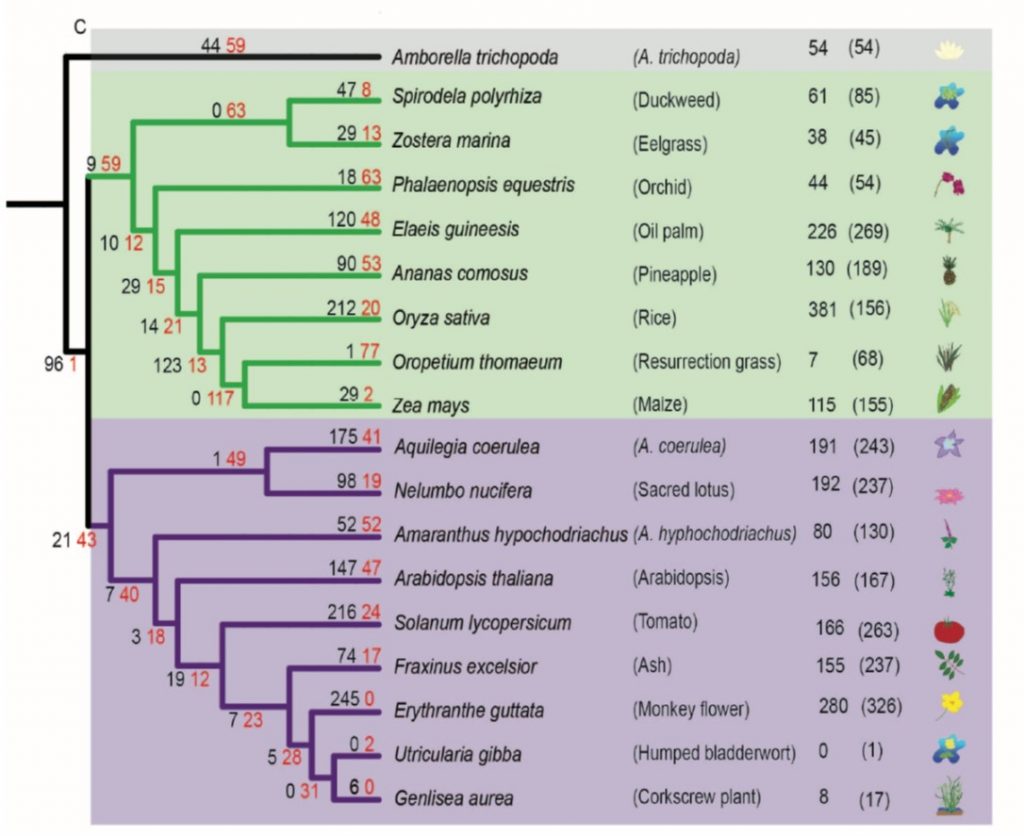
Convergent loss of plant immune receptors and signaling pathways (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors (NLRs) are important components of the plant immune system. They are intracellular receptors that act downstream of the cell-surface receptors, and initiate the so-called effector-triggered immunity (ETI). In most plants, the NLR gene family is large and…
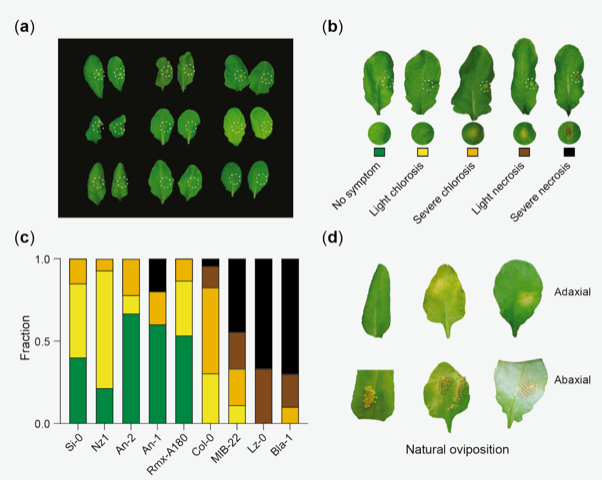
Plant genes for defense against insect eggs (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can recognize eggs of herbivorous insects deposited on leaves and mount defense responses to avoid the future threat of herbivory. Similar to plant hypersensitive response against pathogens, plants can cause localized cell death to defend themselves against insect eggs. This response is called…
