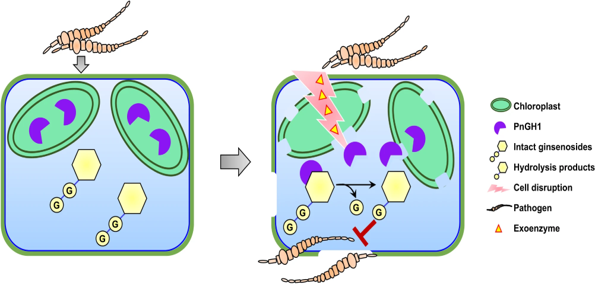
Chemical defense: Exploring two-component plant defense mechanisms in Panax species
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the interesting world of plant defenses, plants have secret weapons called defense metabolites that stay quiet until a pathogen comes knocking. Plants have evolved two-component chemical defence systems to protect against pathogens while striking a balance between growth promotion and defence mechanisms.…
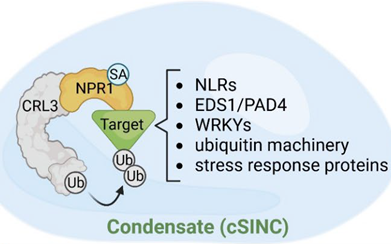
Review: Salicylic acid in plant immunity and beyond
Plant Science Research WeeklySalicylic acid (SA) is a pivotal natural compound in plant science and finds applications in herbal medicine; specifically, aspirin, the renowned anti-inflammatory drug and pain reliever, is a derivative of SA. As summarized in this review by Spoel and Dong, within plants SA serves as a crucial phytohormone…
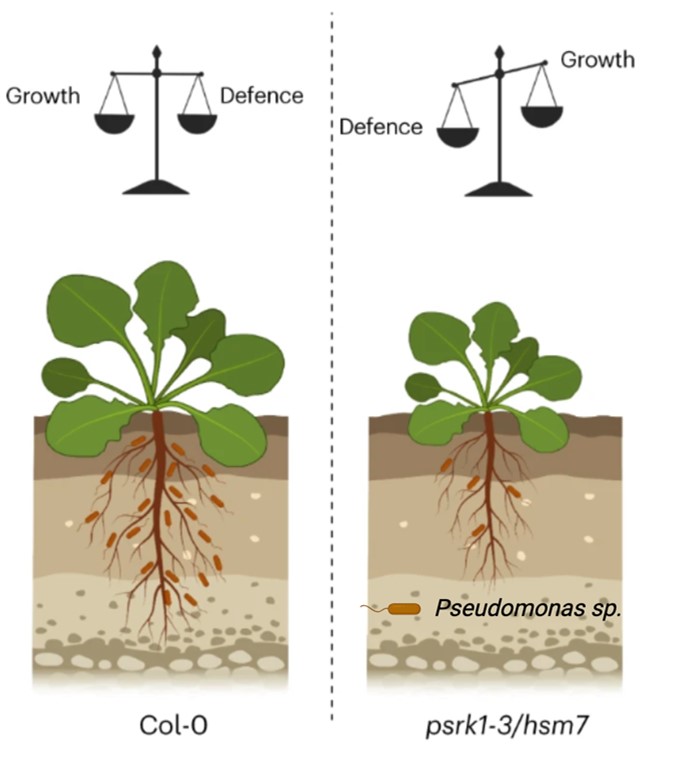
PSKR1 balances the plant growth–defence trade-off in the rhizosphere microbiome
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are colonized by numerous beneficial microorganisms in the rhizosphere, including Pseudomonas fluorescens, that provide benefits including nutrient acquisition and pathogen protection. Host plants must tune their immune systems to restrict microbial overgrowth, while avoiding overstimulation of…

Review: Till death do us pair: Co-evolution of plant–necrotroph interactions
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis interesting and well-written review by Derbyshire and Raffaele takes a step back from the molecular interactions between plant and pathogen and discusses them in light of co-evolutionary processes. The review starts with a useful introduction and definition of concepts about “robustness” in…
Review: Challenges to improving plant growth through introduced microbes
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are closely associated with large numbers of microbes that live in, on, and around them; these are collectively called the plant microbiota. Microbes can be pathogenic, neutral, or beneficial. Beneficial microbes might enhance nutrient uptake by the plant or suppress pathogenic microbes. There…

Listening to the whispers in the air: Plant eavesdropping in action
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants release a variety of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including green leaf volatiles (GLVs), terpenoids, and amino acid derivatives, in response to herbivore damage and injury. Healthy neighboring plants detect these VOCs as warning signals, prompting them to activate defense mechanisms. This…

Mechanism by which viruses are excluded from plant stem cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyHorticulturalists have long used the technique of meristem culture to propagate plants, as meristems are generally considered to be free of viruses. However, the mechanism by which the stem cells in meristems exclude viruses has been unclear. Here, Incarbone and Bradamante et al. identified roles for…

Review: Improving RNA-based crop protection through nanotechnology and insights from cross-kingdom RNA trafficking
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe German physician Paul Ehrlich (not to be confused with the American scientist of the same name) coined the term “magic bullet” (zauberkugel) to describe something that is perfectly and accurately effective. As much as we dream of magic bullets, they are rarely found, but the idea of using spray-on…

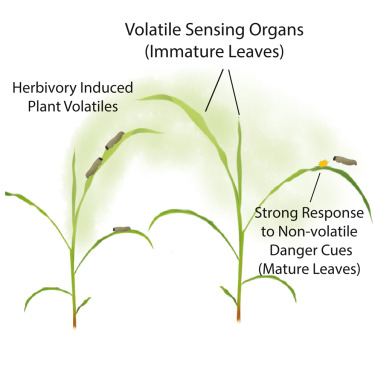
Immature leaves are the dominant volatile-sensing organs of maize
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s well established that damaged plant tissues emit volatile compounds that bolster defense responses in nearby plants, but how those neighbors sense these compounds has remained obscure. This new work by Wang et al. reveals some important clues. First, as the title indicates, immature leaves are…

