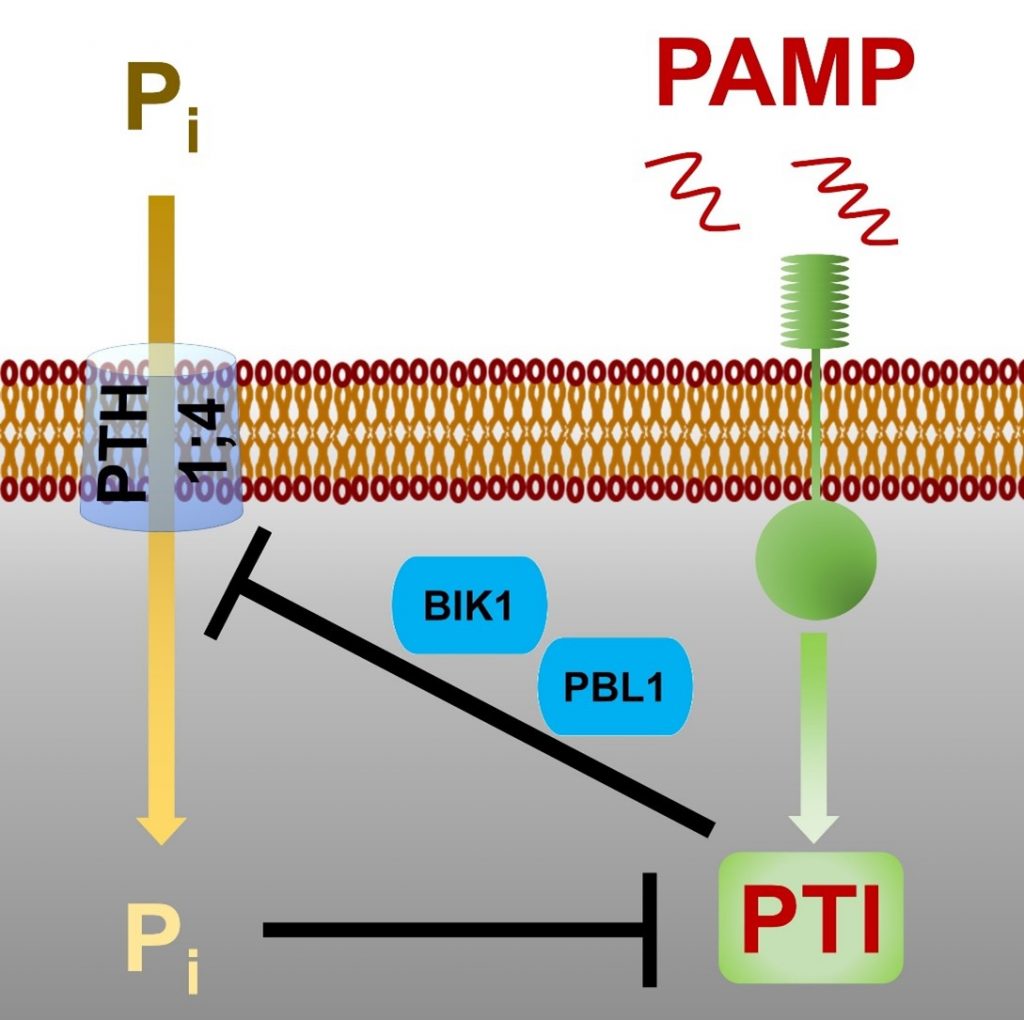
Crosstalk between phosphate transport and plant immunity (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have evolved signaling cascades to survive biotic and abiotic stresses, and recent studies have shown that there is crosstalk between many of these pathways. In a recent study, Dindas et al. developed a micro-electrode-based system to detect active inorganic phosphate (Pi) transport in Arabidopsis…

Focus Issue on Architecture and Plasticity (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe November issue of Plant Physiology is a Focus Issue on Architecture and Plasticity. One of the most intriguing aspects of plant growth and development is the environmental responsiveness (also known as “plasticity”) of plant architecture (growth form). Depending on environmental conditions, roots…

