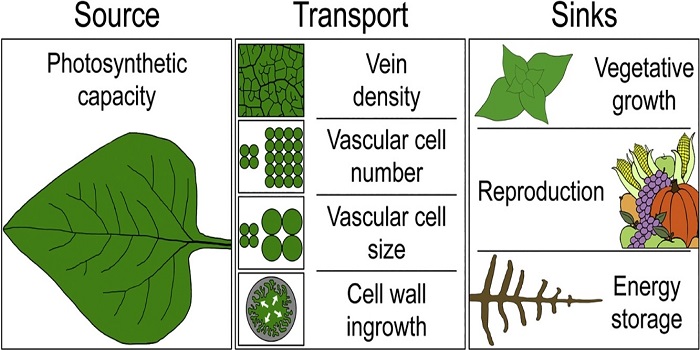
Review: Environmental regulation of intrinsic photosynthetic capacity: an integrated view ($)
0 Comments
/
Photosynthetic capacity varies hugely within an individual over time, between individuals in different environments, and between species. Demming-Adams et al. review the processes that affect intrinsic photosynthetic capacity. Plants modulate their intrinsic photosynthetic capacity according to input…

Sugar suppression of aquaporin expression and leaf hydraulics ($)
Sugar is a signal as well as an energy source, and plants monitor sugar levels to maintain an appropriate growth rate and rate of photosynthesis. A new study by Kelly et al. points to a role for sugars in the expression and activity of plasma-membrane (PIP) aquaporins. Aquaporins (AQP) are membrane channels…
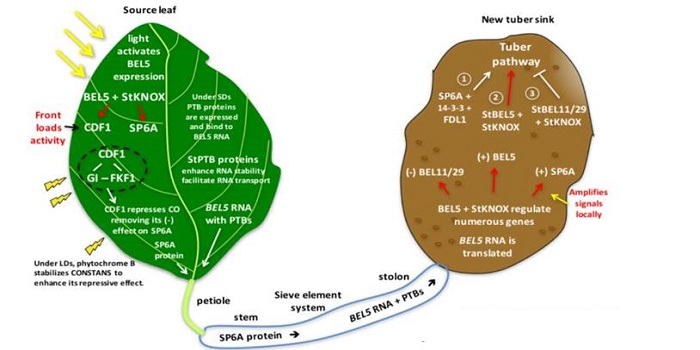
Update: The multiple signals that control tuber formation
Potato is an important food crop, but unlike most of the other major foods, it is a tuber, not a seed. Classic studies showed that there is a mobile, photoperiod-induced signal that moves from the shoot to the stolen tip (an underground, stem-like structure) to initiate tuberization. Experimental studies…
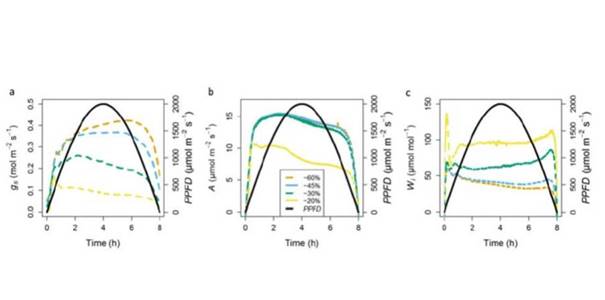
Update: Diurnal variation in gas exchange: the balance between carbon fixation and water loss
Stomatal control of transpiration is critical for maintaining important processes, such as plant water status, leaf temperature, as well as permitting sufficient CO2 diffusion into the leaf to maintain photosynthetic rates (A). Stomatal conductance (gs) often closely correlates with A and is thought…

Review: Secrets of succulence ($)
“Succulence is a phenomenon that has long eluded a decisive consensus definition,” begins Males in his review of the physiology and evolutionary developmental biology of succulence. Succulence can broadly be defined as the storage of water such that the plant can maintain physiological activity in…