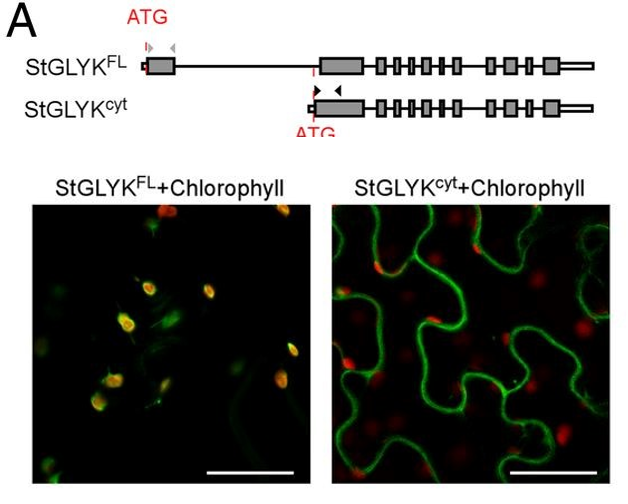
Shedding light on plant immunity: Light-regulated defense against P. infestans (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhile infection by pathogens and the reciprocal immune responses are well studied in plants, the influence of other abiotic factors on these processes is not very clear. In an attempt to understand the role of light on plant defense, Gao and colleagues have shown that the AVRvnt1 effector protein secreted…
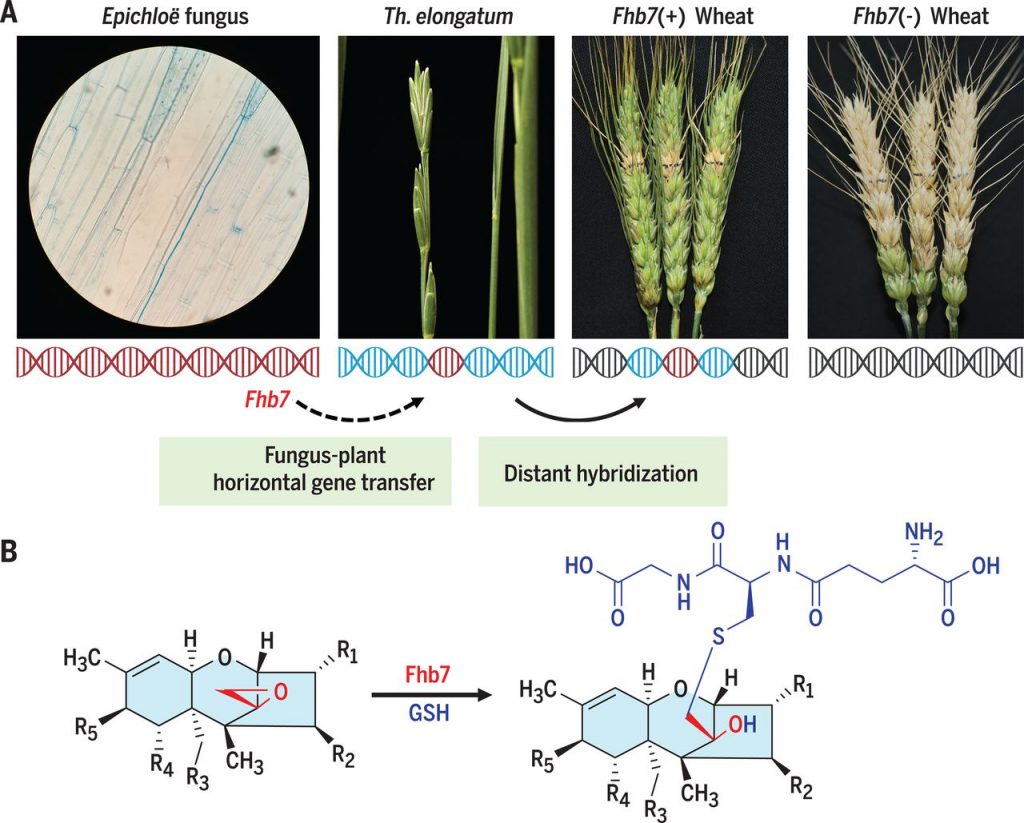
Horizontal gene transfer of Fhb7 from fungus underlies Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMycotoxins are fungal toxins with harmful health effects on humans and other animals. Fusarium head blight is a fungal disease of wheat inflorescences that can contaminate