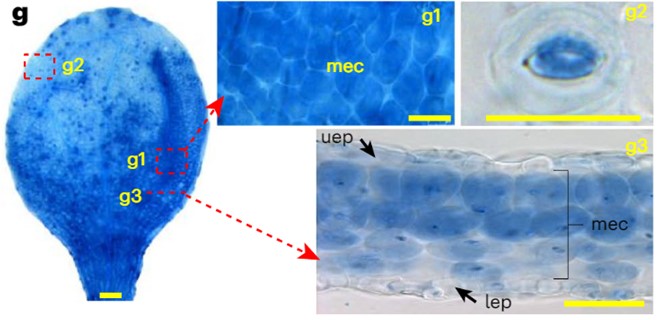
Visualizing plant intracellular inorganic orthophosphate distribution
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus is the second most essential macronutrient in terms of limiting plant growth, acquired in the form of orthophosphate (Pi) by plant roots. The intricate processes of sensing, uptake, transport, storage, utilization, and cellular compartmentalization of Pi are finely orchestrated by a complex…

Cross-enrichment of rhizobacteria improves iron nutrition during intercropping
Plant Science Research WeeklyIntercropping, the system of growing at least two crops simultaneously, increases crop productivity and ecological sustainability. An intercropping system of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and maize (Zea mays) has been previously found to improve the yield of peanut, specifically its iron nutrition and…
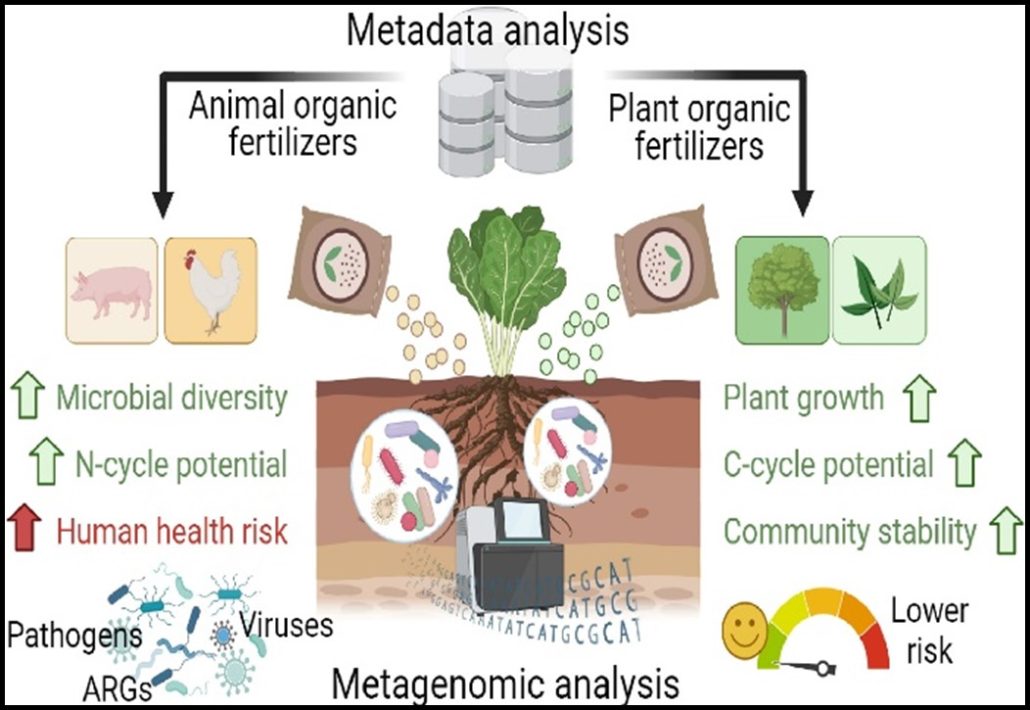
Effect of plant-derived versus animal-derived fertilizers on the rhizosphere microbiome
Plant Science Research WeeklyYu et al. conducted a meta-analysis of published 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequenced soil samples to compare the effects of plant-based fertilizers (e.g. compost, seaweed fertilizer) versus animal-based fertilizers (e.g., dung, manure) versus control, unfertilized samples on soil microbial diversity and…
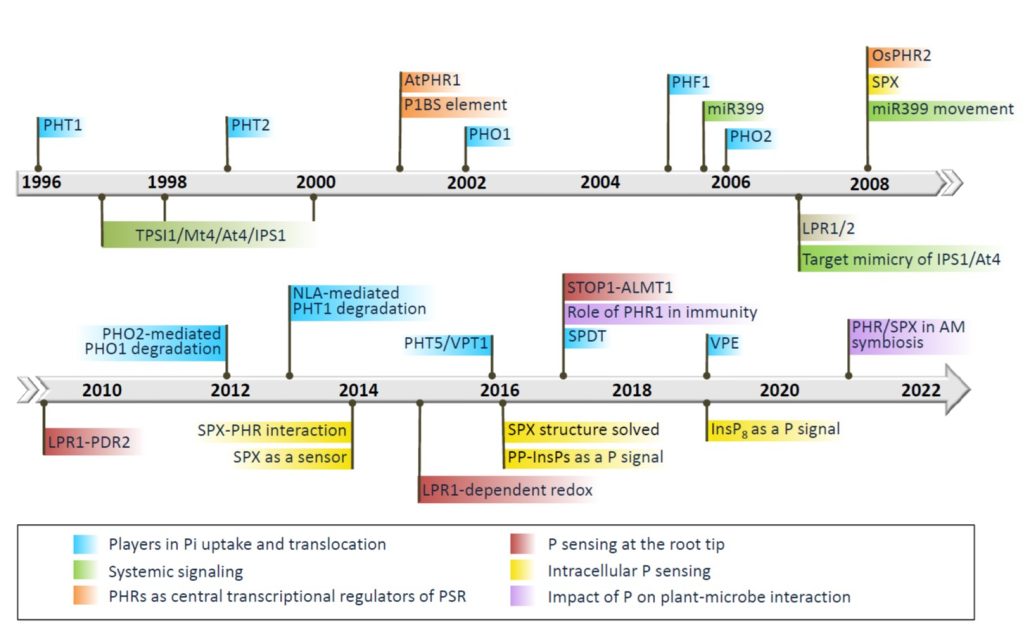
