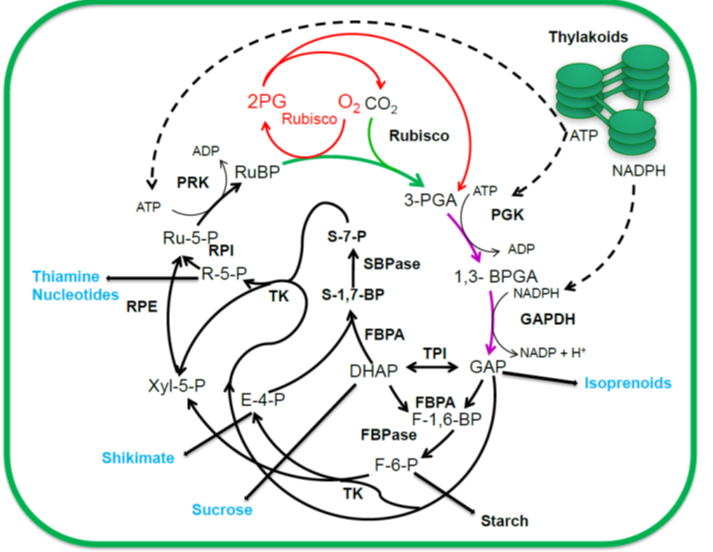
Review: Strategies to improve photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants assimilate carbon by using light energy. However, with the solar energy conversion efficiency of many crop plants less than 1%, it is inefficient. Therefore, there is interest in manipulating photosynthesis for increased efficiency. Here, Croce et al. identifying…
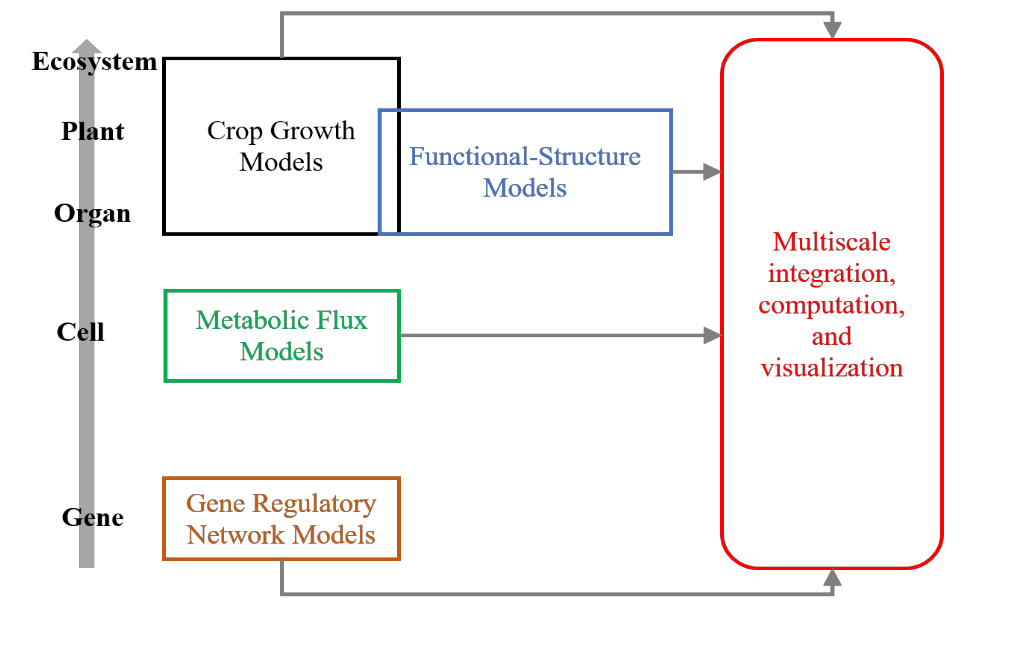
Perspective: Multiscale computational models for crop improvement (Plant J)
Throughout the plant science community, the use of computational or in silico analyses which precede traditional