the grain and harm its consumers. Previously, Fhb7 was identified in the wheat relative Thinopyrum elongatum as a quantitative trait…
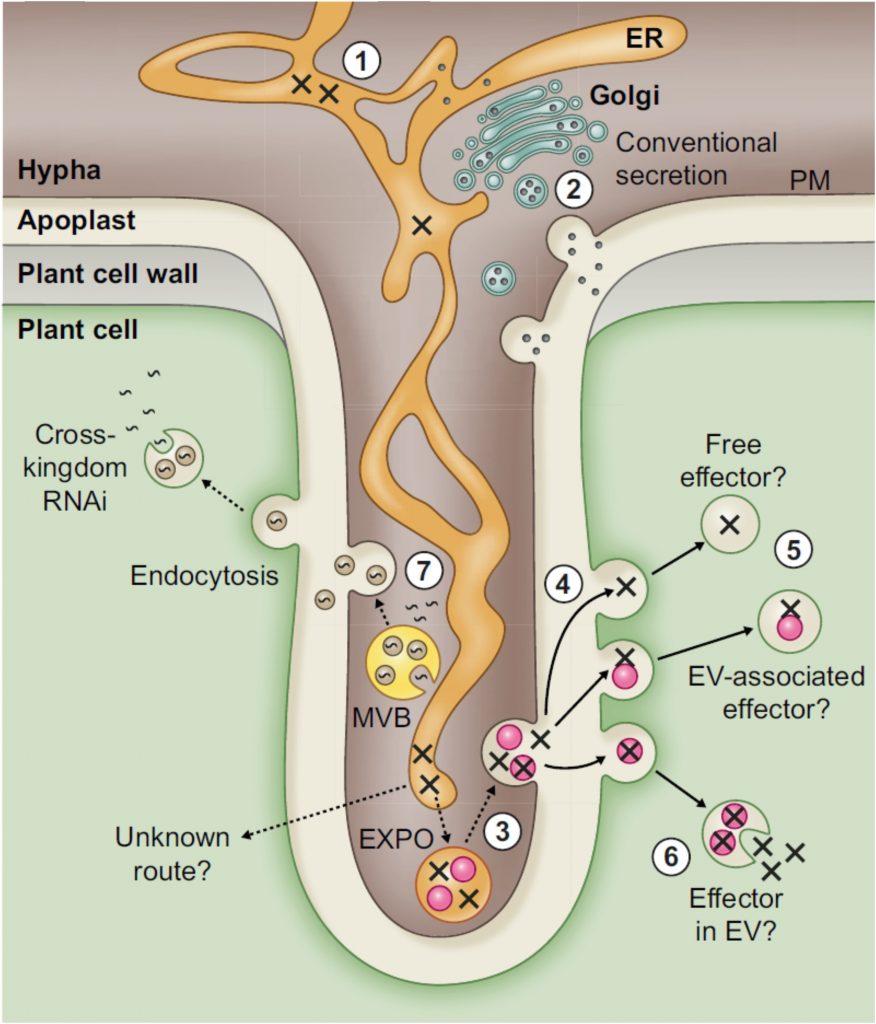
Review: Devastating intimacy: the cell biology of plant–Phytophthora interactions (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytophthora are plant-destroying oomycetes. Within this genus are several infamous disease-causing agents: P. infestans of the potato late-blight fame, P. sojae of soybean root rot, P. ramorum of sudden oak death, and many other lesser-known species. This fine new review by Boevink et al. explores the…
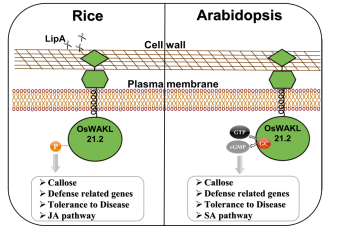
A moonlighting kinase induces immune responses in rice and Arabidopsis ($) (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBacterial infections are a serious issue for