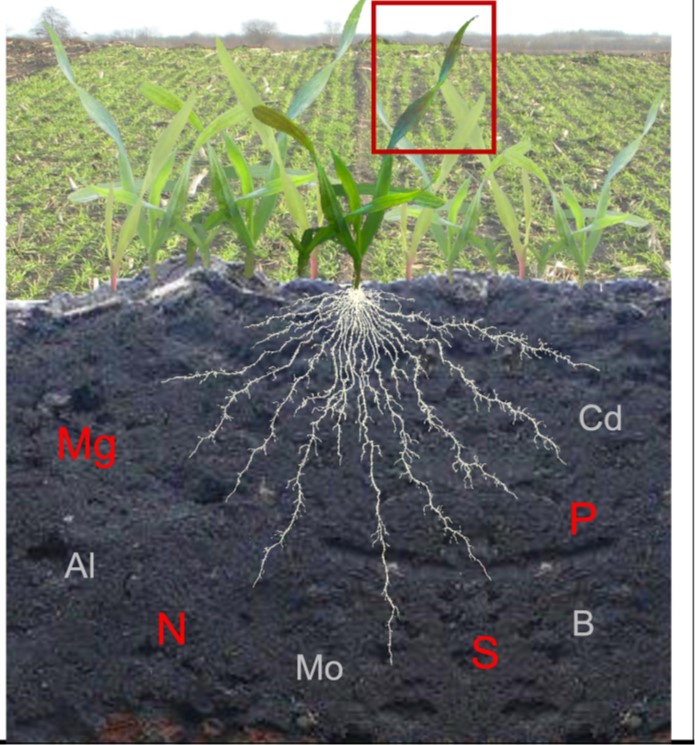
Review. Milestones in understanding phosphorus uptake, transport, sensing, use, and signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient and critical component of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and other molecules. Yang et al. provide a historical (since 1996) overview of the processes controlling its uptake and use. Plants take up P from the rhizosphere primarily in the form of orthophosphate (Pi).…
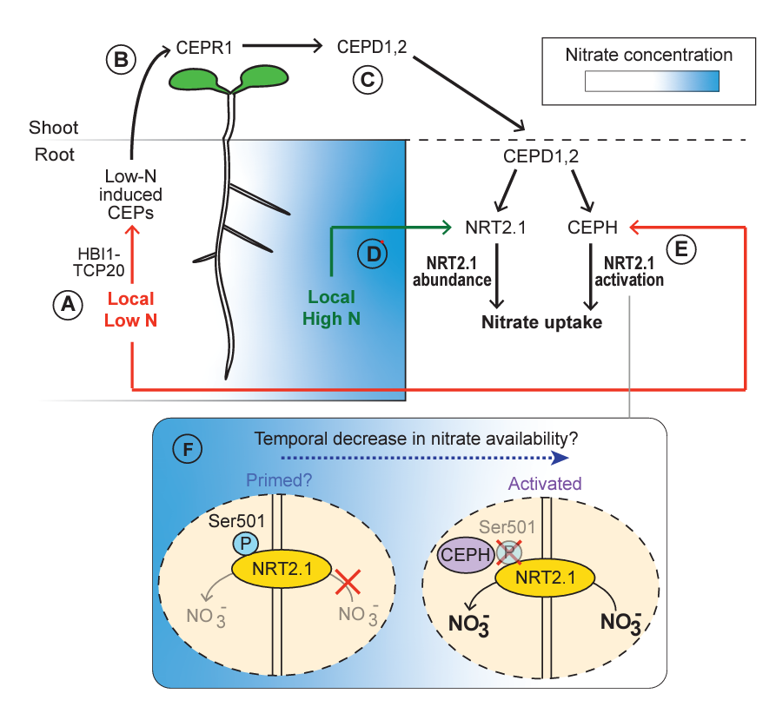
Review: CEP hormones at the nexus of nutrient acquisition and allocation, root development, and plant–microbe interactions
Plant Science Research WeeklyC-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) is a multigene family of peptide hormones originally described as systemic long-distance signals in response to nitrogen limitation. Over the years since the discovery of these peptide hormones, the literature on CEP biology has expanded the repertoire of developmental…
Review: Development of organs for nutrient uptake in parasitic plants and root nodule symbiosis
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis review by Cui et al. makes the interesting comparison between the developmental processes involved in root nodule formation and haustoria formation by roots of parasitic plants. As the authors observe, both are organs that are produced for the purpose of nutrient acquisition through “intimate…