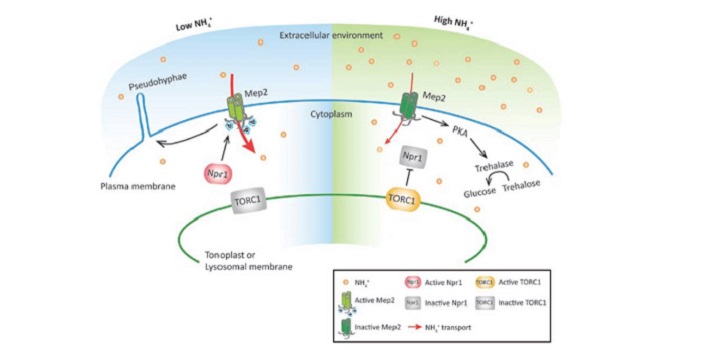
Review: Ammonium as a signal for physiological and morphological responses ($)
Ammonium is one of the major forms in which nitrogen is assimilated. Besides being a nutrient, it also acts as signal that affects gene expression and root system architecture. Some ammonium-induced genes are also induced by low pH (ammonium acidifies the apoplast), whereas others are specifically induced…
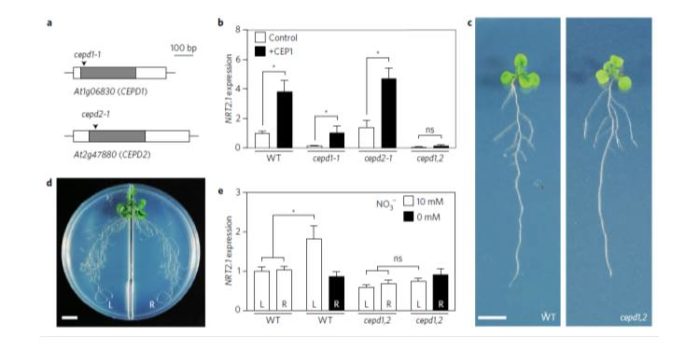
Shoot-to-root mobile polypeptides involved in systemic regulation of nitrogen acquisition ($)
To balance nutrient uptake (usually from heterogeneous sources) with nutrient demand, plants use a root-shoot-root signaling pathway. Previously, a root-to-shoot mobile peptide C-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) was shown to translocate from N-starved roots to the shoot, where it interacts with a leucine-rich…
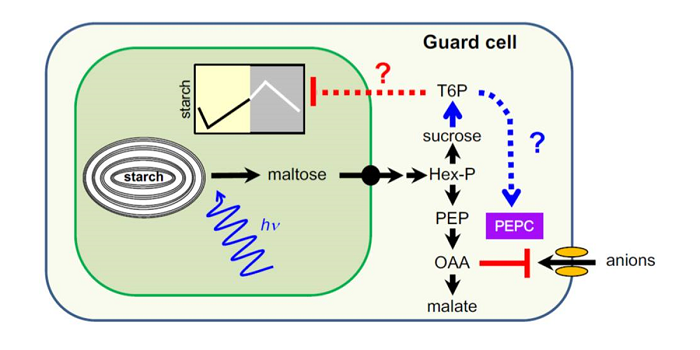
Update: Transitory starch metabolism in guard cells: unique features for a unique function
In leaf mesophyll cells, some of the sugars produced by photosynthesis are stored as transitory starch, which is then broken down to provide the cells with energy during the night. Recent advances in imaging and staining and the use of mutants have enabled the pattern of accumulation of transitory starch…
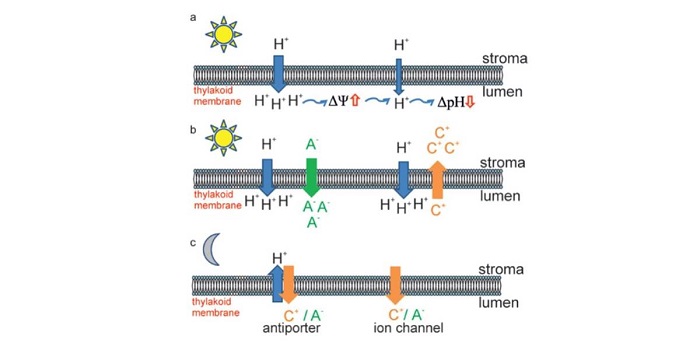
Review: Impact of the ion transportome of chloroplasts on the optimization of photosynthesis ($)
In photosynthesis, light energy generates proton motive force (pmf) across the thylakoid membrane. The establishment and maintenance of pmf involves numerous membrane transporters as well as other ions. Szabò and Septea review how various ions (including K+, Na+, Fe2+, Cu+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Cl–) contribute…