crop plants and it is thus imperative to understand the mechanisms employed by plants to develop resistance against pathogens. Malukani et al. have identified a receptor kinase in rice, WALL-ASSOCIATED KINASE-LIKE 21 (OsWAKL21.2) that perceives pathogen-induced…
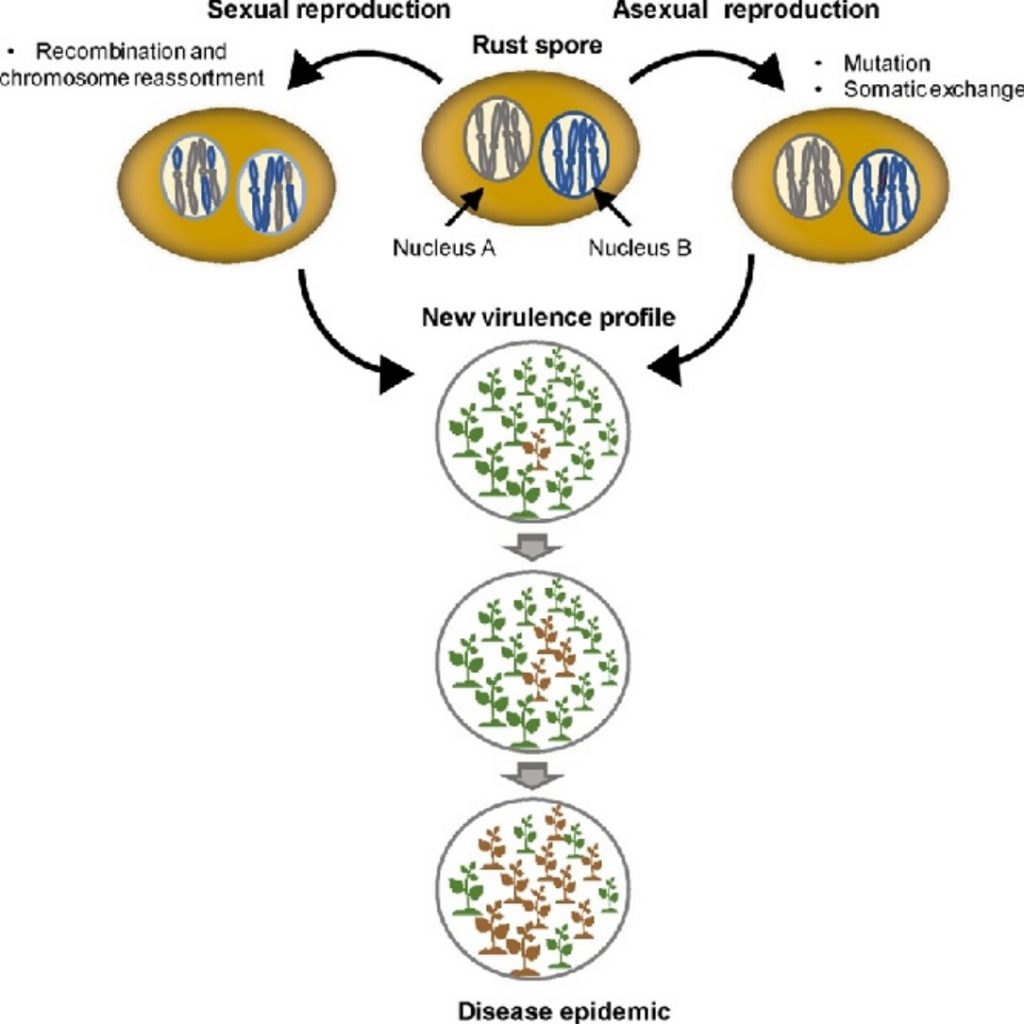
Review: Evolution of virulence in rust fungi — multiple solutions to one problem (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRust fungi are a diverse group (more than 7800 species) of phytopathogenic fungi that cause considerable economic loss. (Coincidently, I’m writing on Robigalia, the Roman “anti-rust” festival, which dates from before we understood that microbes, not gods, cause disease). Figurero et al. have written…
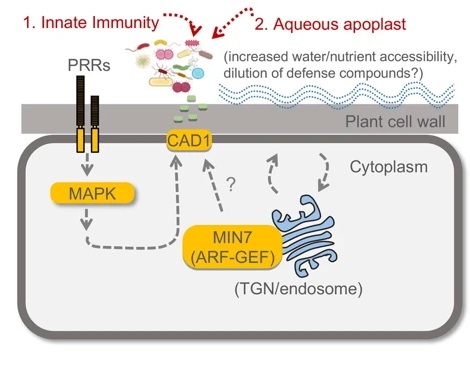