studies are gaining traction to identify research opportunities. Multiscale computational models are those which assimilate data from all biological system levels from gene to ecosystem. Benes…
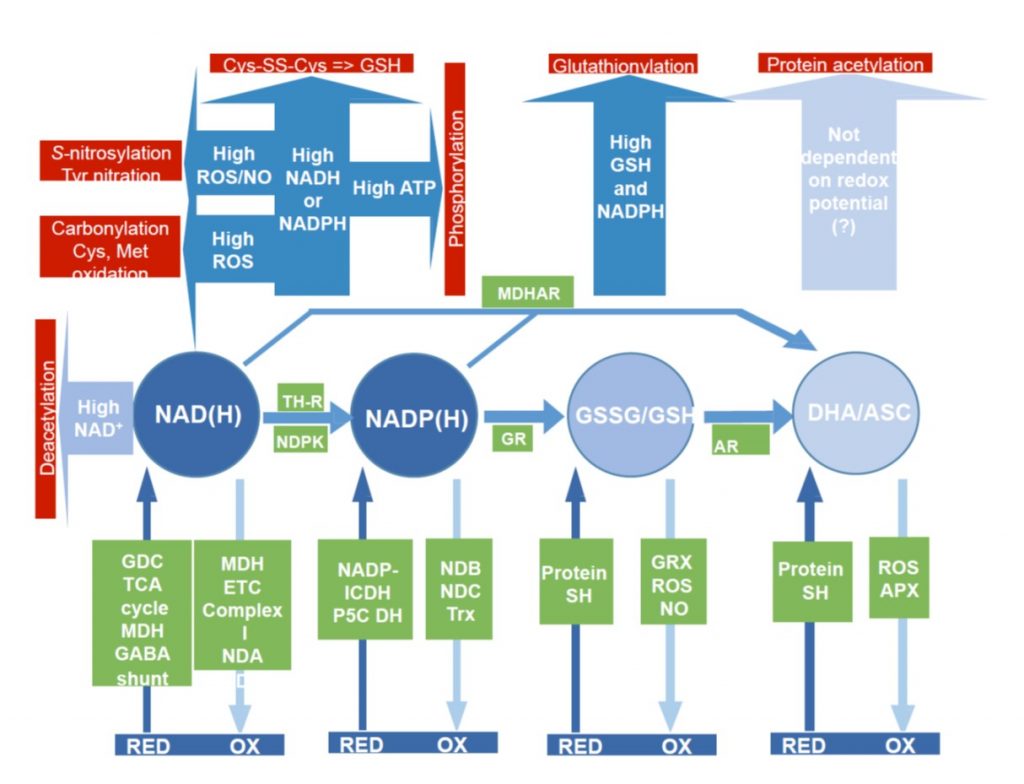
Review: Matrix redox physiology governs the regulation of plant mitochondrial metabolism through post-translational protein modifications
Mitochondrial metabolism provides ATP and reducing power to drive myriad reactions in the plant cell, and is constantly being fine-tuned in response to environment and demands. Post-translational modifications (PTMs) of proteins, including redox reactions of methionine and cysteine and carbamylation…