Review: Difficult situations cause blushing in plants, much as they do in people
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs with people, plants blush in difficult circumstances. Situations such as nutrient stress make plants uncomfortable, resulting in the accumulation of anthocyanins in different plant tissues and color changes in the tissues. Jezek et al. reviewed how and why anthocyanins accumulate in foliar tissues…
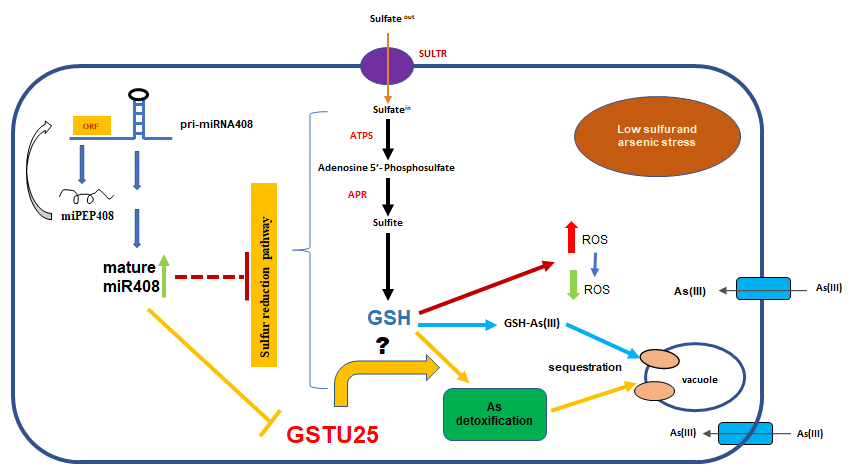
MicroRNA encoded peptide affects arsenic sensitivity
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that down-regulate their targets through translational repression or mRNA cleavage. Some pri-miRNAs encode small regulatory peptides (miPEP) which regulate plant growth and development by modulating subsequent miRNA expression. How different biotic or abiotic…

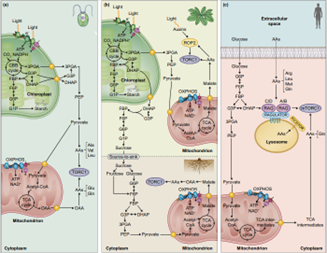
Tansley Insight: Analyzing the impact of autotrophic and heterotrophic metabolism on the nutrient regulation of TOR (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA protein kinase, target of rapamycin (TOR), controls cell growth and metabolism in all eukaryotes. The role of TOR in regulating synthesis and breakdown of organic compounds in response to nutrients, hormones and cellular energy to promote growth and development is universal in autotrophs and heterotrophs.…