How plants keep their microbiota healthy (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe large apoplastic intercellular space of plant leaves creates nutrient-rich niches for microbial colonization. To date, whether and how plants control the composition of leaf microbiota is poorly understood. Chen et al. reported that the Arabidopsis quadruple mutant (min7fls2efrcerk1 or mfec)…
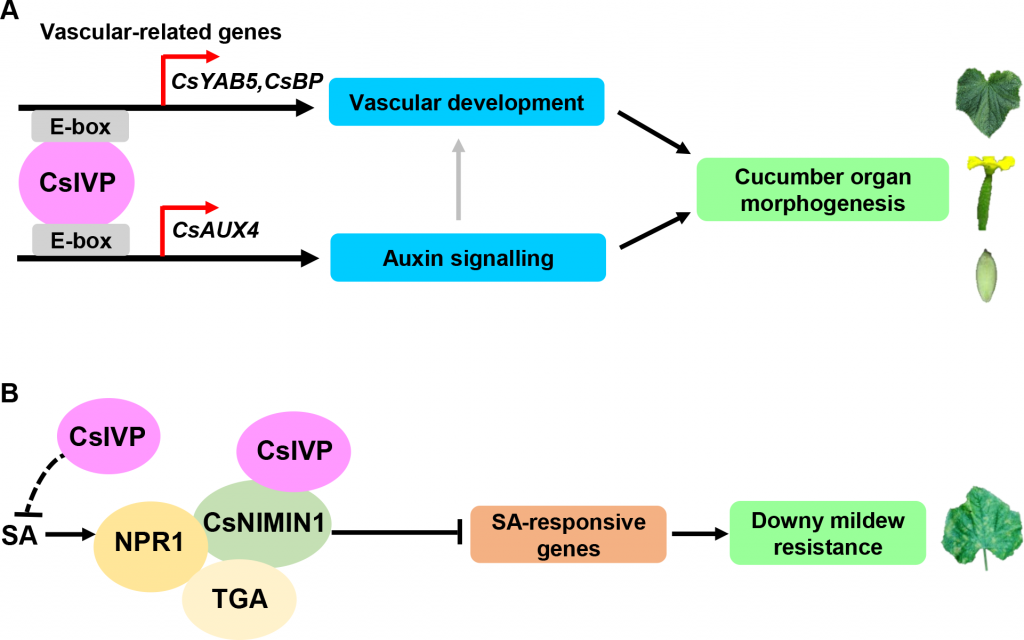
CsIVP functions in vasculature development and downy mildew resistance in cucumber (PLOS Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHigh yielding crops are often less resistant to pathogens and vice versa, suggesting that there is an underlying mechanism co-regulating development and disease resistance in plants. Yan et al. identified a transcription factor in cucumber (CsIVP) that regulates vascular development and resistance to…