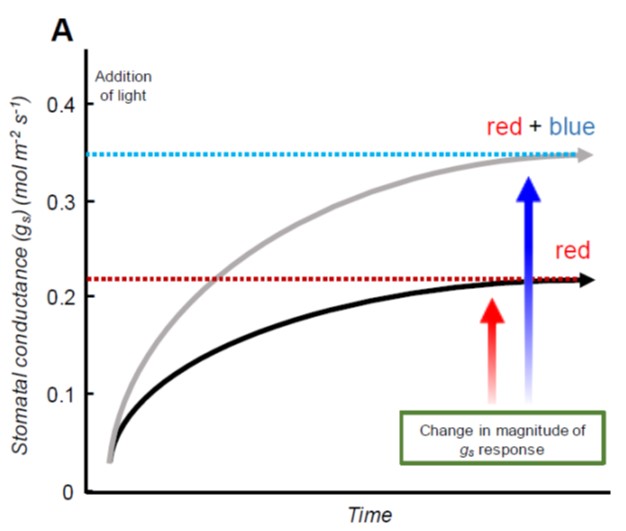
Review: Role of blue and red light in stomatal dynamic behaviour (J Exp Bot)
Guard cells are extremely sensitive and dynamic, and their behaviour controls rates of gas exchange and transpiration, which affect evaporative cooling and transport in the xylem. Matthews et al. review the roles of light signalling pathways in guard cell responses. Cues that control guard cell ion channels…
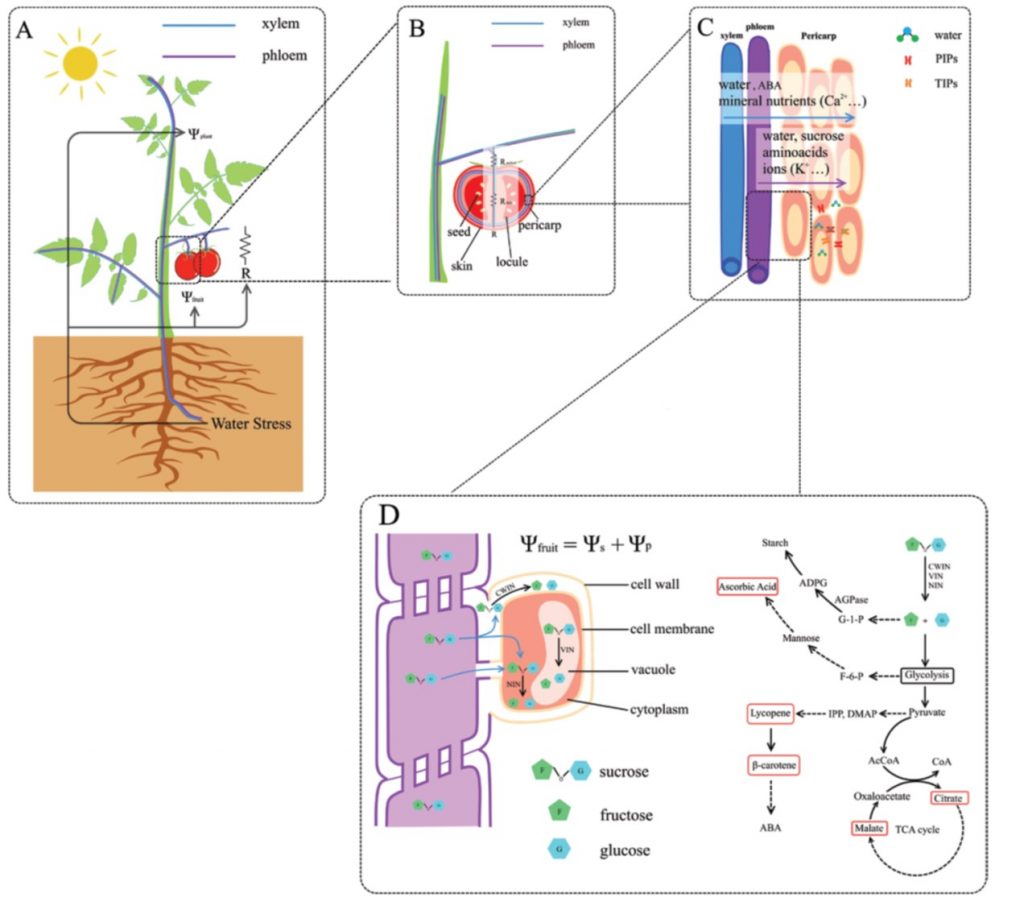
Review: Tomato fruit water accumulation and solute metabolism under water shortage (J. Exp. Bot.)
Deficit irrigation is water-conserving strategy in which a growing plant is given just enough but never too much water. Previous studies have shown myriad physiological changes caused by deficit irrigation including decreased growth rate and shoot:root ratio, and also a lower fruit water content. Here,…
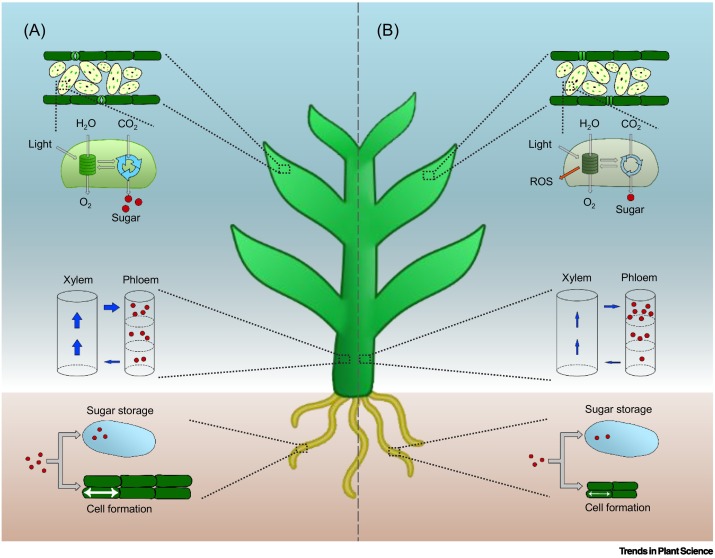
Review: Source–sink regulation in crops under water deficit ($) (Trends Plant Sci)
Plants have a remarkable ability to coordinate cellular activities across huge distances, yet we have only a basic understanding of how these remote activities are coordinated. A review by Rodrigues et al. summarizes what we know about the relationship between source (e.g., photosynthetic tissues) and…
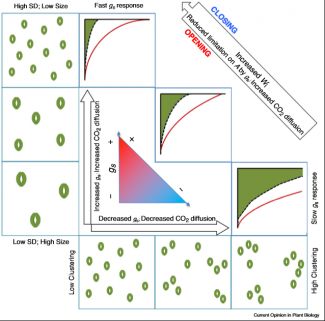
Review: Exploiting natural variation and genetic manipulation of stomatal conductance for crop improvement (COPB)
Identifying methods to improve crop productivity is vital considering the devastating consequences of climate change (e.g., frequent droughts). Stomatal conductance influences photosynthesis and water use efficiency, which are two important indicators of crop yield. Here, Faralli et al. discuss advances…

Special Issue: Root Biology (Physiologia Plantarum)
The year 2019 kicks off with a special issue on root biology, with all articles free to access for six months. Topics include interactions of roots with parasites and symbionts, root branching, transport in the root system, and roots of woody species. (Summary by Mary Williams) Physiologia Plantarum…
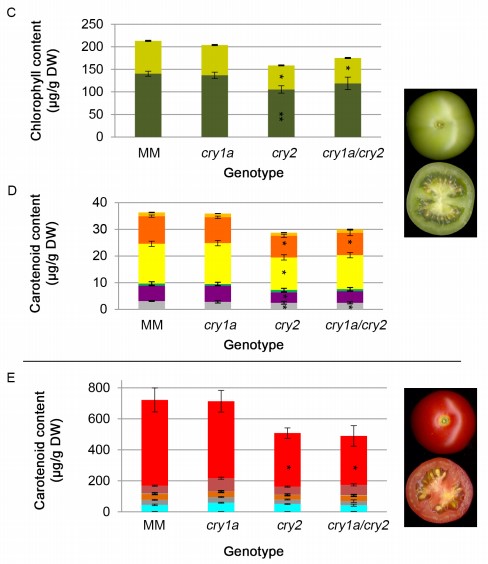
Pivotal roles of cryptochromes 1a and 2 in tomato development and physiology (Plant Phys)
Cryptochromes are a class of flavoproteins found in plants and animals that are sensitive to blue light. In Arabidopsis, cryptochromes are involved in many important physiological processes including de-etiolation, flowering, circadian rhythms, cotyledon opening and expansion, anthocyanin accumulation,…

